A complementary technique, based on the Holographic Optical Tweezers (HOT) technique, which enables several locations within the same sample to be probed simultaneously, is developed.
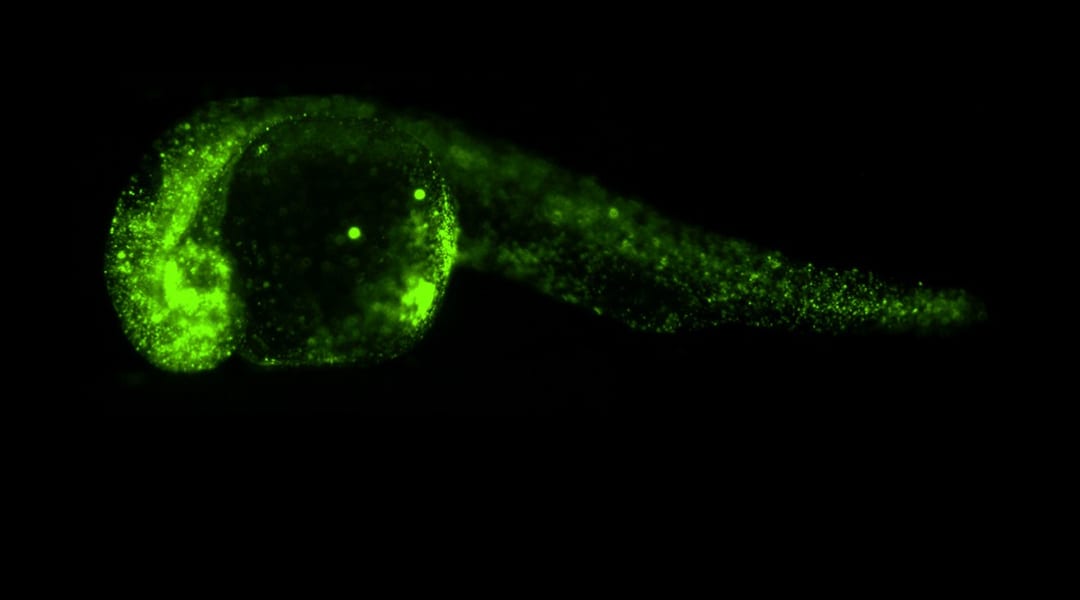

A complementary technique, based on the Holographic Optical Tweezers (HOT) technique, which enables several locations within the same sample to be probed simultaneously, is developed.
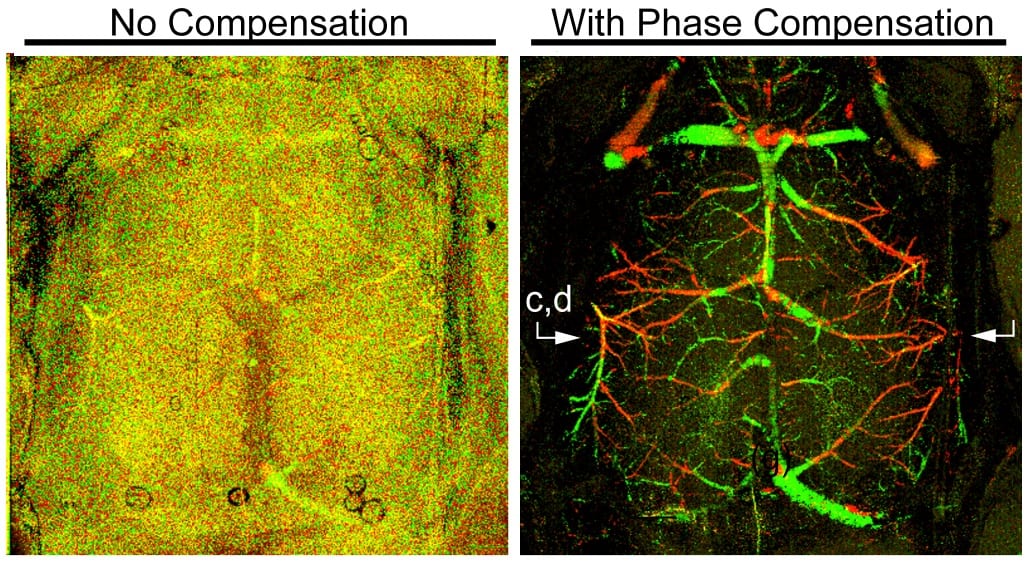
An American team of scientists develop a novel phase stabilization technique with significant improvement in the phase stability of a micro-electromechanical (MEMS) vertical cavity surface-emitting laser (VCSEL) based swept-source optical coherence tomography (SS-OCT) system.

A team of scientist from the Center for Optical and Electromagnetic Research in China developed a new laser spectroscopy method measuring gas to detect necrosis in the hip joints.
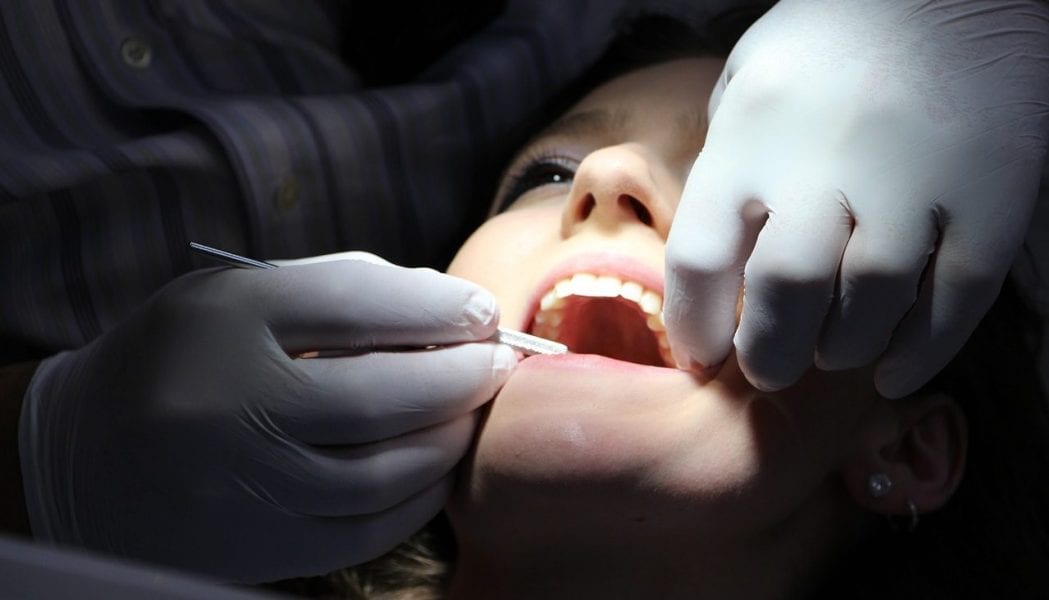
A team of German scientist developed a new laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy approach that can differentiate between hard and soft tissue in the mouth region and could help improve surgical dental treatment.

A team of German scientists used fast spontaneous Raman and Stimulated Raman Scattering (SRS) combined imaging to study the distribution and composition of lipids related to cardiovascular disease.
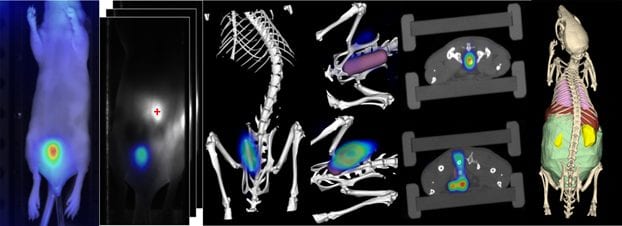
German scientists recently developed an improved FMT reconstruction for the imaging of deep tissue regions which could be beneficial in imaging colon cancer and inflammatory bowel disease.
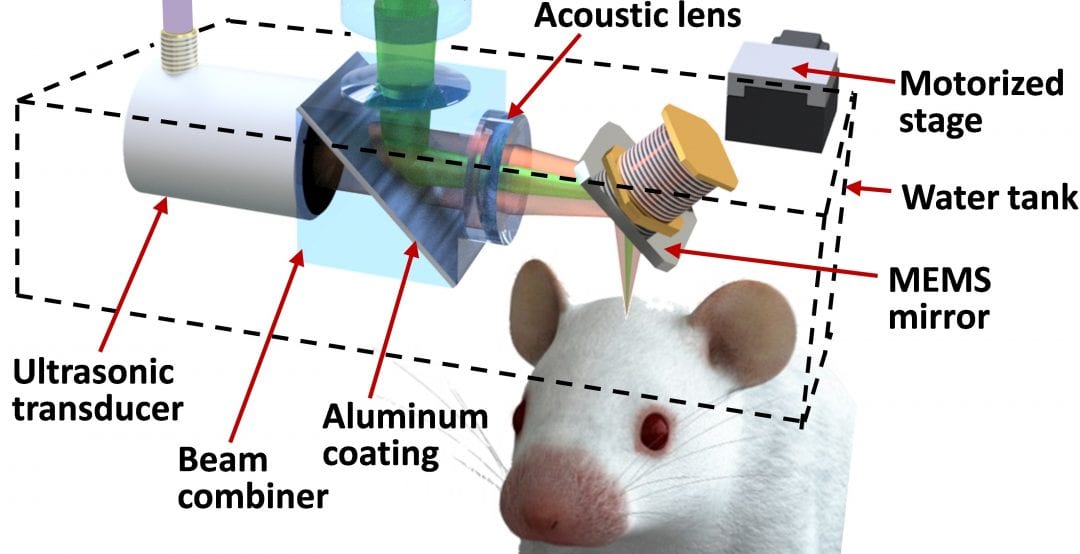
American neuro-scientists recently demonstrated getting a small step closer to creating a better understanding of so-called mini-strokes, which are related to cognitive decline and dementia, using high-speed optical-resolution photoacoustic microscopy.
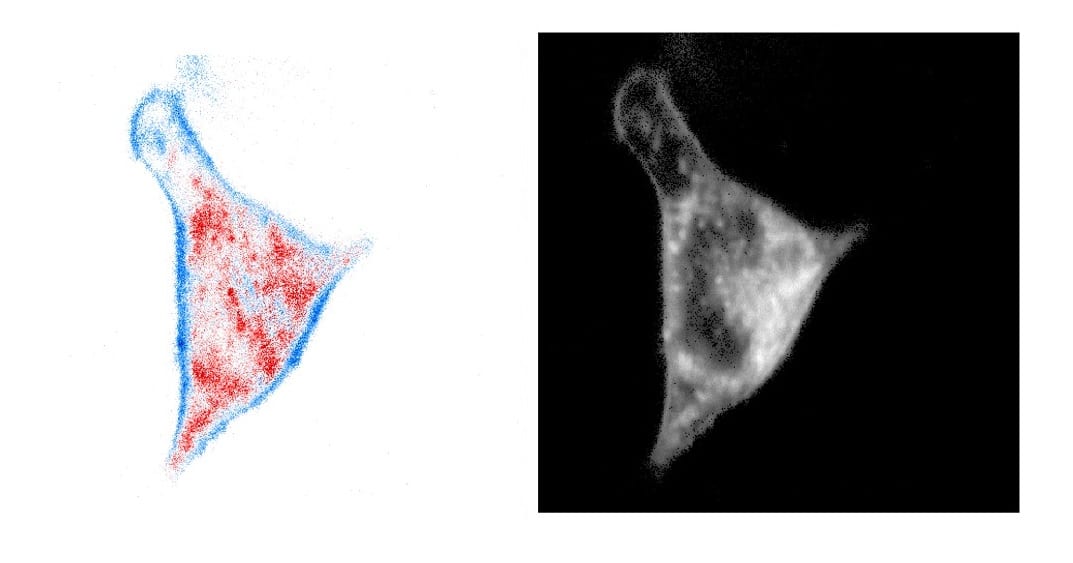
German and British researchers tested a novel Noise-Corrected Principal Component Analysis (NC-PCA) method for time-domain FLIM data and showed how useful and robust this new technique can be.
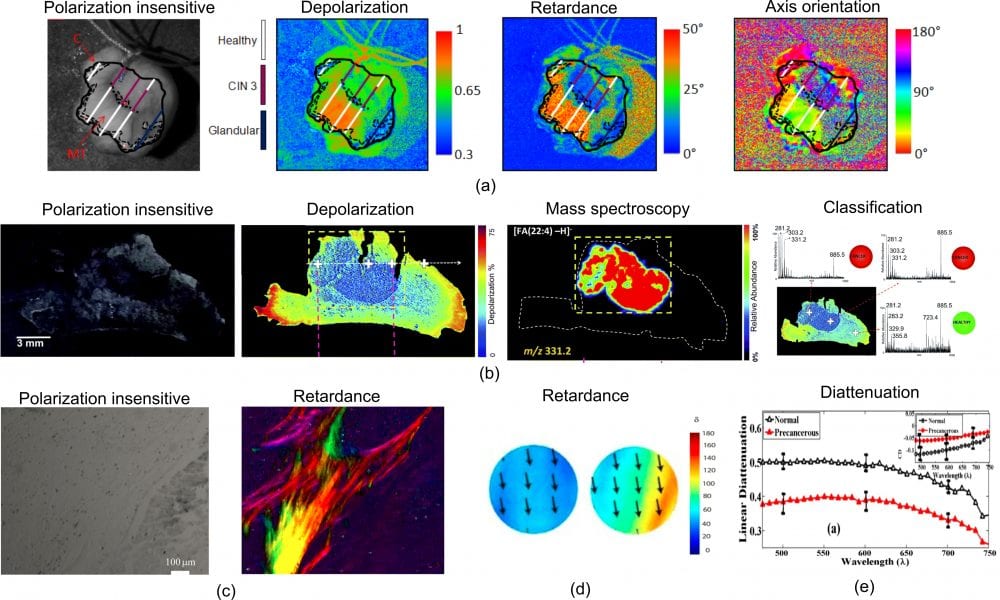
In a recently published review Dr. Ji Qi and Dr. Daniel S. Elson take a closer and critical look at Mueller polarimetric imaging and review the latest advances in this field in relation to surgical imaging.
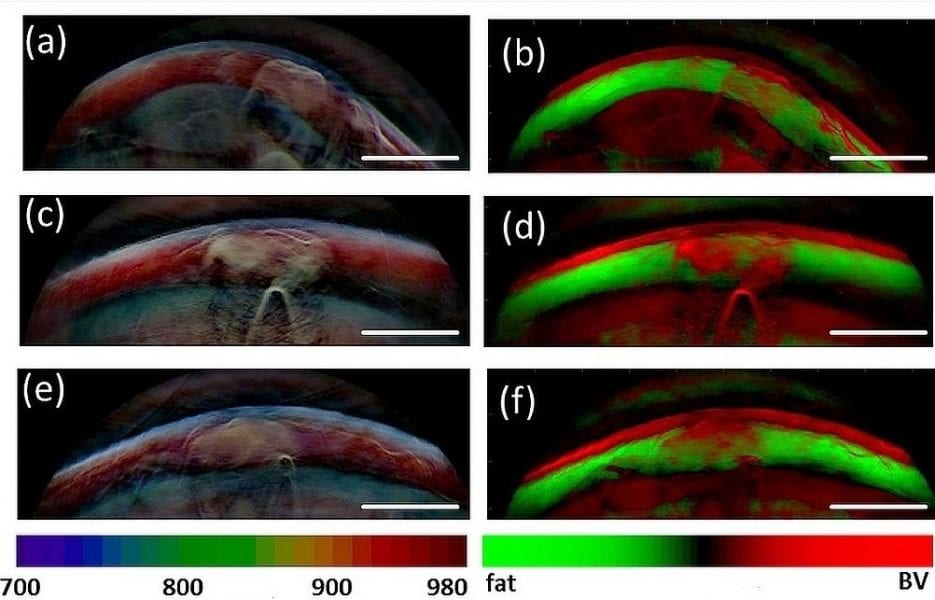
German scientists recently optimized optoacoustic imaging by multispectral optoacoustic tomography (MSOT) to improve the diagnosis of fatty tumors.