A new drug called momelotinib reduces the need for blood transfusions in anemic patients suffering from myelofibrosis.
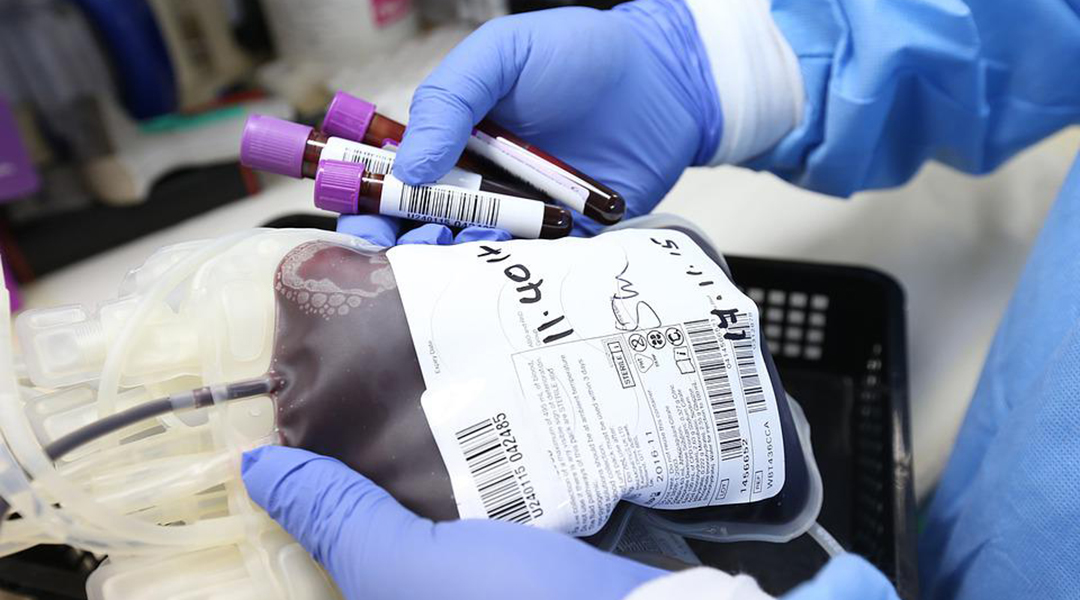

A new drug called momelotinib reduces the need for blood transfusions in anemic patients suffering from myelofibrosis.
Self-sensing materials will find a range of applications from tissue engineering to building lightweight aircraft.

Researchers show that through aging the number of stem cells contributing to blood cell production significantly shifts.
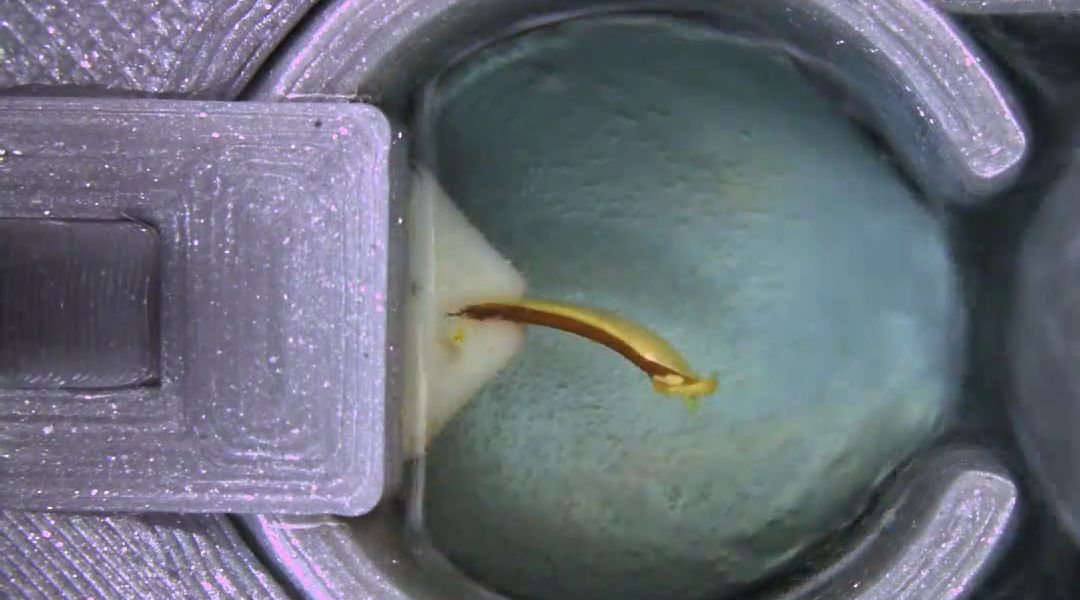

Scientists have developed the first artificial muscles made from natural proteins that contract autonomously and consume chemical fuel.
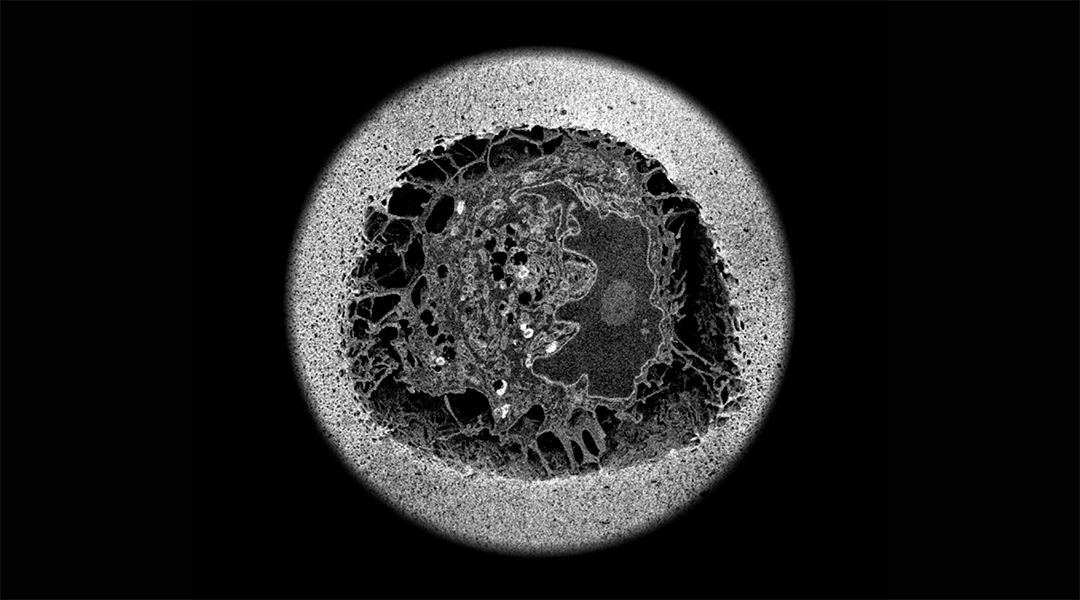
A natural chemical tether helps researchers attach cells to inert biomaterials for better cell models and therapies.
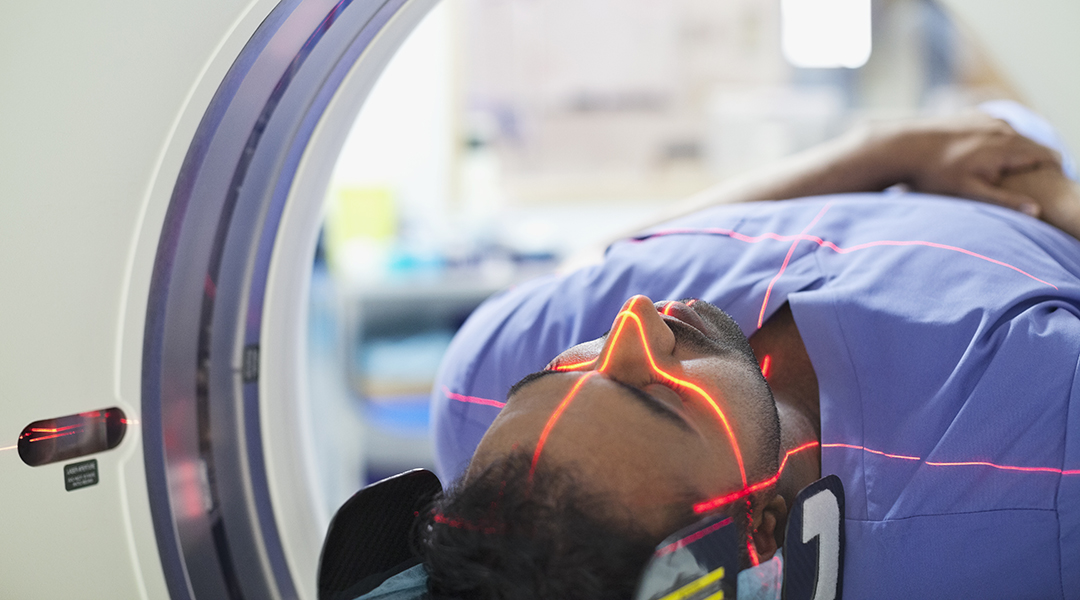
While stem cell therapies have been touted as “miracle cures”, data indicates that there are still hurdles keeping them out of the clinic.
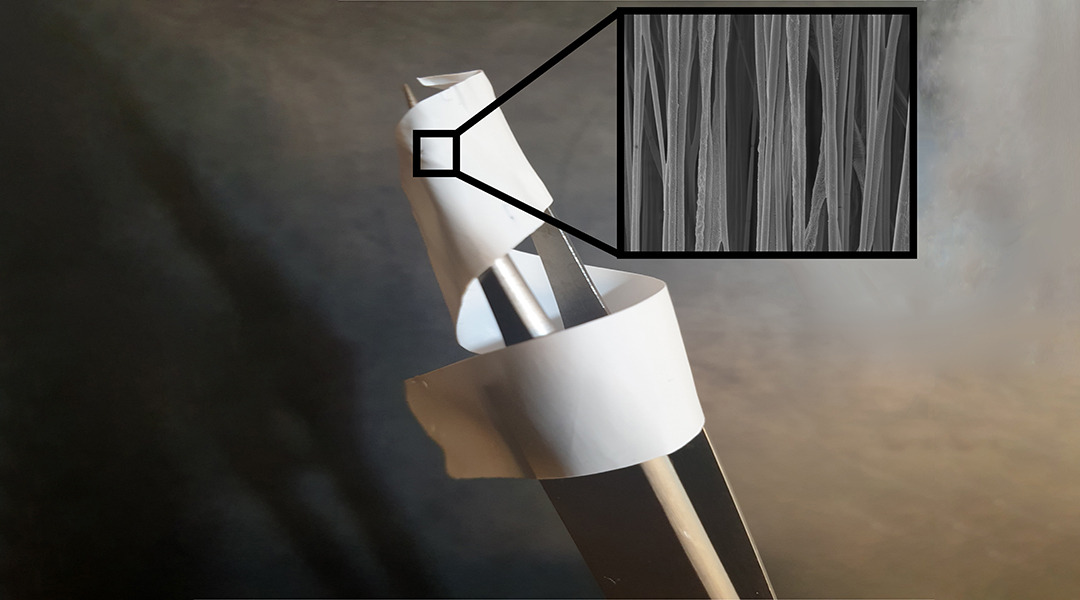
This implantable device acts as mechanical support for damaged tendons and mimics the bioelectrical cues usually provided by collagen during wound healing.
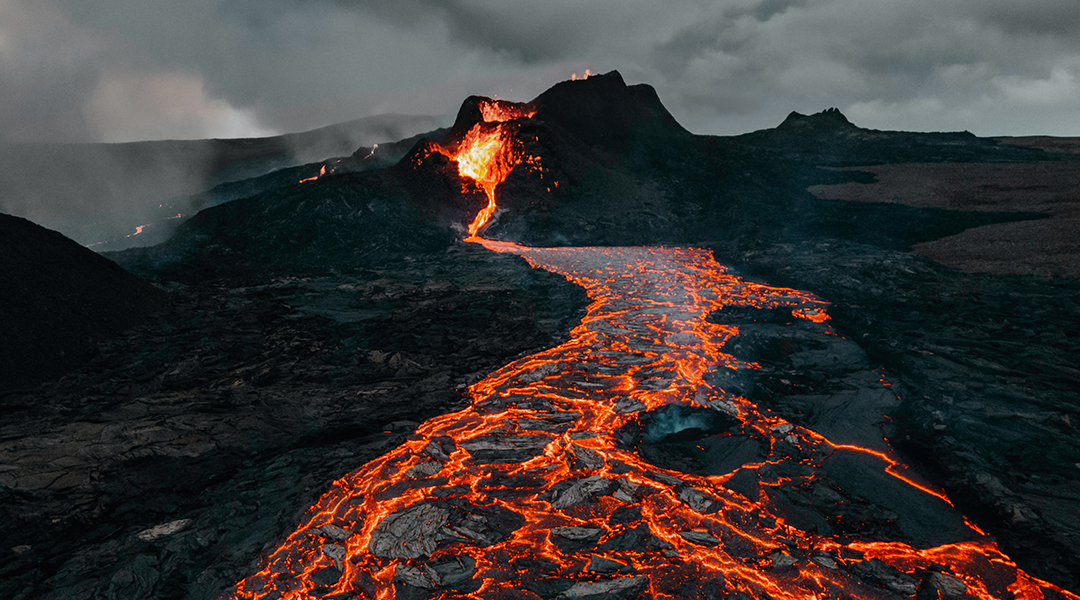

The weathering of the Earth’s surface serves as a geological thermostat and new research says that the breakdown of rocks at volcanic sites could help consume some of the world’s atmospheric carbon.

A charged microneedle patch for pain-free delivery of anesthetics could replace anxiety-inducing needles in dental work.
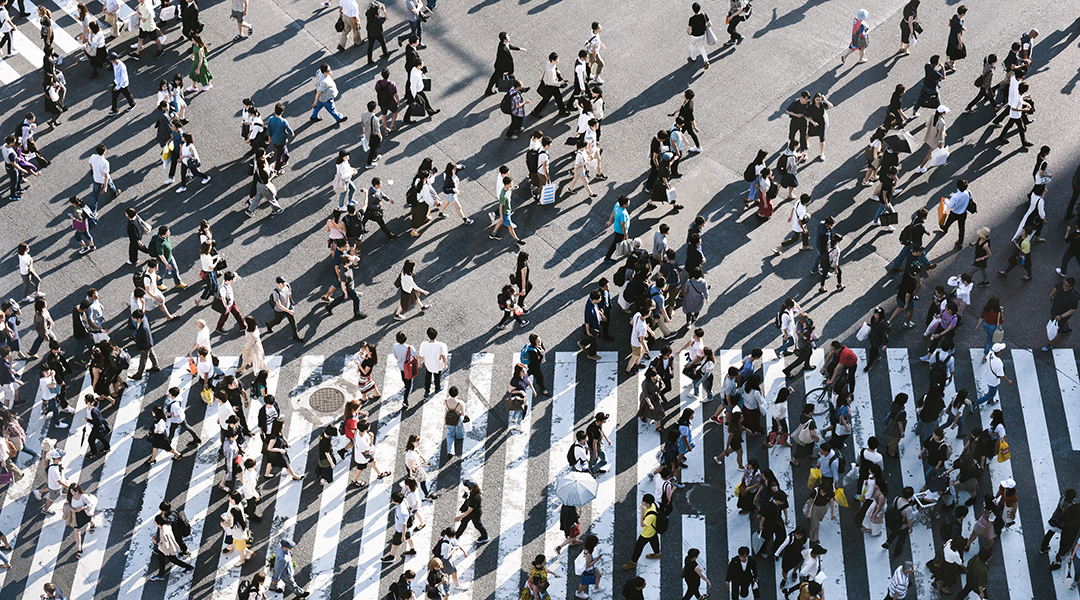

The Anthropocene has been defined by its carbon emissions, but modern technological advancements may hold the key to breaking this habit.