Personalized medicine for diseases that affect the central nervous system requires renewed focus on visualising the behaviour of drugs in the brain.


Personalized medicine for diseases that affect the central nervous system requires renewed focus on visualising the behaviour of drugs in the brain.
A new computational technique allows researchers to model biological processes with better accuracy and at a lower computational cost.
Models that can predict and help us to understand the body’s thermal state could help optimize temperature management strategies in a clinical setting.
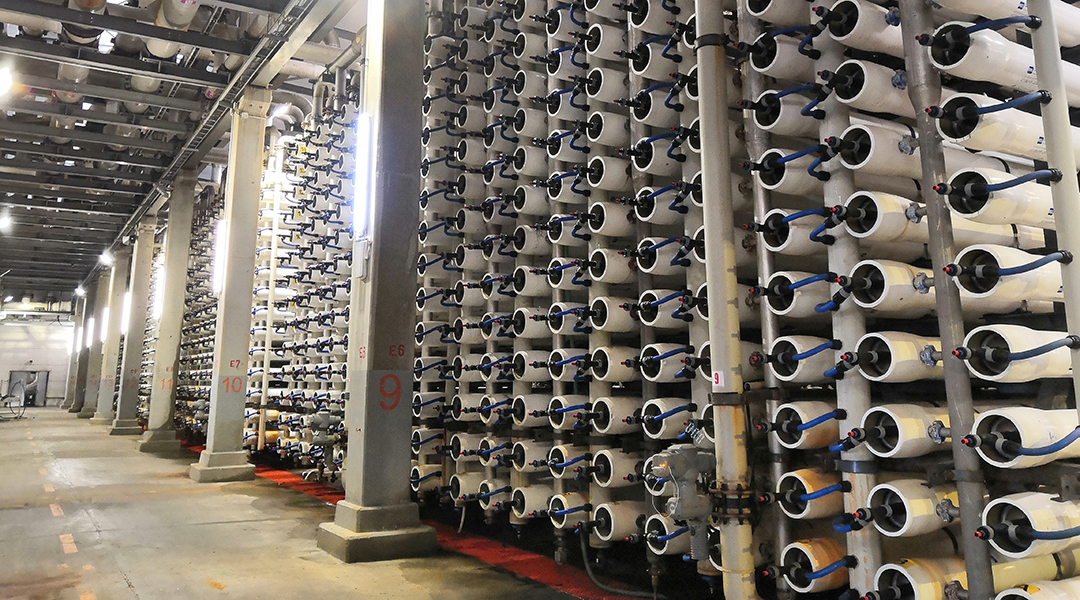

Scientists question whether technologies such as desalination will create solutions to climate change or just shift the problem.

Recent advanced in nanoparticle-based SERS imaging has led to better diagnoses of diseases like cancer, and improvements in image-guided tumor surgeries.

Hybridizing biofabrication processes will lead us to superior “living” tissue and organ substitutes that can be used to treat patients in lieu of donor grafts and metal and plastic devices.
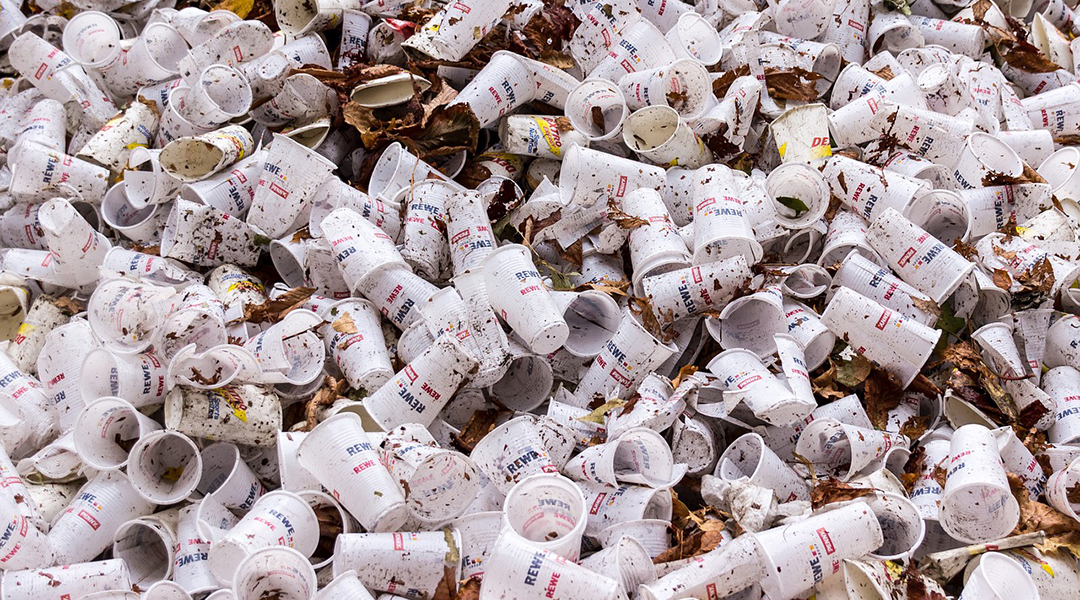

While plastic waste is an issue, its prominence in the general public’s concern for the environment is overshadowing greater threats.
How can computational modeling help to better understand and predict when the power cells of our gut fail?

Computational chemistry is key to understanding the unusual properties of eumelanin.
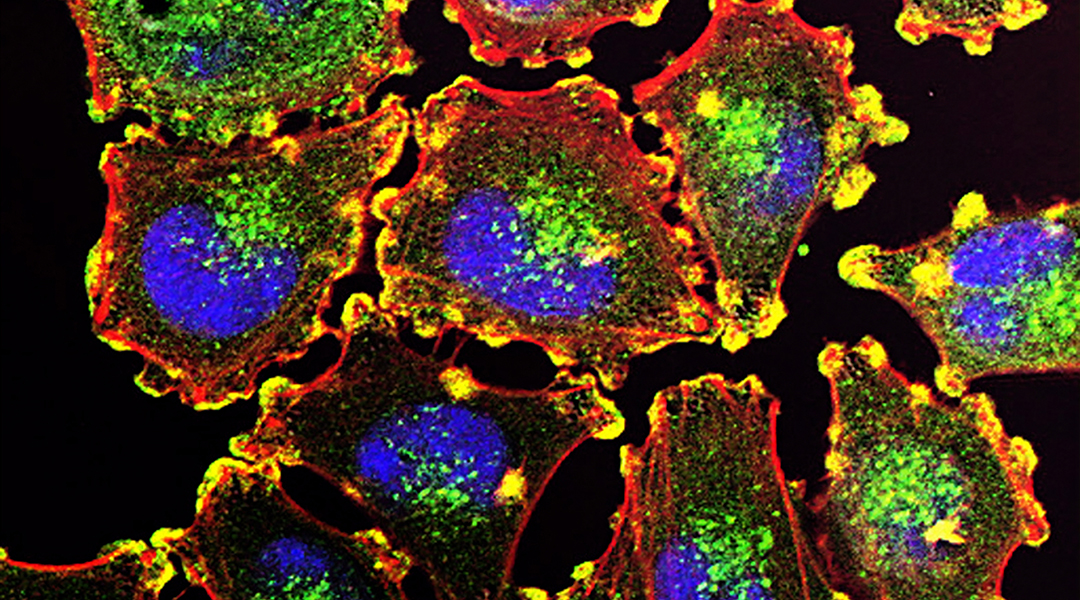
Light-activated proteins enable scientists to study and engineer subcellular structures for research and biotechnological applications.