An interface that models inflammation and infection will allow researchers to investigate biomolecular dynamics changes in local microenvironments.
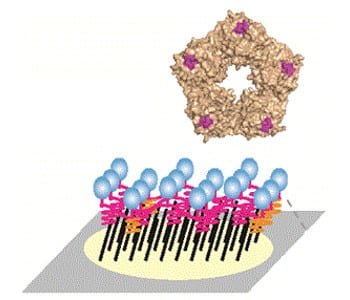

An interface that models inflammation and infection will allow researchers to investigate biomolecular dynamics changes in local microenvironments.
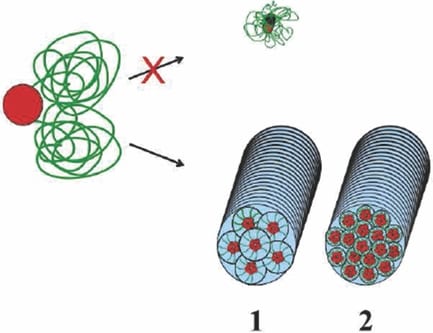
Researchers have reported an attempt to mimic nature’s concepts in forming synthetic hydrogel fibers via a bottom-up self-assembly process.
A research team has improved the DNA/RNA transfection ability of carbon nanotubes by optimizing the plasma processes used in their functionalization.

Rate of improvement of quantum dot devices is one of the most rapid seen for a solar technology.
Here are the currently most read articles in Macromolecular Rapid Communications.

We’ll be attending the EMRS Spring Conference in Lille next week, and we’re going to keep you updated on all the latest.

The Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems ISE in Freiburg, Germany has developed a new solar cell structure for crystalline silicon.

Silica-coated gold nanorods with absorption at precisely 780 nm cause action potentials in nerve cells when exposed to laser light.
Researchers create an artificial chemical sensor based on one of the human body’s most important receptors.
RRAMs, magnetic microwires, and spin Hall effects – these and more in our March’s physics highlights.