An allergy to red meat known as alpha-gal syndrome is brought on by tick bites and is becoming a global issue.


An allergy to red meat known as alpha-gal syndrome is brought on by tick bites and is becoming a global issue.
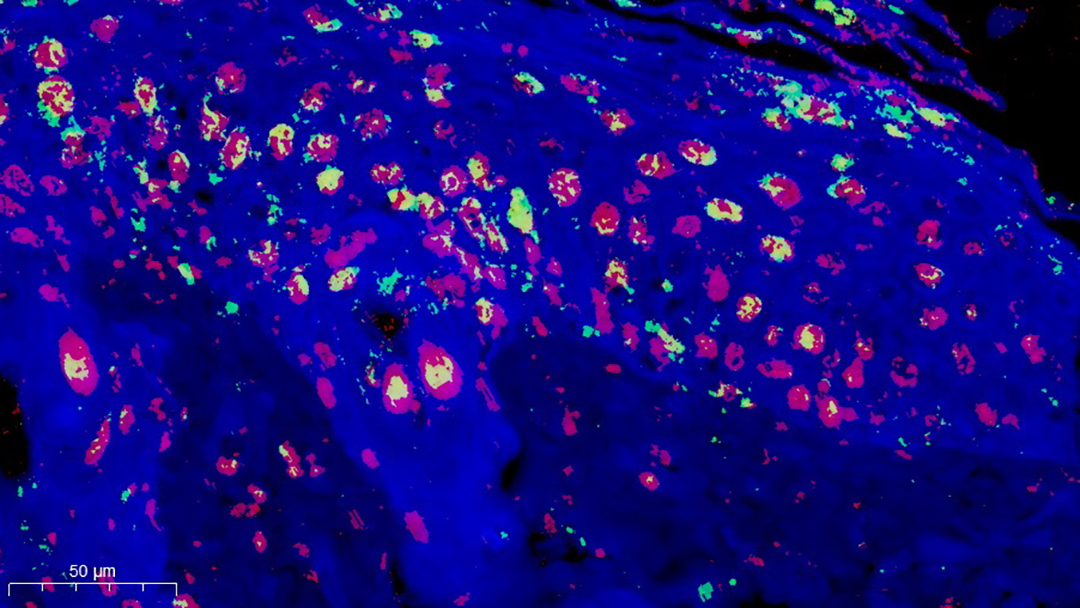
Zwitterionic hydrogels boost healing in diabetic wounds by balancing the immune response, reducing inflammation, and promoting tissue growth.

Future astronauts may be protected from galactic cosmic rays thanks to a novel organ-on-chip system containing interconnected human tissue.

Switching to less processed does not guarantee a healthy diet; the types of foods may be more important than their level of processing.
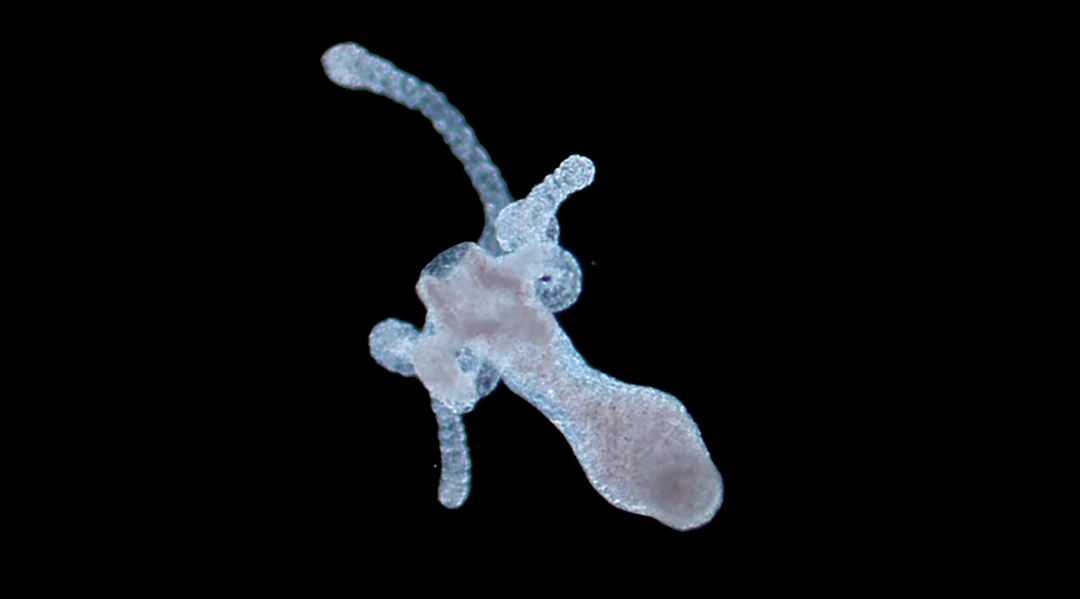
Gold nanoparticles and near-infrared light speed up regeneration and reproduction in hydras, providing insights for regenerative medicine.
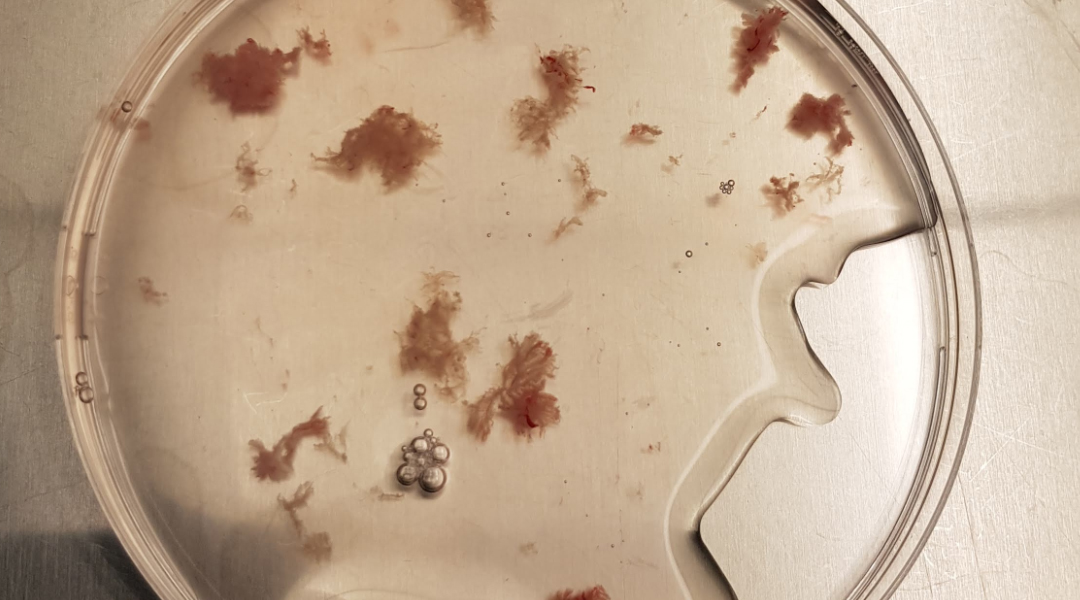

Nanoparticles disrupted the placenta’s secretion of biomolecules essential for blood vessel growth, hormone production, and immune function.
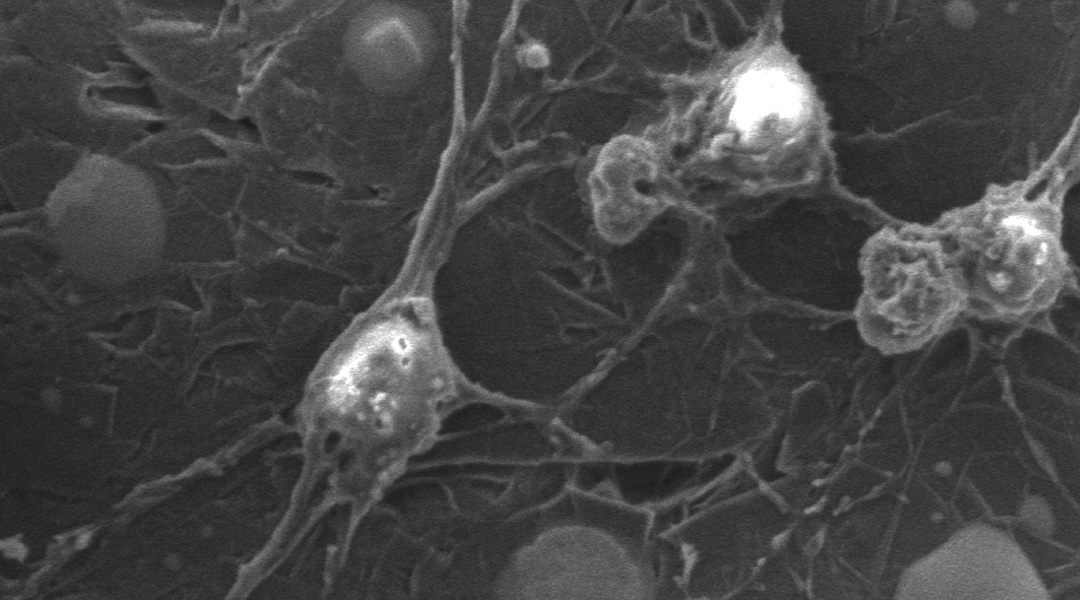
A patch delivers electrical pulses to help support stem cell growth, helping mice recover mobility in their hind legs in preliminary studies.
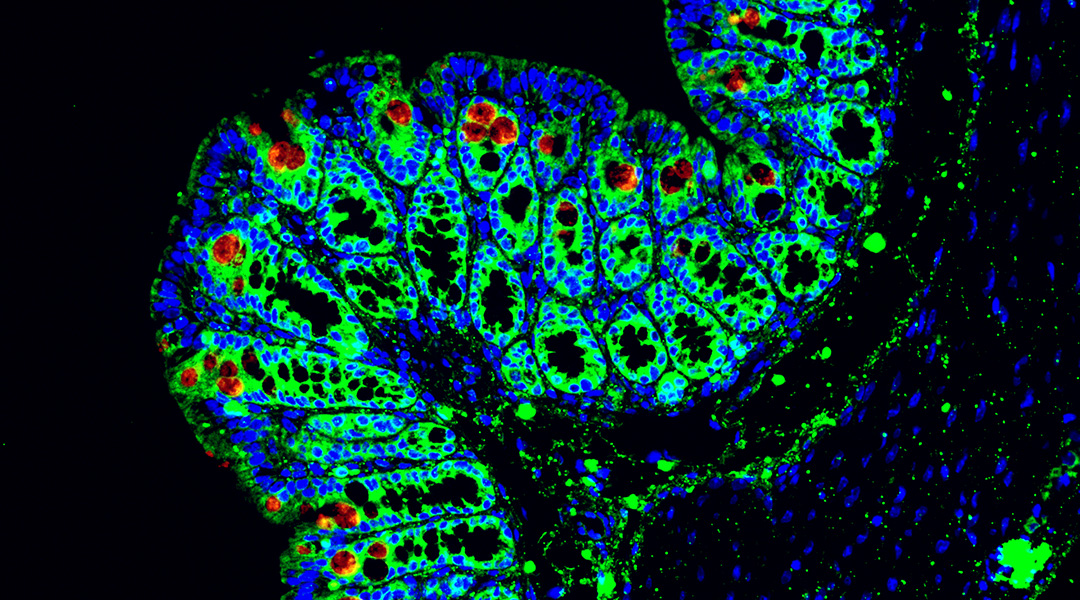
Scientists discover interactions between gut bacteria and immune cells that cause inflammatory bowel disease in glycogen storage disease.
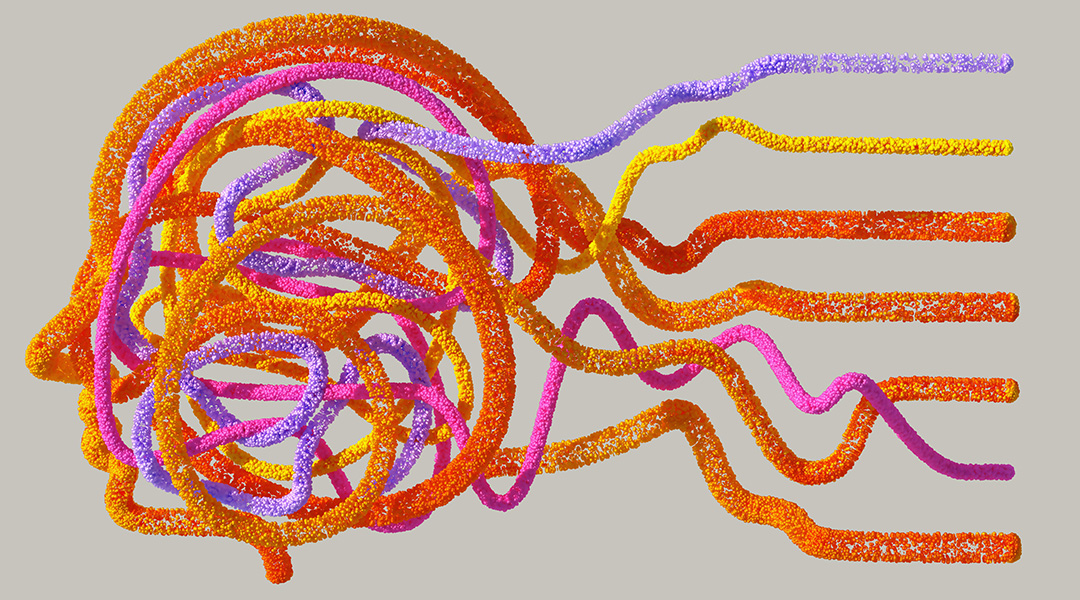
Preventing sudden and unexpected death hinges on accurately predicting the onset of epileptic seizures, even those with the rarest occurrences.
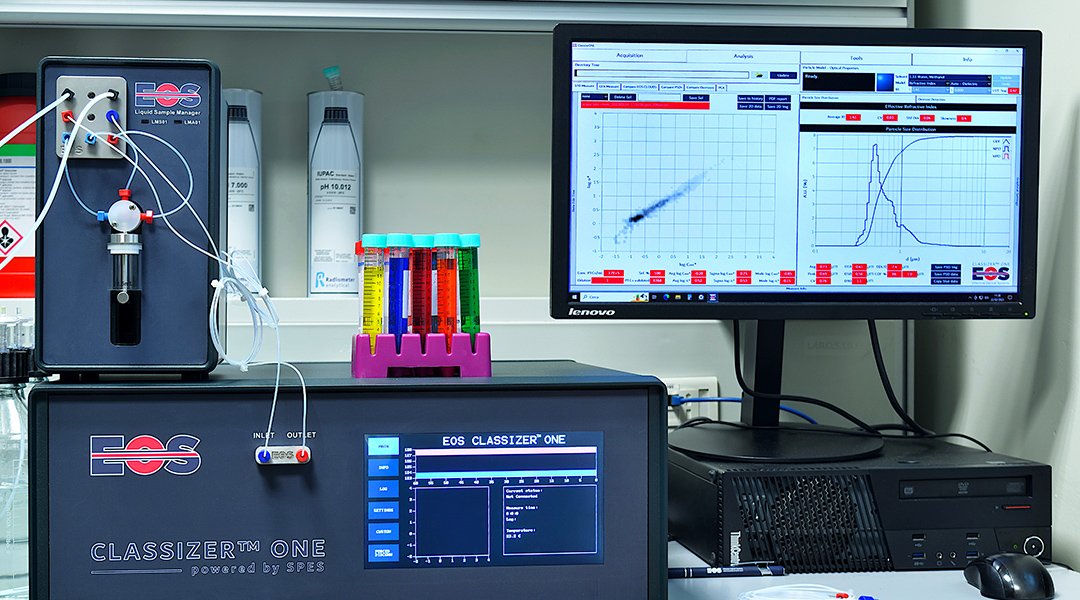

Applying an advanced light-scattering technique, scientists could quantify the microplastics released when plastic containers were heated.