Tackling heat transfer, diamond layers help build 3D circuits with lower power consumption, faster signaling, and increased performance.

Tackling heat transfer, diamond layers help build 3D circuits with lower power consumption, faster signaling, and increased performance.
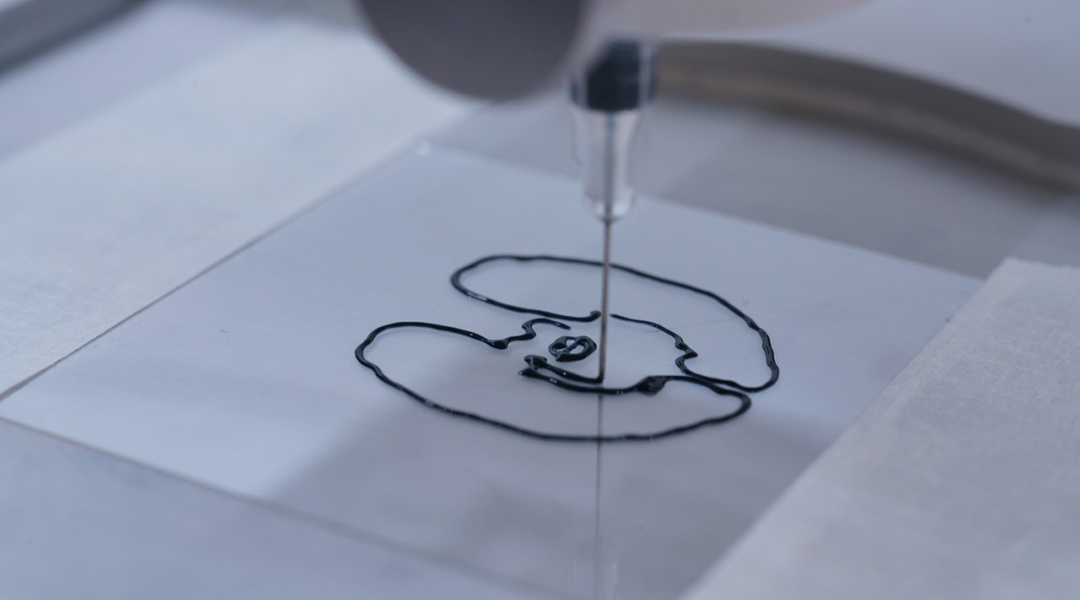

Researchers demonstrate the controlled growth of artificial synapses, paving the way for computers that can grow, evolve, and adapt like the human brain.
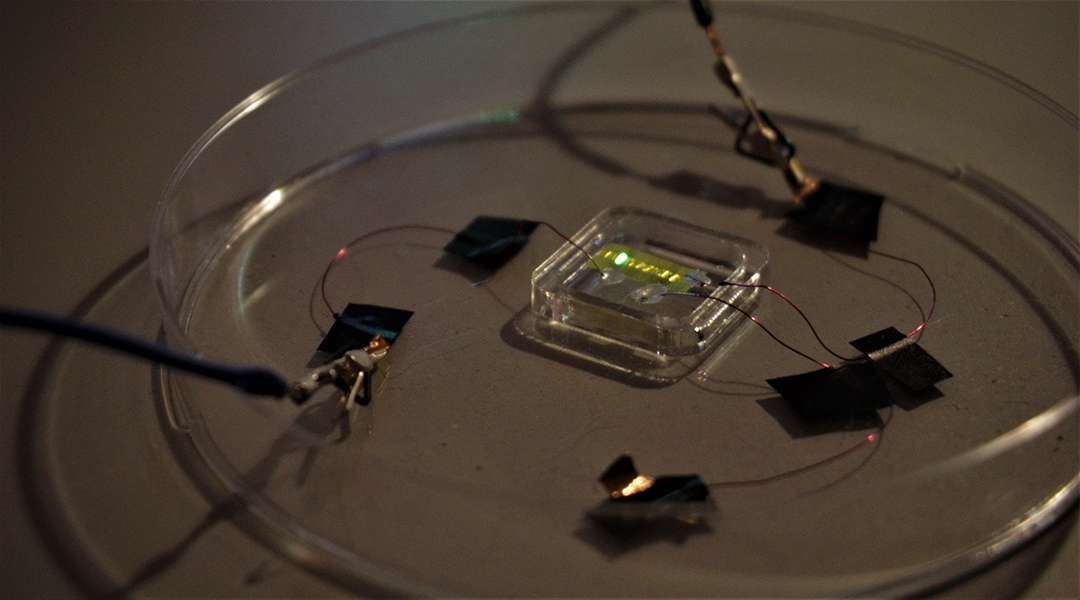
A new fabrication method allows researchers to create ultra-thin OLED materials that can be applied to the skin using temporary tattoo paper.
The importance of understanding the experimental process is ubiquitous in research. And while we have a huge range of techniques at our disposal, we should be aware of and properly consider their limitations, so that we may present reliable methods and conclusions to...
For decades the density of integrated circuits has grown exponentially, according to the empirical Moore´s law published in 1965. In this period, the storage density has increased by a factor of about 100 million. Yet, this rapid development is approaching fundamental...
A recent Progress Report on the recommended methods of studying resistive switching devices is reviewed.

A peek into the Advanced journal archives reveals some of the interesting and creative work published over the years that is still being cited today.
Jeong et al. argue that a change in paradigm away from the CPU+Memory computing approach and towards a materials approach which mimics biological neurons as synapses is needed.
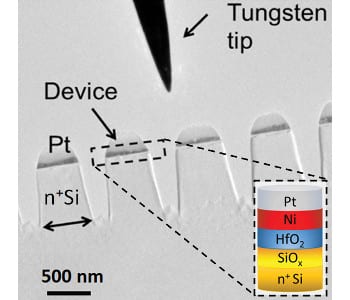
A potentially major breakthrough has been made in the study of ReRAM memory devices.

Professor Sirringhaus, from the University of Cambridge, is one of the outstanding researchers in the field of organic electronics.