Researchers combine nanoplasmonic architectures and interferometry to bring nanoscale biosensors to near-commercial levels of sensitivity.


Researchers combine nanoplasmonic architectures and interferometry to bring nanoscale biosensors to near-commercial levels of sensitivity.
A roundup of the latest materials science research from the past week.

Continental and Fraunhofer join forces to develop rubber made from dandelion plants for tire production.
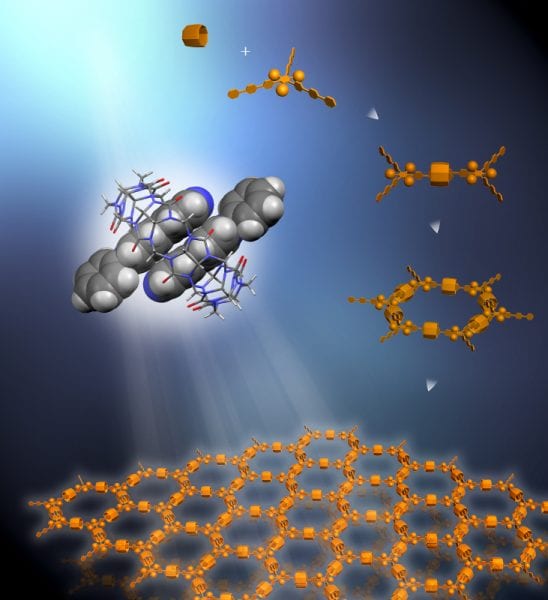
Researchers at Berkeley Lab’s Molecular Foundry create first soluble 2D supramolecular organic frameworks.
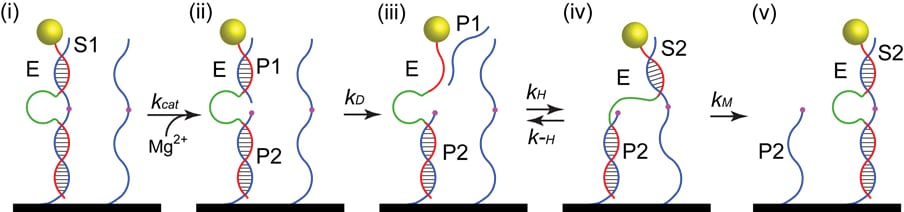
Researchers have created a new type of molecular motor made of DNA and used it it to transport a nanoparticle along the length of a carbon nanotube.
Physicists have developed a “planet-satellite model” to precisely connect and arrange nanoparticles in three-dimensional structures.
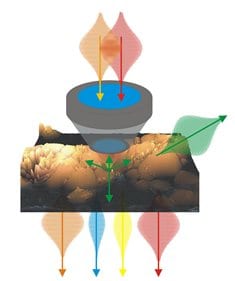
Multimodal nonlinear microscopy has matured to a key imaging modality in life science and biomedicine.
Researchs show that combining nanoparticles and DNA nanotechnology can amplify the signal obtained from imaging the extracellular matrix.
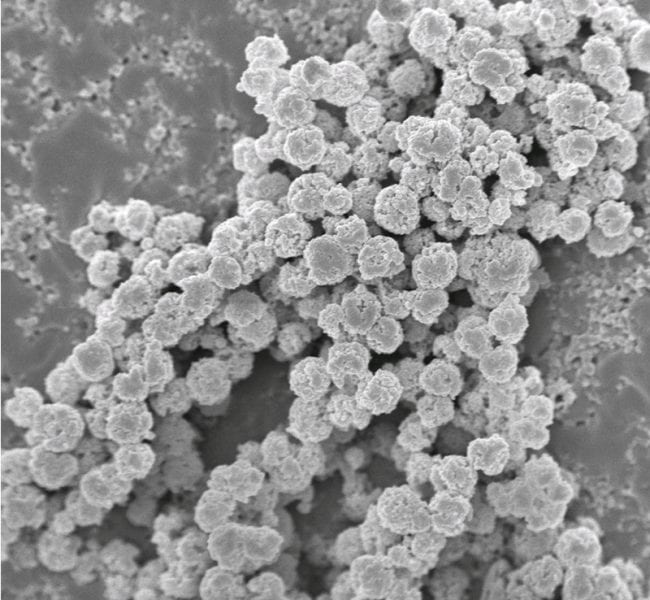
An antigen delivery system based on quaternized chitosan hydrogel microparticles has been developed at the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Nanowires, solar cells, and silicene – these and more in September’s physics highlights.