Stimuli-sensitive drug carriers can aid in the treatment of diabetes as glucose biosensors and glucose-triggered insulin delivery systems.
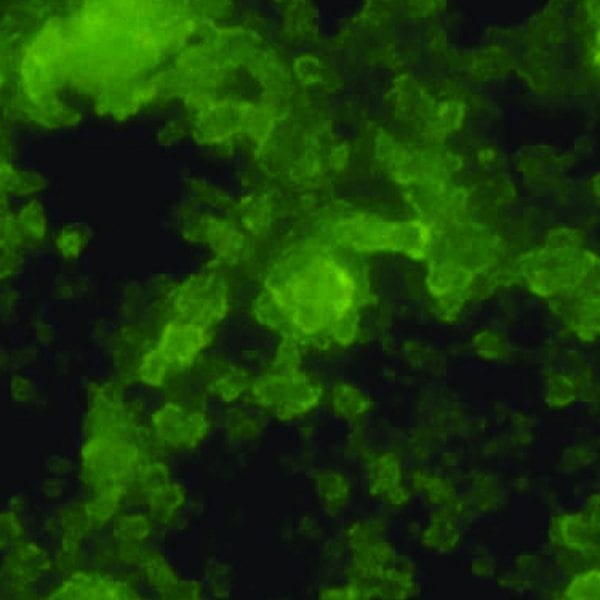

Stimuli-sensitive drug carriers can aid in the treatment of diabetes as glucose biosensors and glucose-triggered insulin delivery systems.
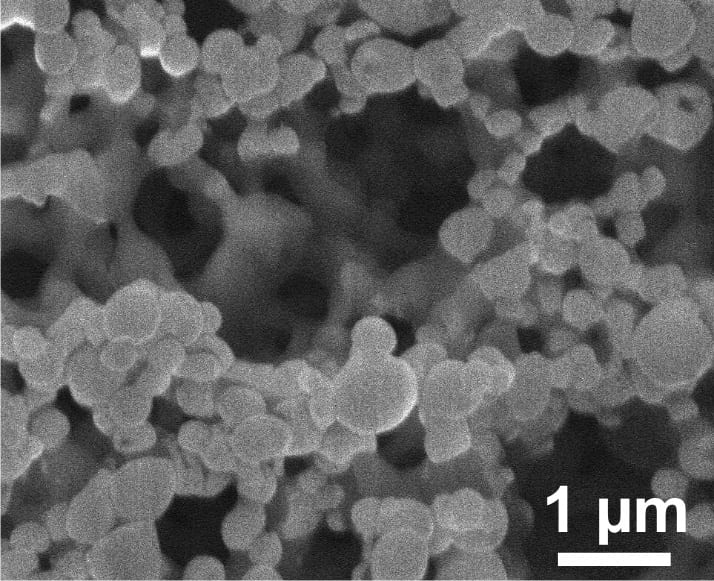

Researchers have developed a network of nanoscale particles that can be injected into the body and release insulin when blood-sugar levels rise.
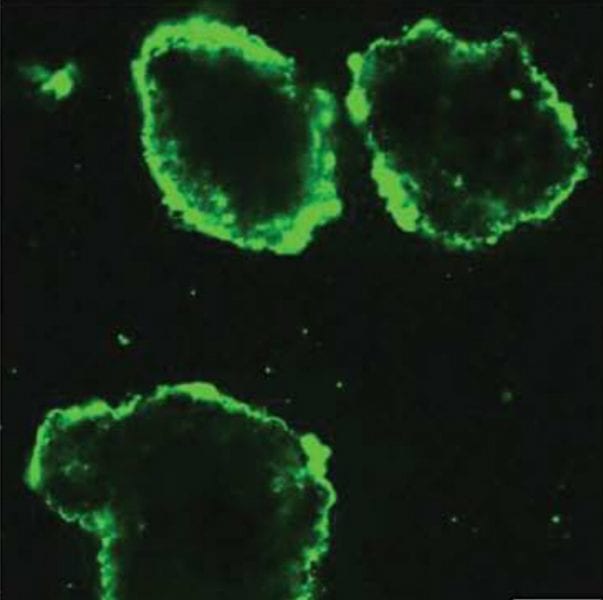
American researchers report new coating to improve promising treatment for Type 1 diabetes.
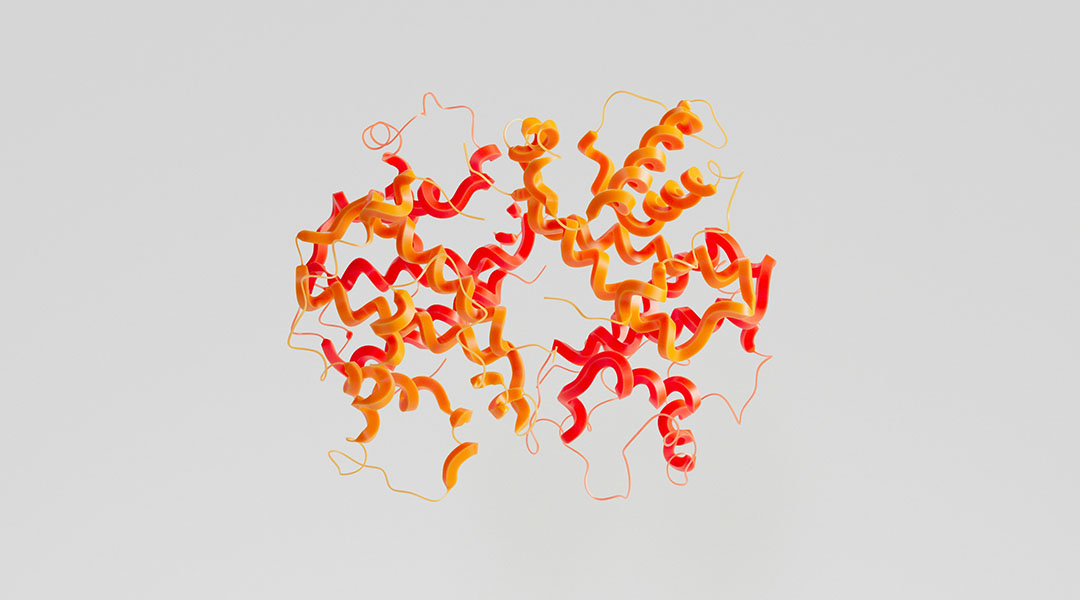
A new study identified the potential pathway responsible for linking high hemoglobin to polycystic ovary syndrome.
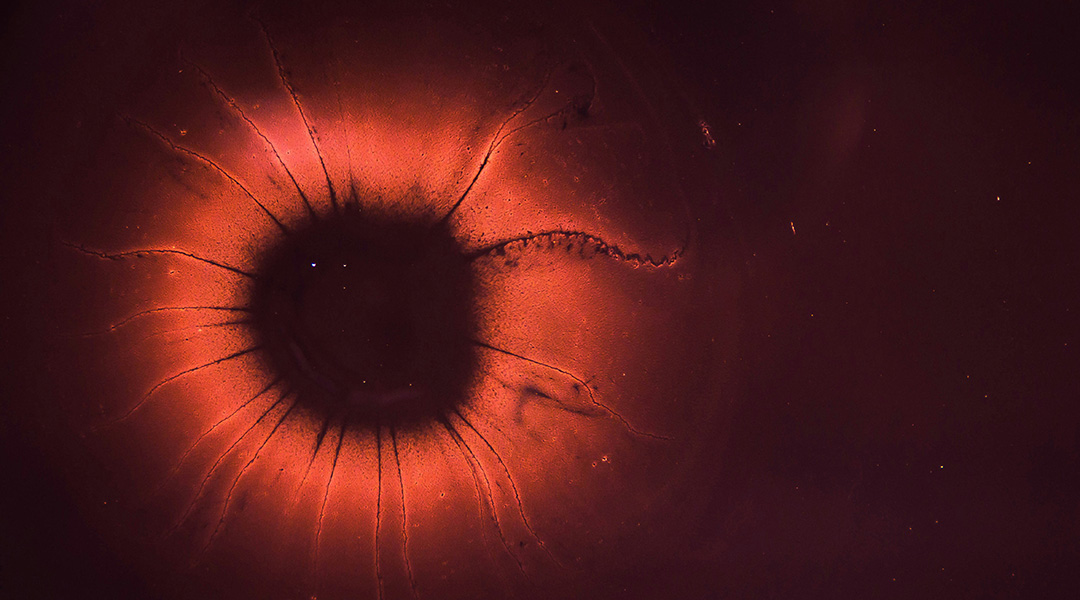
Cells that can no longer divide may play a role in the chronic inflammation that weakens the immune system and contributes to aging.
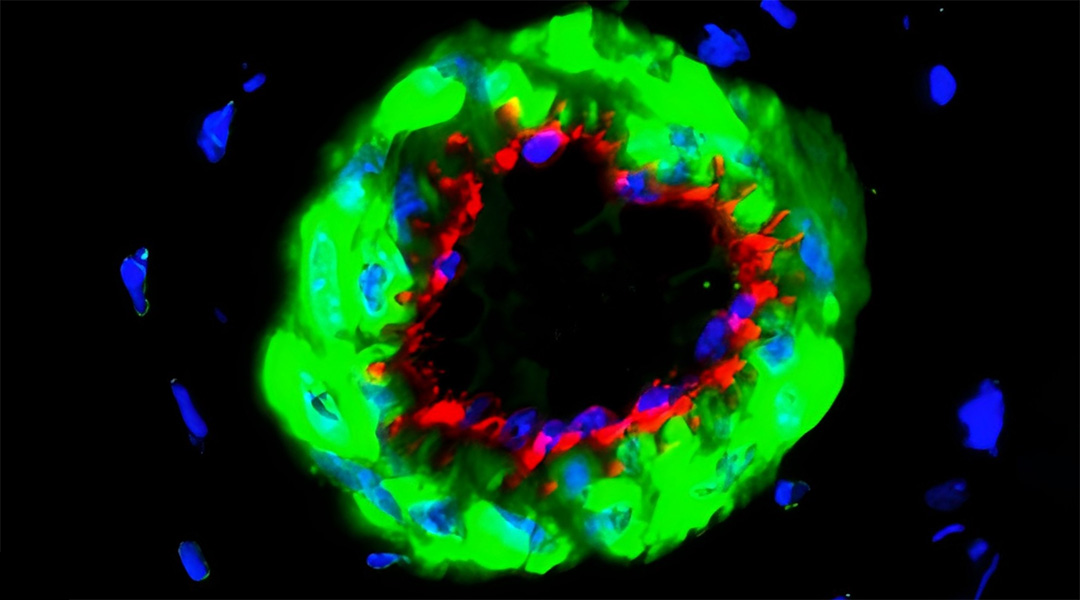
This safer, non-surgical treatment for diabetic limb ischemia could help patients with severe blood flow complications.

The protein helps convert white fat tissue into calorie-burning beige fat, providing a potential target for weight loss and obesity treatments.
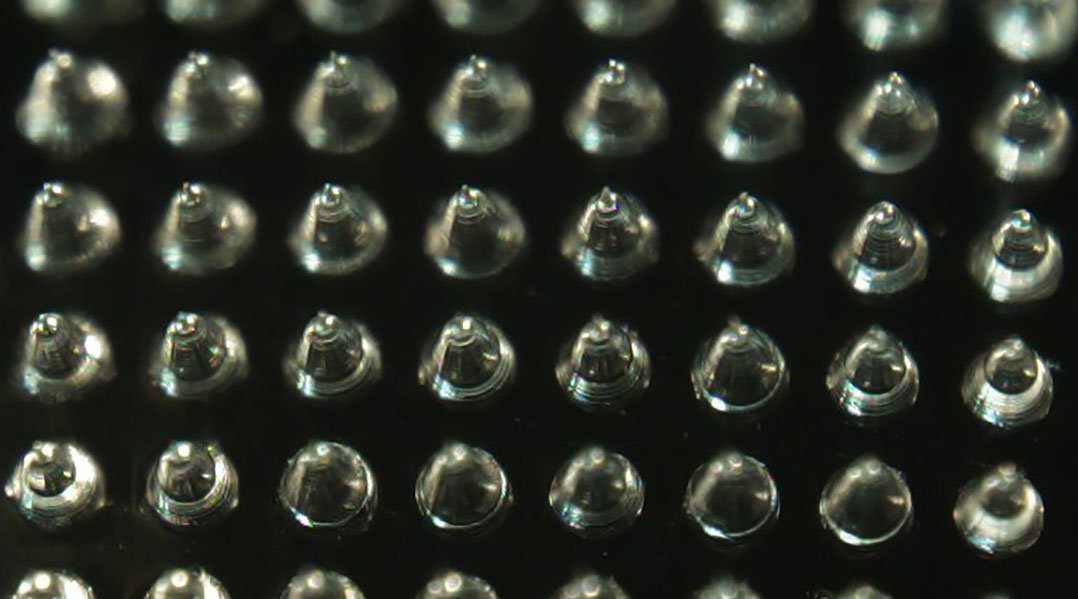

Microneedles allow scientists to precisely control the delivery of drugs to chronic wound sites and restore natural healing processes.

Researchers have discovered that a protein produced by parasitic worms in the gut enhances wound healing in mice.
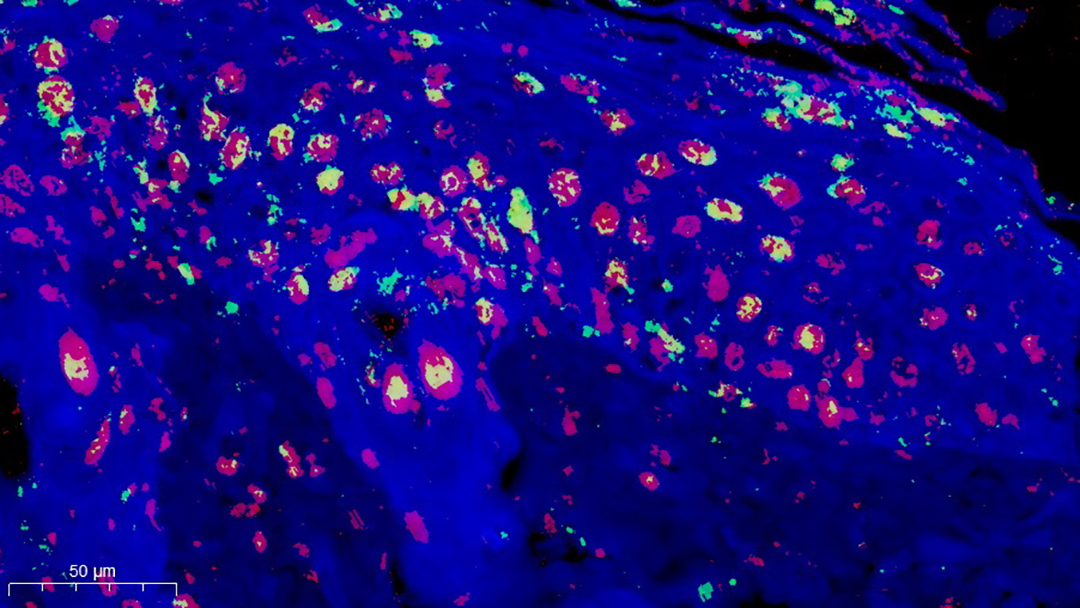
Zwitterionic hydrogels boost healing in diabetic wounds by balancing the immune response, reducing inflammation, and promoting tissue growth.