This book is a collection of papers from The American Ceramic Society's 35th International Conference on Advanced Ceramics and Composites, held in Daytona Beach, Florida, January 23-28, 2011. This issue includes papers presented in the Ceramics for Electric...

New Bayer Material Meets Demand for Tougher Turbine Blades
Bayer’s new polyurethane systems could meet the demand for stronger, more durable wind turbine blades.

Printing Skin: An Inkjet for Tissue Engineering
Scientists in Lausanne have developed an inkjet printing system to produce artificial living tissue.

What Is My (Nano)Material Good For?
Whatever happened to curiosity-driven research aimed at the creation of fundamental knowledge without the need for immediate application?

Stuffing nuclear waste glasses
Research into waste management is a major part of international nuclear policy. New work offers an in-depth look into one solution, glasses.

Beyond enlightenment: Non-optical genome sequencing
Ion-sensitive field-effect transistors meet scalable CMOS technology to yield low-cost, high throughput DNA sequencing modules.
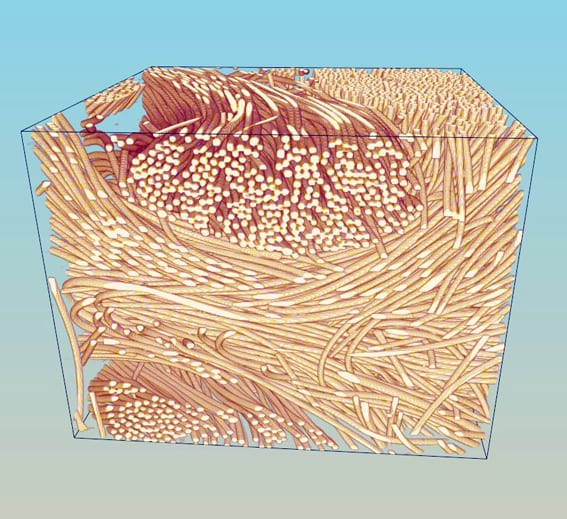
Understanding Carbon Reinforced Carbon
Carbon fiber-reinforced carbon has outstanding material properties and many applications but is extremely expensive – how to improve the processing of this useful material?
Powering the Planet with Energy Nanomaterials?
How can nanomaterials make a difference in the grand challenge: efficient and green global scale production, storage and use of energy? Professor Geoffrey Ozin from the University of Toronto gives his response to this question.

Advanced Energy Materials: Free online access to inaugural issue
The January 2011 issue of new journal Advanced Energy Materials is now freely available online at www.advenergymat.de.
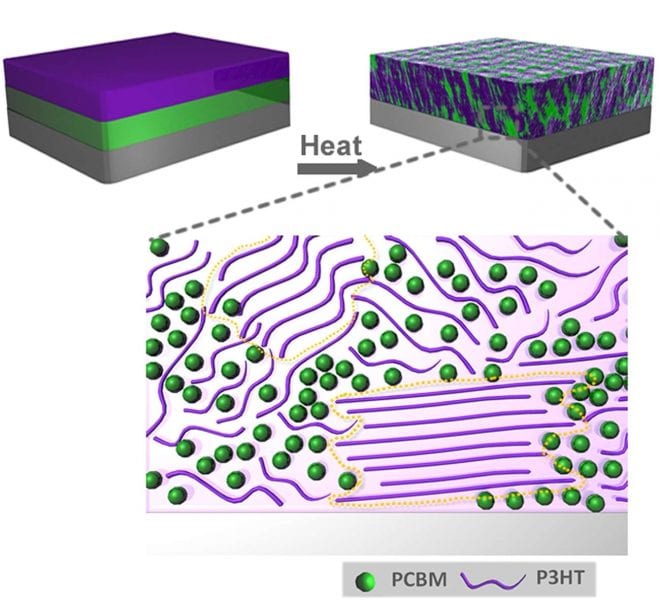
Morphology Changes in Plastic Solar Cells
Understanding the morphology changes in plastic solar cells may hold clues for the development of new high-performance materials.










