Phosphorescent conjugated polymer dots (Pdots) are developed for cancer cell imaging and therapy.
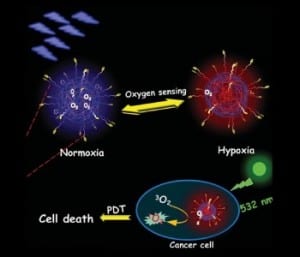

Phosphorescent conjugated polymer dots (Pdots) are developed for cancer cell imaging and therapy.
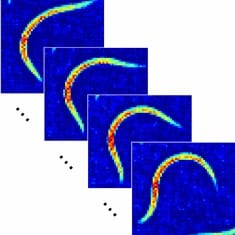
Quantum cascade lasers enable the quick and efficient real-time mid-infrared microspectroscopy of living microorganisms.

Enhanced electric fields through the optical magnetic mirror effect enable subwavelength imaging resolution.
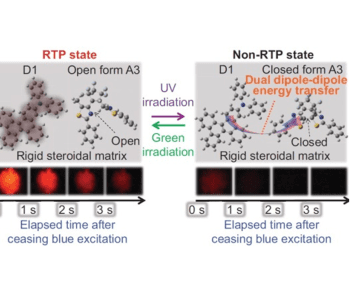
A host–guest–guest material demonstrates the photoreversible on–off recording of persistent room-temperature phosphorescence from the phosphorescent guest.
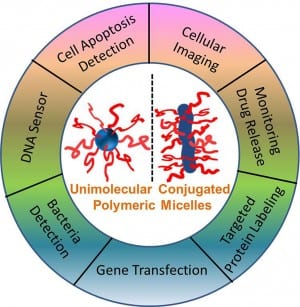
Fluorescent materials have drawn much attention as probes for imaging, diagnosis, and therapy in biological science.
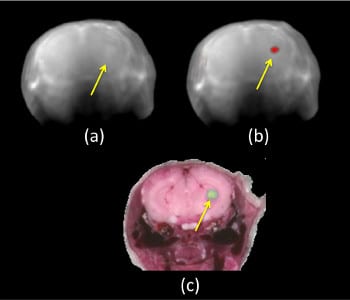
Molecular optoacoustic imaging is a powerful tool for research and for diagnostics. Multiple excitation wavelengths tend to increase its sensitivity .
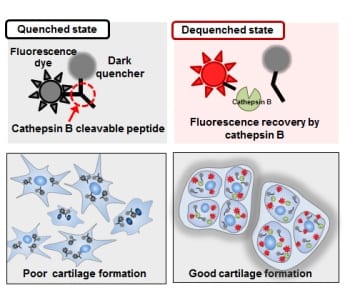
Cathepsin B molecular imaging has been shown to be a powerful tool in reflecting the potential of cartilage formation and predicting the quality of cartilage.
Tumour development is closely monitored through infrared emission from copolymer nanoparticles.
Fully automated, easy-to-use, class-leading Raman imaging system “apyron” combining unrivaled spectral resolution in 3D confocal Raman imaging and extremely sensitive laser power determination with a mouse click. The device is presented for the first time at Pittcon 2015 in New Orleans, the major fair for lab instrumentation worldwide.
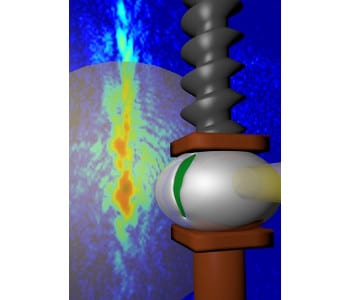
An X-ray ptychography study follows the destruction of a microscale composite during compression in unprecedented detail.