A new AI diagnostic tool uses microbiome data and lifestyle factors to predict risk of multiple diseases, ushering in a new era of personalized healthcare.

A new AI diagnostic tool uses microbiome data and lifestyle factors to predict risk of multiple diseases, ushering in a new era of personalized healthcare.
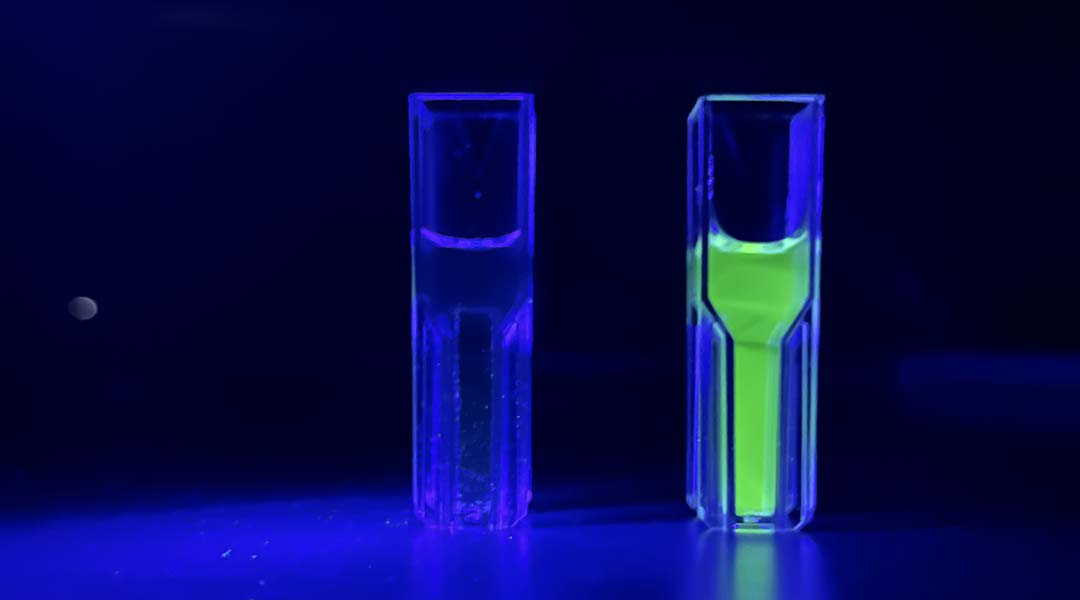

Analyzing biomolecules found in the breath, scientists can detect early signs of deadly blood clots found in diseases like COVID-19, heart disease, sepsis, and more.
A self-assembling helix formed from nateglinide, a complementary diabetes treatment, provides a protective coating that could open the door to an oral insulin medication.
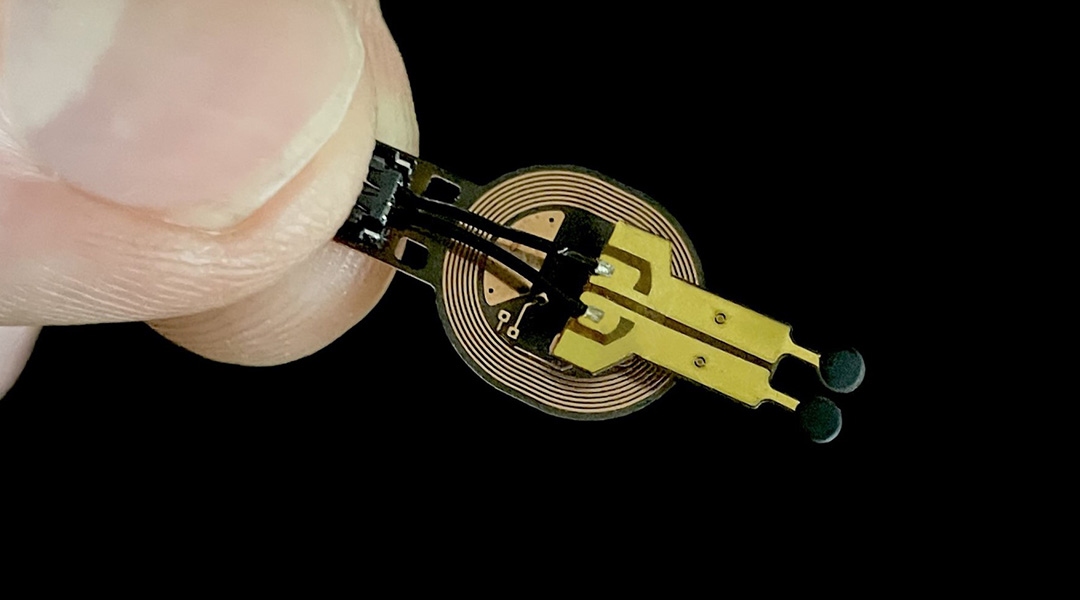
Scientists develop a sensor that predicts wound healing rate with more than 70% accuracy.
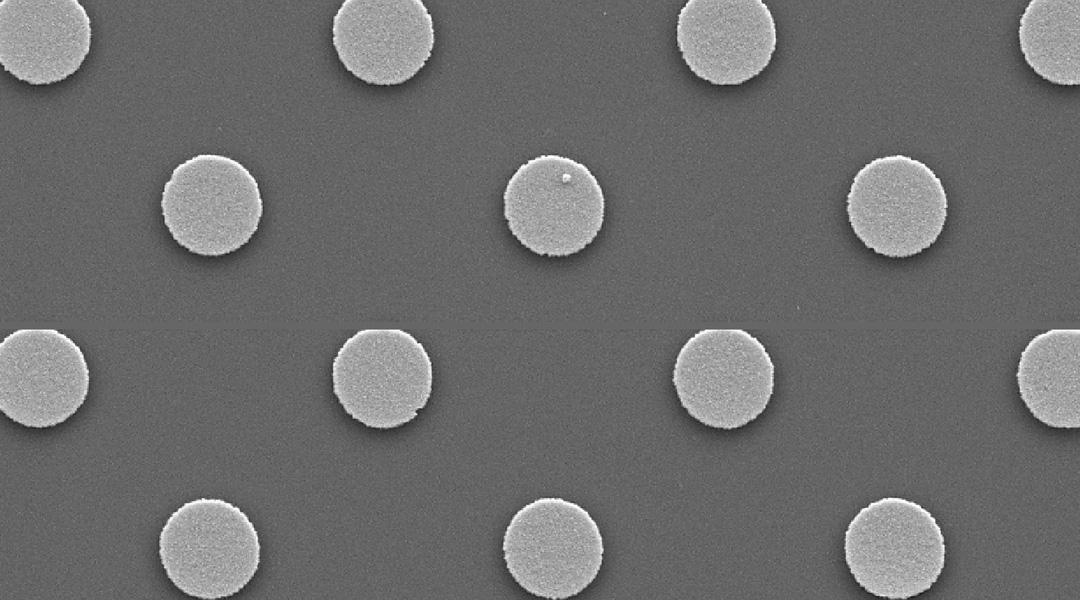
A membrane embedded with magnetic microdisks mechanically stimulates pancreatic cells to produce insulin, which could help treat diabetes.
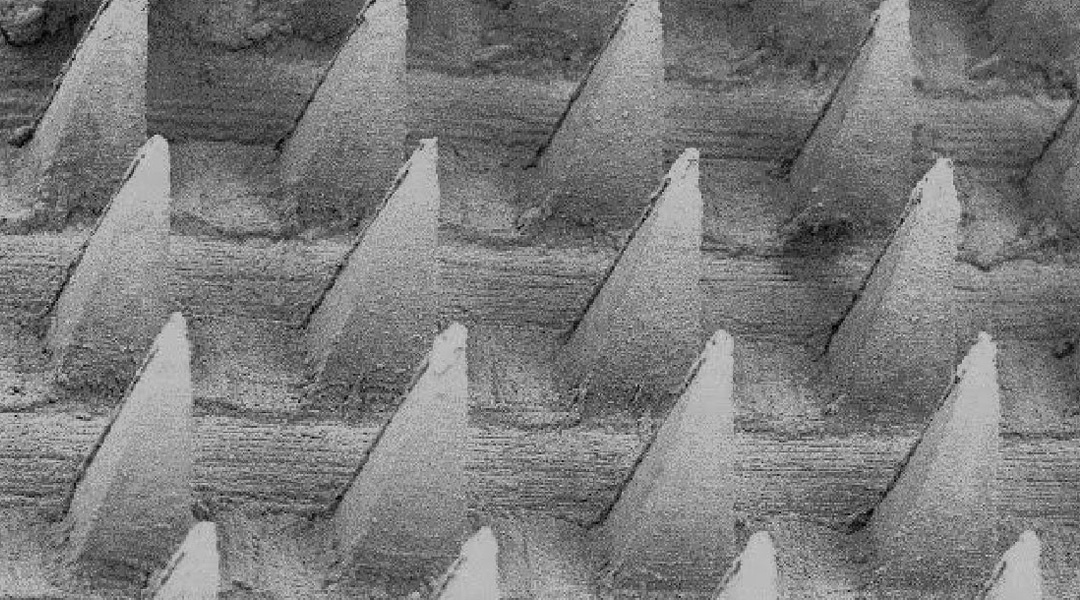
Researchers demonstrate a technique for reliably coating microneedles with antibacterial agents
Revolutionizing respiratory disease detection with a portable E-Nose for non-invasive breath analysis.
Catalysts that mimic antioxidase enzymes show promise in treating inflammatory diseases, such as gum disease, lupus, or cancer.

The infant microbiome can be built from a dizzying array of different sources.
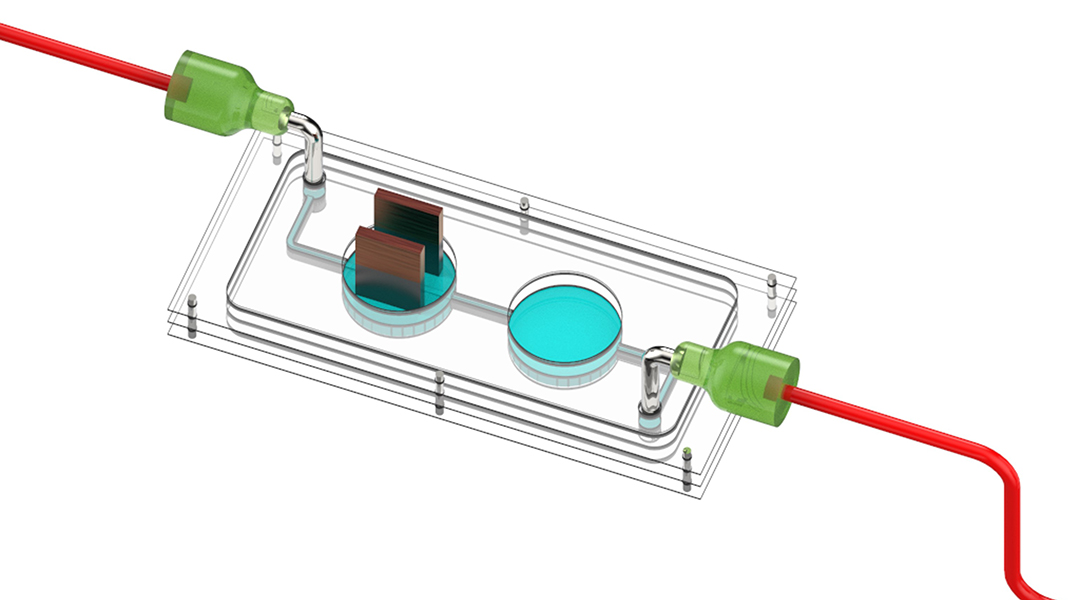
The device provides a powerful tool for studying and treating diabetes, allowing personalized modelling by using patients’ own cells.