Scientists convert harmful microplastics into valuable graphene using plasma, offering a promising solution for this type of pollution.
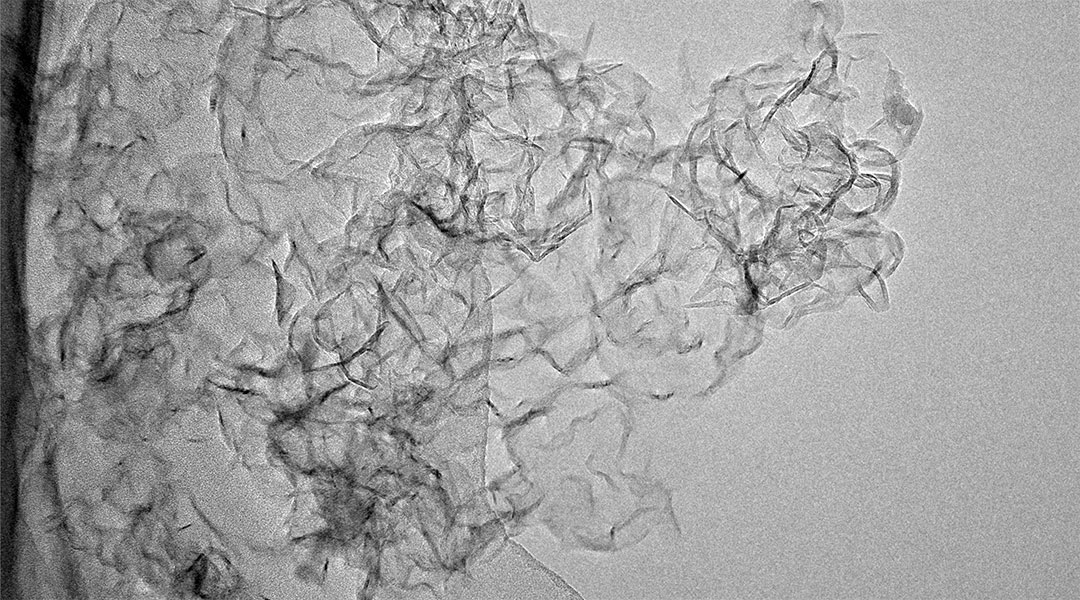


Scientists convert harmful microplastics into valuable graphene using plasma, offering a promising solution for this type of pollution.
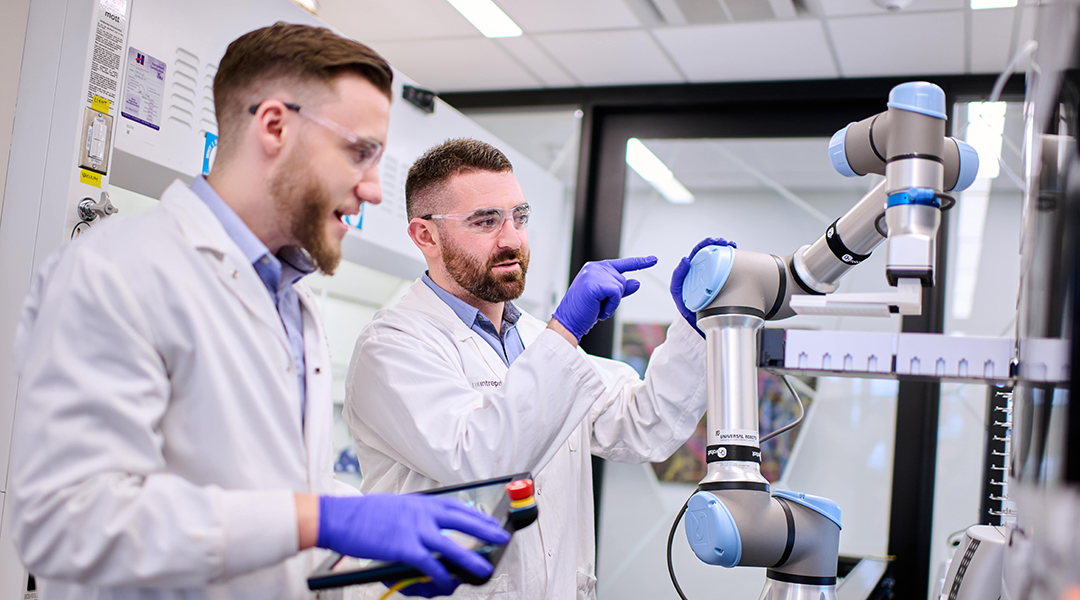

Scientists are speeding up drug formulation to breath new life into old medications and reduce risk of clinical trial failure.
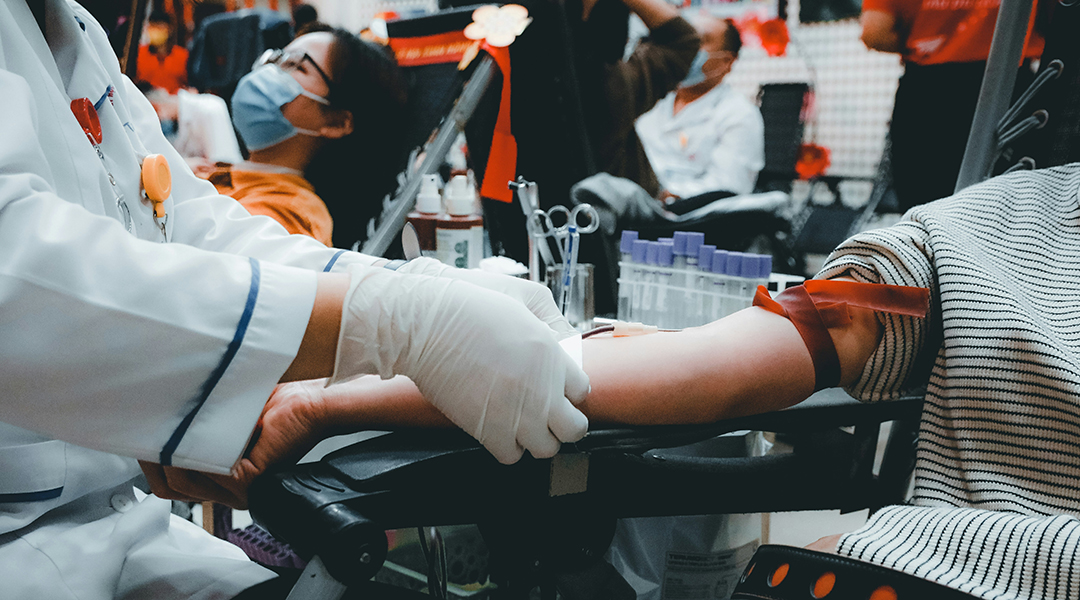
Taking inspiration from plankton, researchers create engineered blood cells that are an important step toward a universal blood supply.
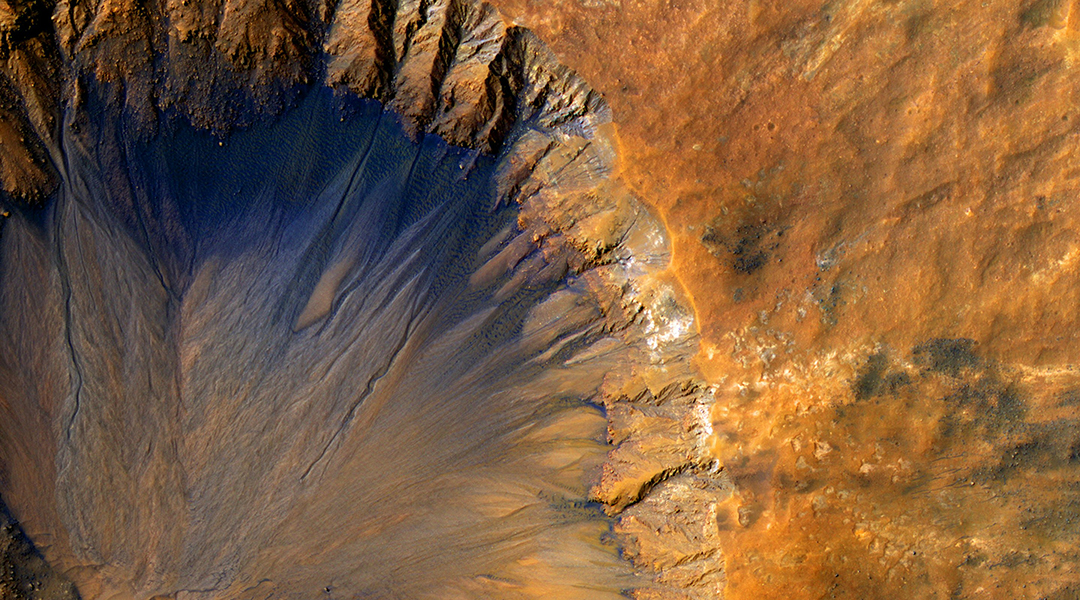

Engineering mineral rich dust and releasing it as an aerosol could warm the planet and kickstart the thickening of the atmosphere.
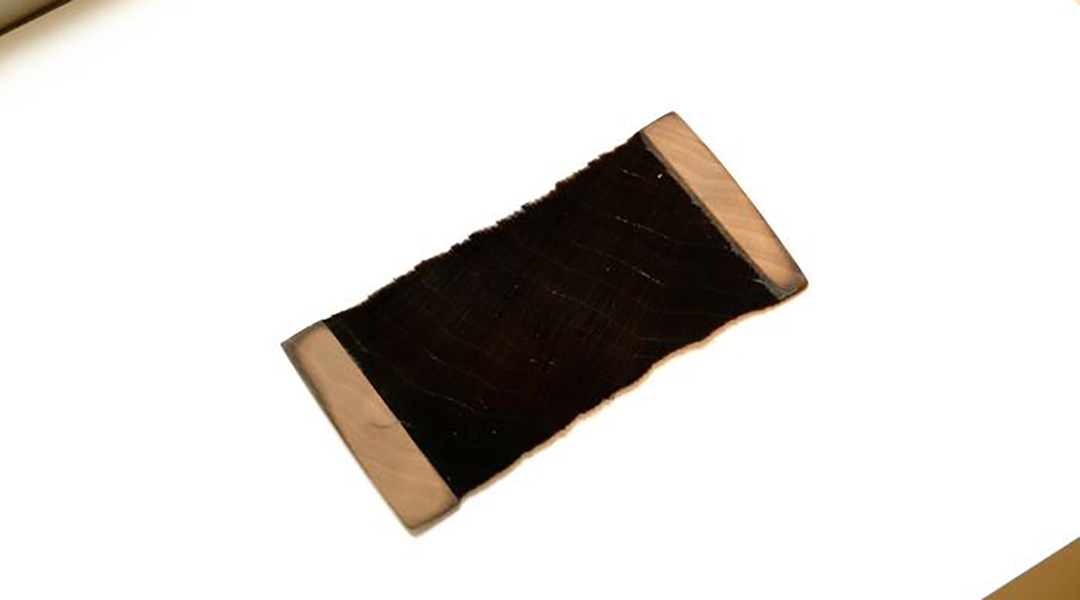

This material absorbs more than 99% of the light that strikes it, making it useful in applications ranging from solar energy to astronomy.
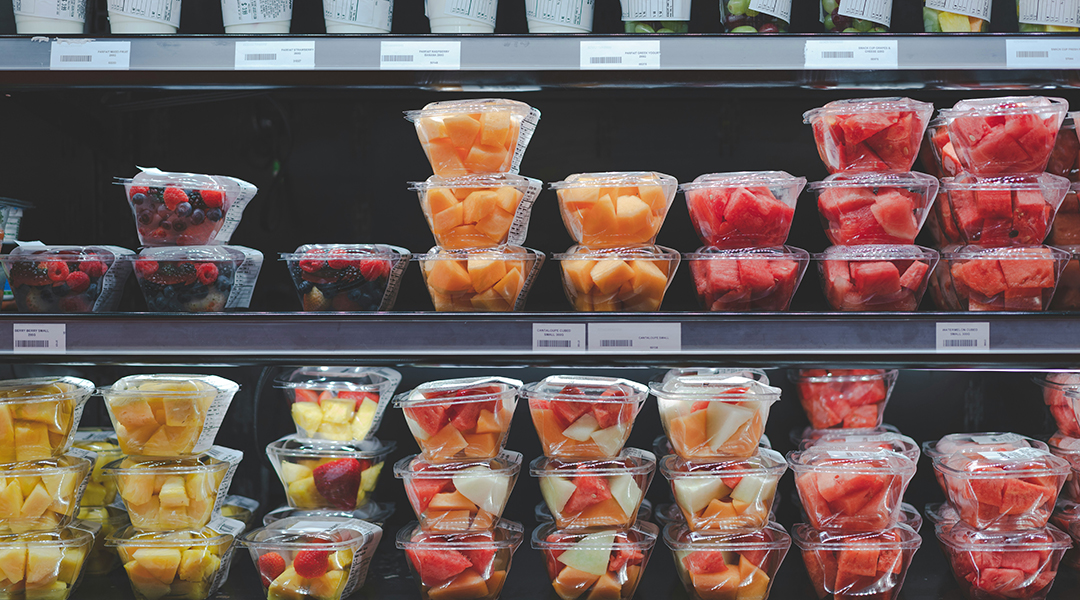

Switching to less processed does not guarantee a healthy diet; the types of foods may be more important than their level of processing.
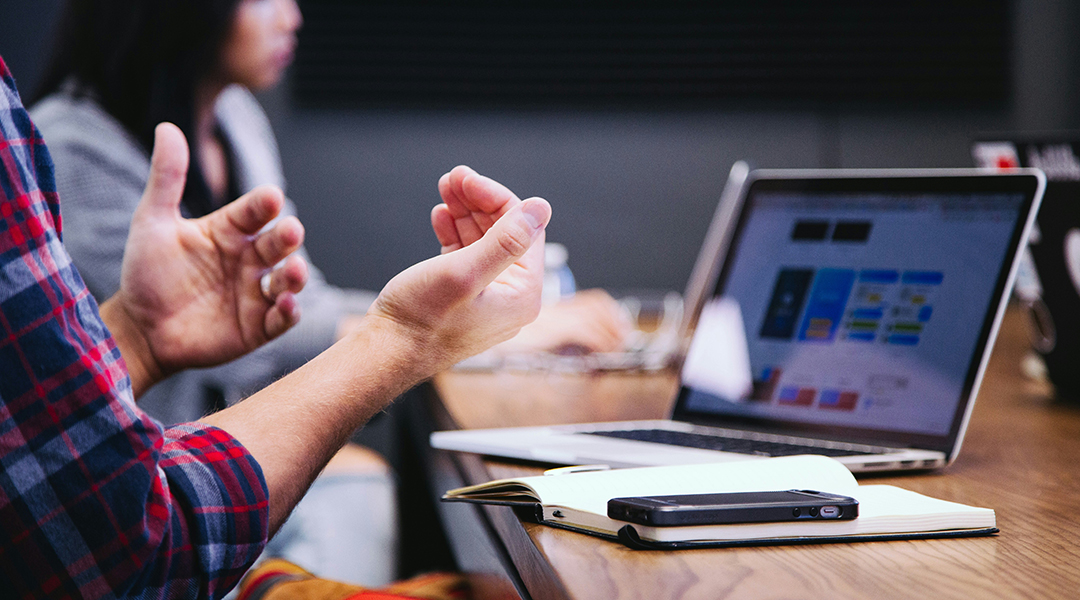

Participants with lie-detecting AI were more likely to trust it, more readily agreeing when it falsely labeled something a lie.

Fitted with nanoscale grippers, these microrobots offer new opportunities for imaging and manipulating single cells.
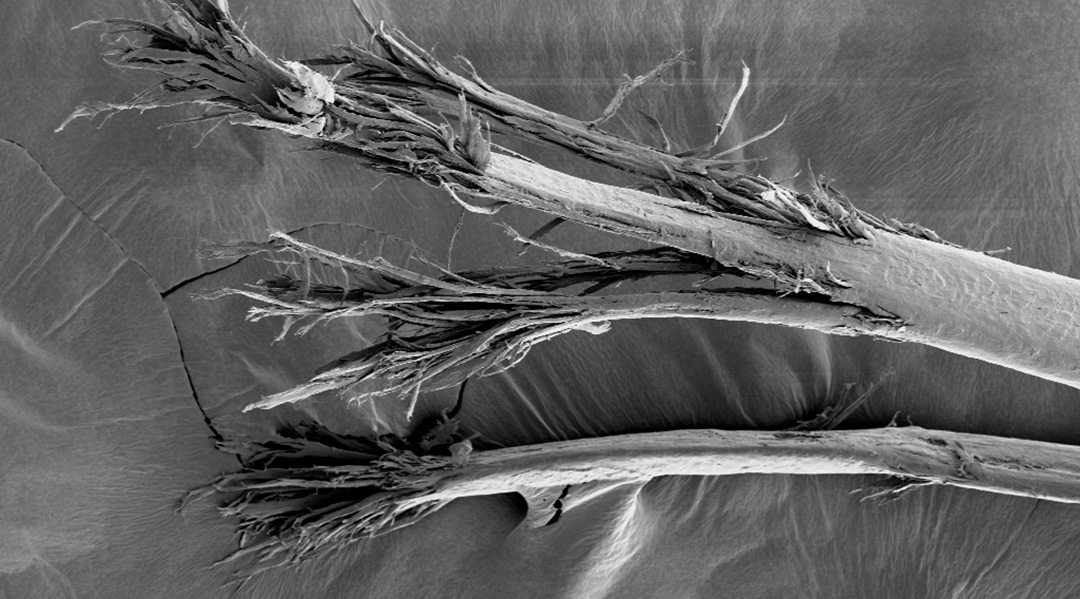
Materials scientists are applying biomechanics to understand how split ends contribute to our bad hair days—and what can be done to fix them.

Scientists are approaching disease and diagnosis in a new way, leverage big data to provide better options for both clinicians and patients.