The combination of two irreversible processes is shown to lead to damage recovery and reversible restoration of particle shape.


The combination of two irreversible processes is shown to lead to damage recovery and reversible restoration of particle shape.
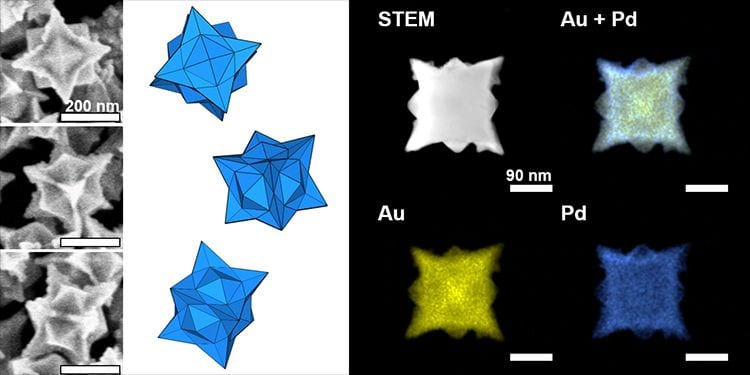
Discover how iodide can be used to control the shape of bimetallic nanoparticles for application in catalysis, solar-energy conversion and therapeutics.
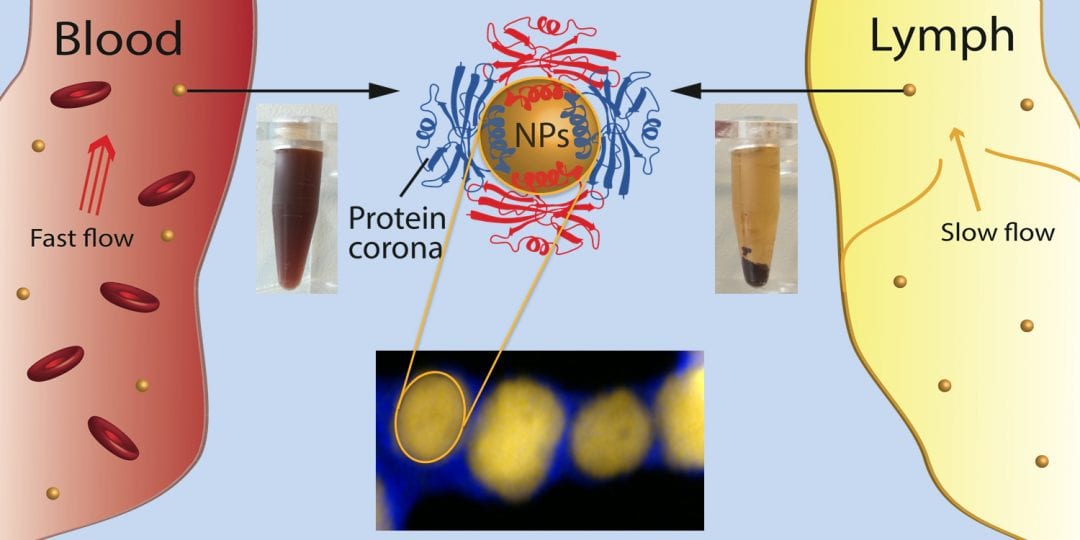
Interactions of nanoparticles with their surroundings, both in vitro and in vivo, are different simply because the environments are different. As such, the first insight towards answering complex questions associated with in vitro-in vivo translation are provided.

A directed self-assembly of gold nanoparticles may be employed for the design of molecular electronic networks for logic or memory applications.
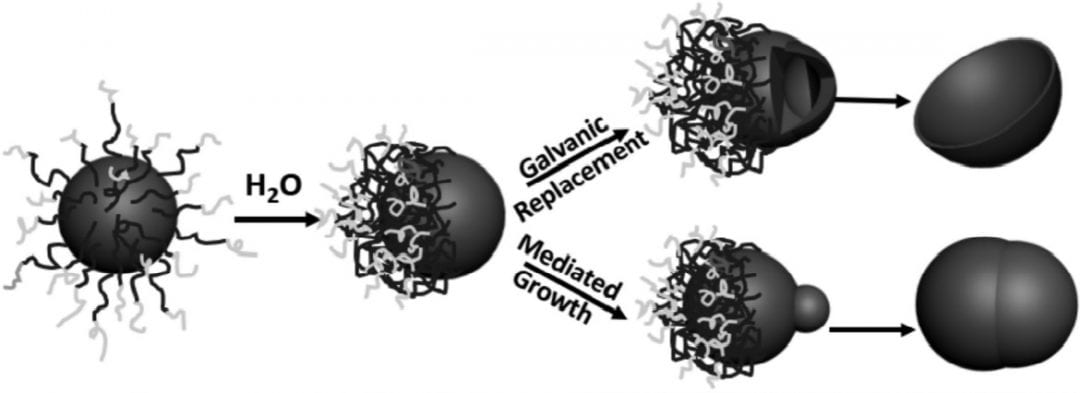
Creating asymmetric nanoparticles is harder than standard colloidal particle synthesis. Here, hydrophobicity unlocks a variety of metal nanoparticle types.

A discussion of how nanoparticles of different plasmonic materials can facilitate the detection of molecular CD spectra is presented.
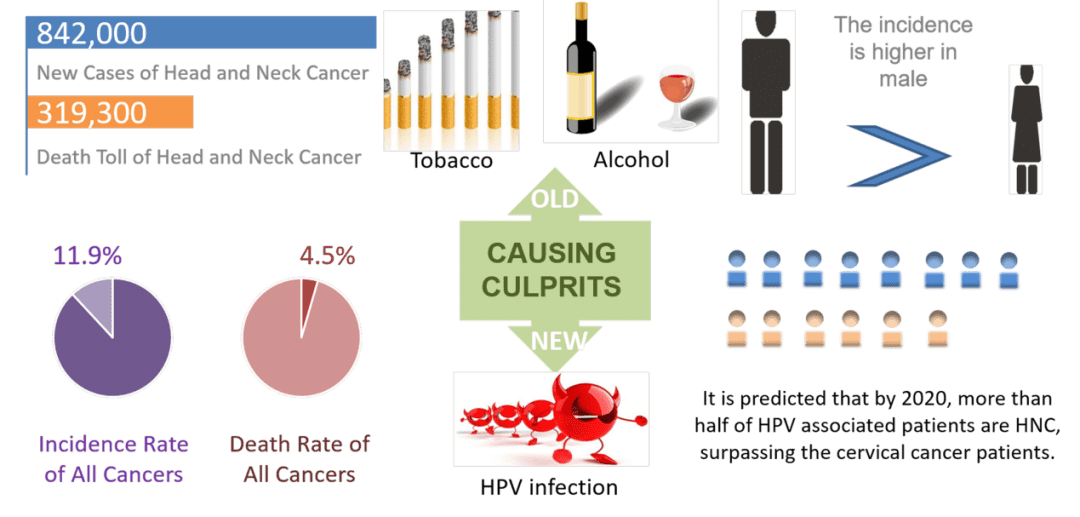
Nanoparticles can assist in treatment of Head and Neck Cancer patients by optimizing distribution of chemotherapy drugs for better outcomes and less side effects.
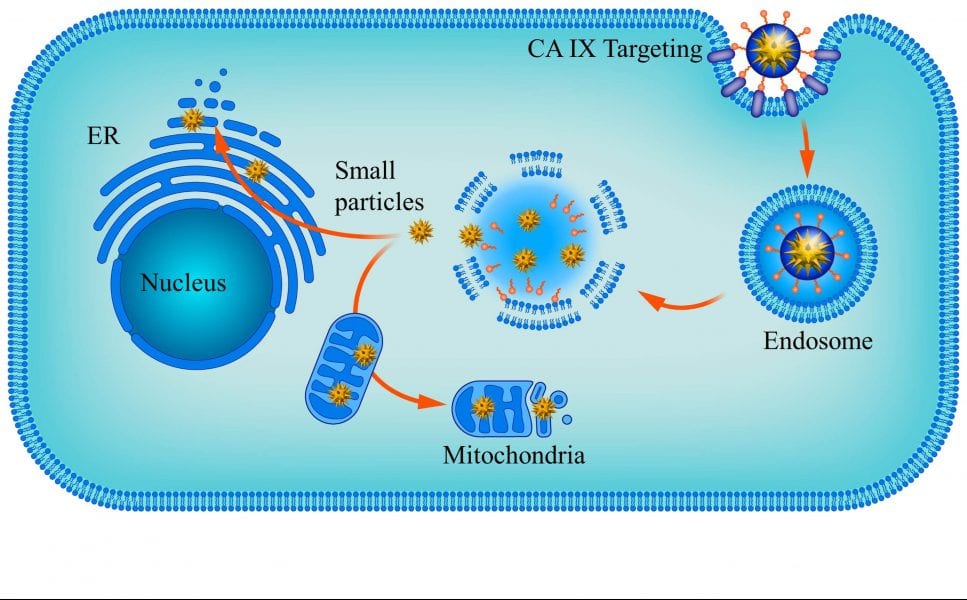
The fabrication of a specific nanomedicine, prickly shaped nanoparticles, enables a novel cancer treatment methodology.
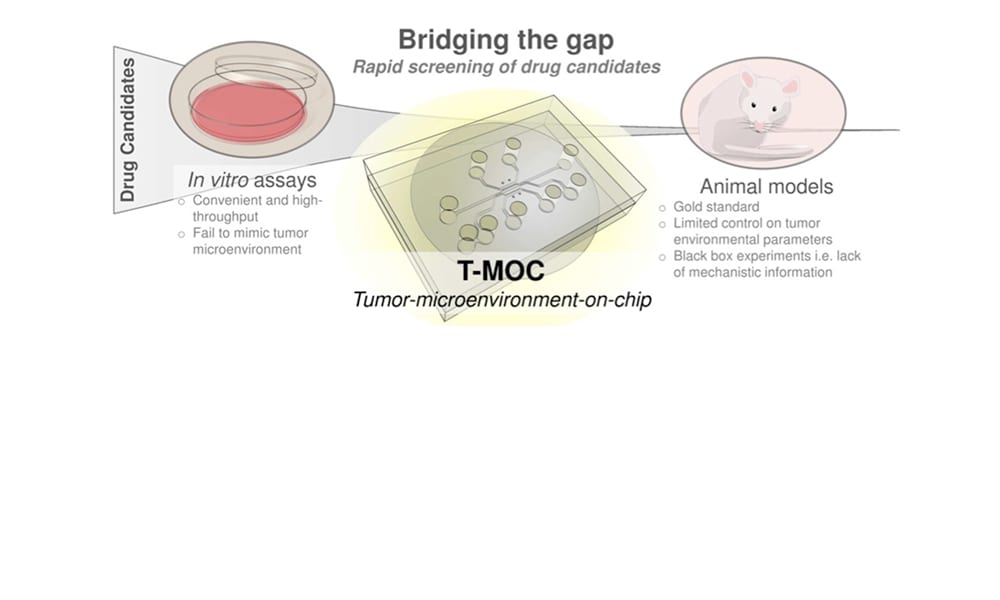
Microfluidics offer significant advantages over traditional macroscale cell cultures by enabling recapitulation of the tumor microenvironment through precise control of physiological cues such as hydrostatic pressure, shear stress, oxygen, and nutrient gradients.
An introduction to the mechanisms governing internalization and trafficking in cells; and a discussion of methods to detect endosomal escape and recent advances in controlling endosomal escape from polymer- and lipid-based nanoparticles are presented in this recent Review.