A new approach to control light with light without the need for optical nonlinearity has been suggested by a Russian-British research group.
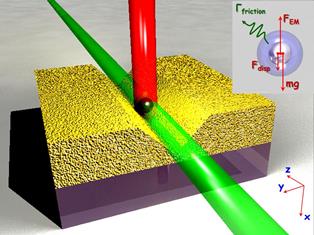

A new approach to control light with light without the need for optical nonlinearity has been suggested by a Russian-British research group.
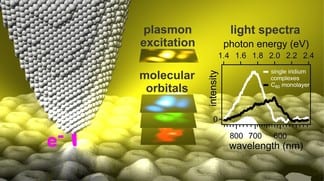
Scientists have discovered how optical signal transmission can be controlled, which could lead to integration of plasmonics with electronic circuits.
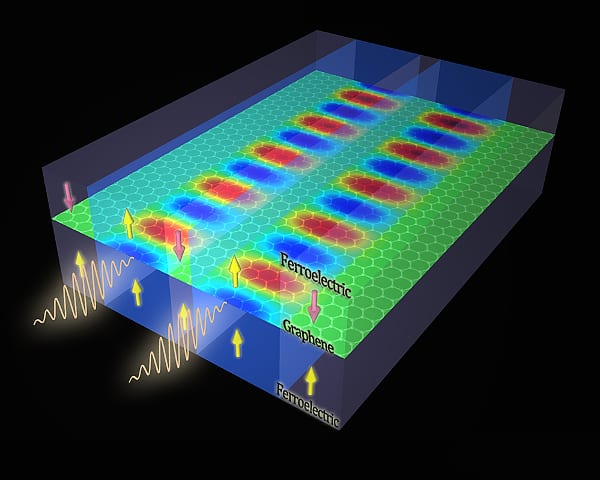
New system uses two-dimensional structures to guide plasmonic waves at ultrashort wavelength, offering a new platform for memory and computer chips.
NIST’s heterodyne magneto-optic microwave microscope can measure collective dynamics of electrons’ spins in individual magnets as small as 100 nanometers.
Topological Insulators, solar-cell silicon, and crystallization kinetics– these and more in January’s physics highlights.

Scientists from Berkeley and TU Munich investigate magnons in a material that becomes helimagnetic below about 30 kelvin: iron silicide doped with cobalt.
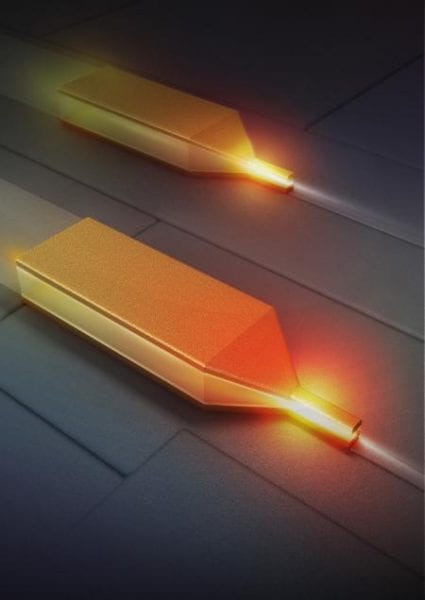
Engineers create a device that can focus light into a point of just a few nanometers, with applications in computing, communications, and imaging.
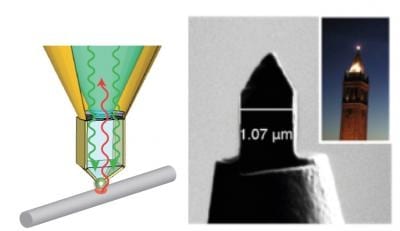
Berkeley Lab scientists develop a new nanotech tool to probe solar-energy conversion.

Graphene and carbon nanotubes could improve the electronics used in computers and mobile phones, reveals new research from the University of Gothenburg, Sweden.
Introduction 1. Gridded ion sources 2. Gridless industrial broad beam ion sources 3. Main operational parameters 4. Regime of non-self-sustained discharge and its importance 5. Ion source and vacuum chamber 6. Oscillations and instabilities in ion sources 7....