Latest
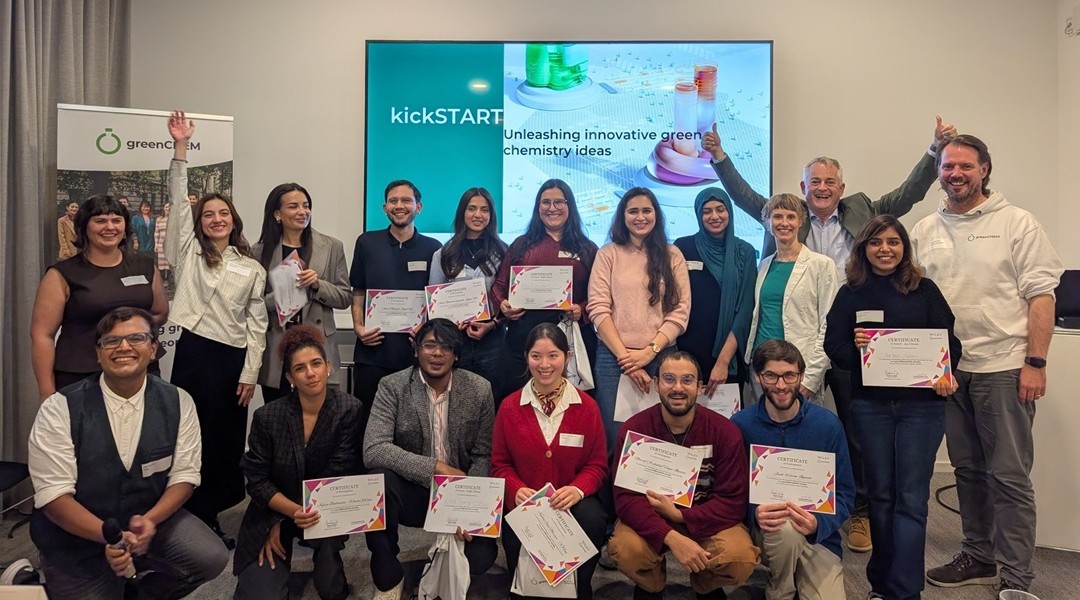

kickSTART: The Beginning of a Green Generation of Chemistry
Young researchers promote the importance and industrial potential of green chemistry via the kickSTART project.
Microneedles enable 98% smaller, cheaper artificial pancreas
New technology could make diabetes management more accessible to those who need it most.

More vulnerable honey bees buffer the hive against heat stress
Honey bees more susceptible to heat are the first to initiate fanning behaviours that help the hive cool down.

More vulnerable honey bees buffer the hive against heat stress
Honey bees more susceptible to heat are the first to initiate fanning behaviours that help the hive cool down.

Microneedles enable 98% smaller, cheaper artificial pancreas
New technology could make diabetes management more accessible to those who need it most.
Tactile sensors from mechanical metamaterials for sensitive wearables and prosthetics
Engineers have developed tactile sensors with increased sensitivity, thanks to auxetic mechanical metamaterials.
Quantum Anomalies in Condensed Matter: From Theoretical Peculiarities to Tangible Science
Making quantum anomalies accessible to experimentalists could redefine next-generation technologies and device engineering.
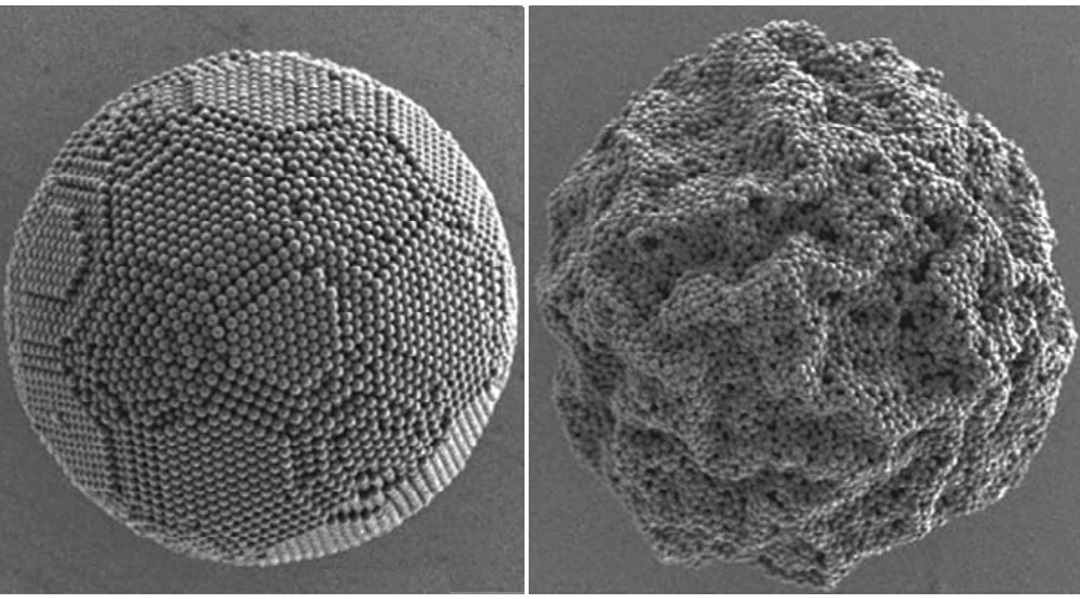
Surfactants Steer Supraparticle Structure
pH-responsive surfactants enable control over buckled supraparticle formation in emulsion-based systems.
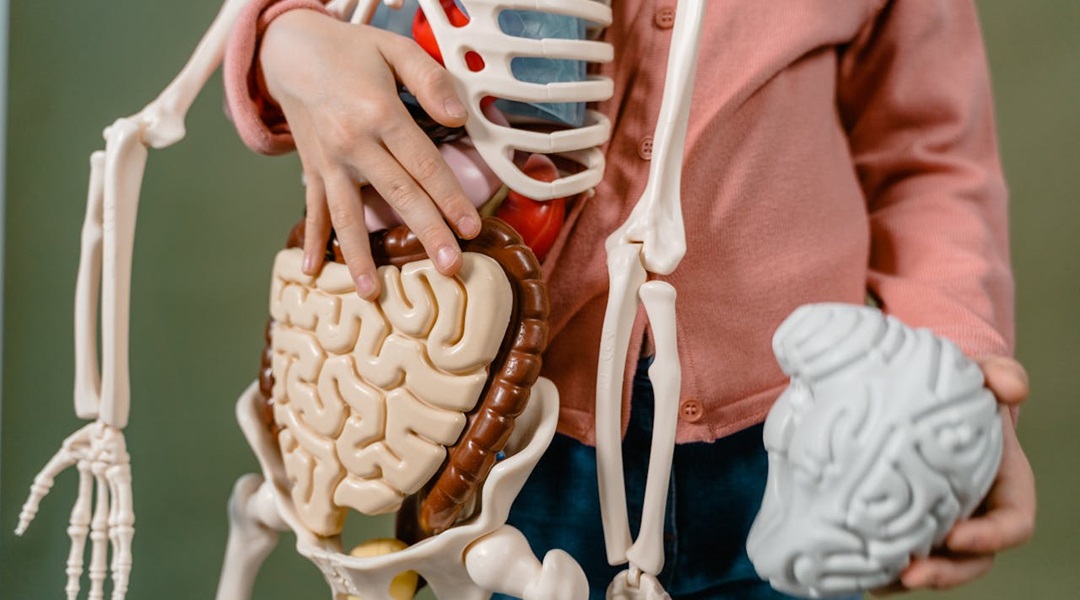
Bone loss in obesity traced to gut microbiota
Obesity changes gut microbiota, causing immune cells to age prematurely and secrete a protein which weakens bones
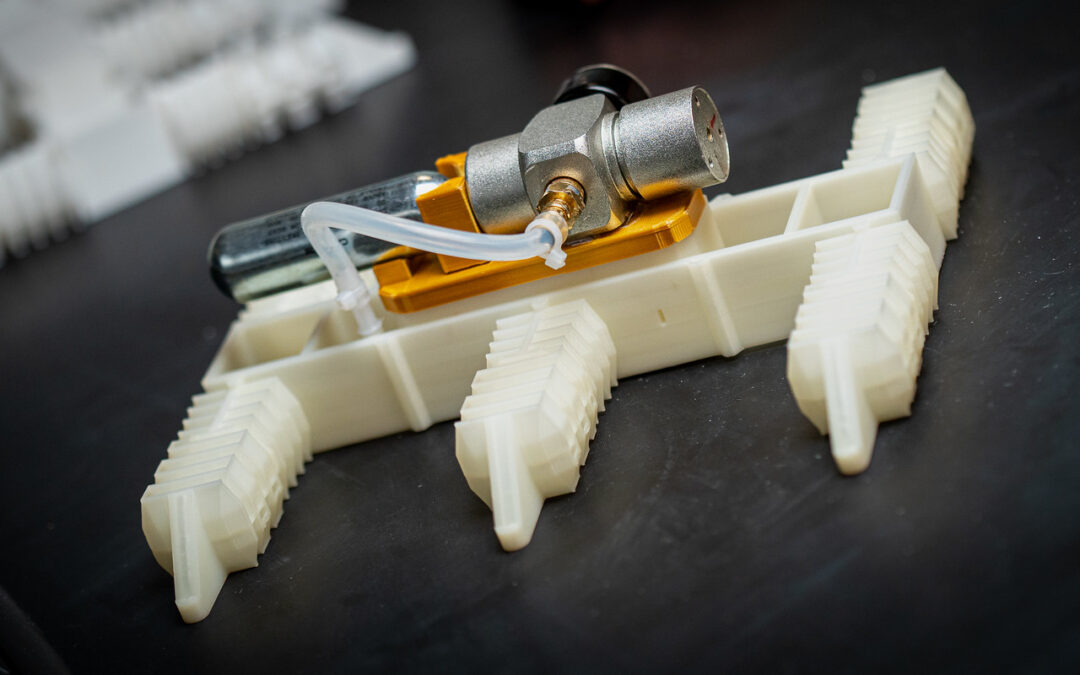
Walking on Air: Pneumatic System Enables Autonomous Motion in Soft Robots
Robot fabrication in a single step with a desktop 3D printer and pressurised gas.
ASN Newsletter
Sign up for our newsletter and receive the latest science news directly to your inbox.
Turning Periods into Power: Menstrual Blood a Valuable Resource for Medical Diagnostics
Wearable sensors help women analyse menstrual blood for affordable, non-invasive health monitoring.

Fermilab Confirms Muon g-2 Measurements
Fermilab releases its final results, testing the Standard Model of particle physics.
Methods Perspectives: Magnetic Force Microscope Calibration Explored by Héctor Corte-León
Héctor Corte-León explores the advantages and disadvantages of the different techniques used to calibrate a magnetic force microscope.

Immune resilience gene signature could hold the key to healthy aging
High levels of a certain biomarker gives people a survival advantage, study finds.
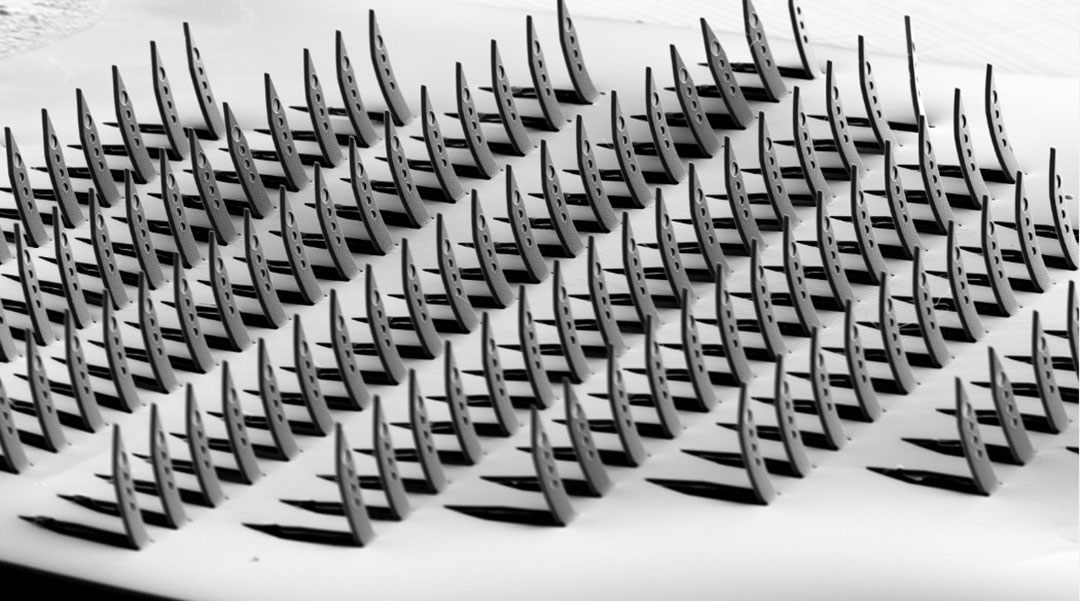

Kirigami-inspired neural probes are a cut above
The flexible and foldable 3D probes were surprisingly durable when inserted into brain tissue to map the deep functioning of neurons.

Machine learning identifies anti-aging neuroprotective treatments
The effects of aging on the human brain could be slowed down with the help of artificial intelligence.

Self-Healing Hydrogels Could Help Injured Ligaments Regenerate
Cell-laden hydrogels could promote tissue regeneration while avoiding immune rejection.
Edible electronics realize safe, complex monitoring devices
Edible electronics from non-toxic materials enable complex ingestible devices for healthcare and food monitoring.

Metabolic–Epigenetic Link Between Sleep Deprivation and Immune Dysregulation
Sleep deprivation alters immune cell metabolism, causing changes to epigenetics through lactylation, triggering immune dysregulation.
Machine learning identifies anti-aging neuroprotective treatments
The effects of aging on the human brain could be slowed down with the help of artificial intelligence.
Self-Healing Hydrogels Could Help Injured Ligaments Regenerate
Cell-laden hydrogels could promote tissue regeneration while avoiding immune rejection.
Edible electronics realize safe, complex monitoring devices
Edible electronics from non-toxic materials enable complex ingestible devices for healthcare and food monitoring.
Metabolic–Epigenetic Link Between Sleep Deprivation and Immune Dysregulation
Sleep deprivation alters immune cell metabolism, causing changes to epigenetics through lactylation, triggering immune dysregulation.

New theory suggests gravity is not a fundamental force
A new theory proposes gravity isn’t a fundamental force but emerges from quantum electromagnetic interactions, potentially reshaping our view of spacetime itself.

Organic materials bring probabilistic computing closer to reality
Scientists created flexible probabilistic bits from custom polymers, offering a new, energy-efficient path for AI and machine learning using classical physics.

Self-interacting inflaton particles may reshape our picture of the early universe
Subtle inflaton interactions may reshape our understanding of cosmic inflation, altering predictions about dark matter, black holes, and gravitational waves.
Ultra-dense electron beams set the stage for breakthroughs in physics and technology
SLAC scientists created ultra-dense electron beams with five times the peak current, using infrared lasers to unlock new frontiers in physics and materials research.
New theory suggests gravity is not a fundamental force
A new theory proposes gravity isn’t a fundamental force but emerges from quantum electromagnetic interactions, potentially reshaping our view of spacetime itself.
Organic materials bring probabilistic computing closer to reality
Scientists created flexible probabilistic bits from custom polymers, offering a new, energy-efficient path for AI and machine learning using classical physics.
Self-interacting inflaton particles may reshape our picture of the early universe
Subtle inflaton interactions may reshape our understanding of cosmic inflation, altering predictions about dark matter, black holes, and gravitational waves.
Ultra-dense electron beams set the stage for breakthroughs in physics and technology
SLAC scientists created ultra-dense electron beams with five times the peak current, using infrared lasers to unlock new frontiers in physics and materials research.
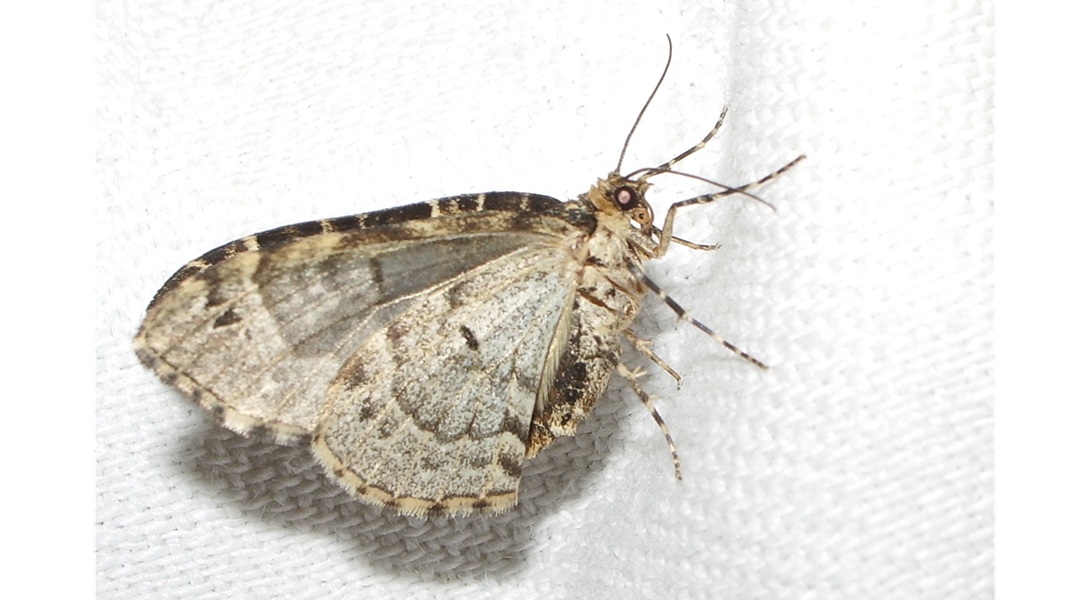

Moth eyes inspire flexible X-ray shields and sensors
Drawing from nature, scientists are creating next-generation X-ray protective clothing and equipment.
New Doppler cloak hides moving objects by making them appear static
Doppler cloak confuses radars by altering the phase of incoming radar waves in real time.

Turning Food into Lasers: A New Era in Information Encoding and Sensing
Fabrication of microlasers using all edible components.

Turning Food into Lasers: A New Era in Information Encoding and Sensing
Fabrication of microlasers using all edible components.
Moth eyes inspire flexible X-ray shields and sensors
Drawing from nature, scientists are creating next-generation X-ray protective clothing and equipment.
New Doppler cloak hides moving objects by making them appear static
Doppler cloak confuses radars by altering the phase of incoming radar waves in real time.
Turning Food into Lasers: A New Era in Information Encoding and Sensing
Fabrication of microlasers using all edible components.
Turning Food into Lasers: A New Era in Information Encoding and Sensing
Fabrication of microlasers using all edible components.

Soy protein fuels the future of eco-friendly solid-state batteries
The world’s most grown legume could be used to make the batteries of the future.

Water-powered gadgets may be on the horizon thanks to new evaporation-based energy device
Scientists created an “evapolectrics” generator that draws power directly from water evaporation, offering a sustainable, battery-free energy source from humidity.

Climate pledges could shrink global cropland
The tradeoff raises concerns about food security, particularly for the Global South.

Sustainable building material extracted from seawater
A sand-like material can be extracted from seawater by adding carbon dioxide, potentially making the building industry more sustainable.
Soy protein fuels the future of eco-friendly solid-state batteries
The world’s most grown legume could be used to make the batteries of the future.
Water-powered gadgets may be on the horizon thanks to new evaporation-based energy device
Scientists created an “evapolectrics” generator that draws power directly from water evaporation, offering a sustainable, battery-free energy source from humidity.
Climate pledges could shrink global cropland
The tradeoff raises concerns about food security, particularly for the Global South.
Sustainable building material extracted from seawater
A sand-like material can be extracted from seawater by adding carbon dioxide, potentially making the building industry more sustainable.

Riccardo Bassoli: How quantum computing will redefine wireless communication
Future 6G wireless networks will rely on quantum computers, but developing the technology and making it sustainable is complex.

Rose Marks, a botanist studying resurrection plants
Rose Marks uses her climbing skills in remote regions of South Africa to study how water-deprived plants might help develop drought-tolerant crops.

Shira Joudan, tackling PFAS and environmental contaminants with chemistry
Chemist Shira Joudan discusses environmental contaminants, setting up at a new university, and building a supportive community.
How a gut-on-a-chip is getting to the bottom of our gut’s microbiome
This artificial gut will allow scientists to gain deeper insights into the biome that exists there and how dysregulation can lead to disease.

Riccardo Bassoli: How quantum computing will redefine wireless communication
Future 6G wireless networks will rely on quantum computers, but developing the technology and making it sustainable is complex.

Rose Marks, a botanist studying resurrection plants
Rose Marks uses her climbing skills in remote regions of South Africa to study how water-deprived plants might help develop drought-tolerant crops.

Shira Joudan, tackling PFAS and environmental contaminants with chemistry
Chemist Shira Joudan discusses environmental contaminants, setting up at a new university, and building a supportive community.

How a gut-on-a-chip is getting to the bottom of our gut’s microbiome
This artificial gut will allow scientists to gain deeper insights into the biome that exists there and how dysregulation can lead to disease.