ETH researchers have developed plasmonic particles that are relatively easy to produce and have a wide range of applications, including cancer treatment.


ETH researchers have developed plasmonic particles that are relatively easy to produce and have a wide range of applications, including cancer treatment.

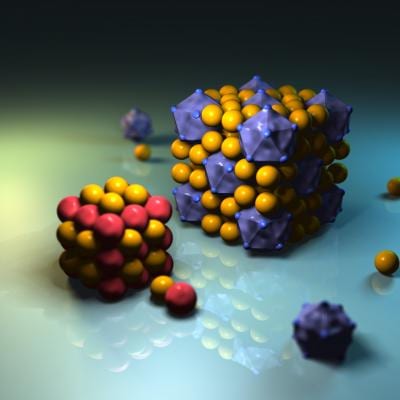
New core/shell structure nanoparticles have been reported by a team led by Peking University researchers.
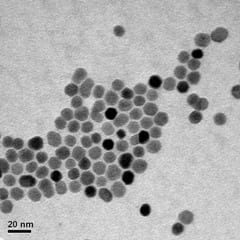
Physicists from the University of York have carried out new research into how the heating effect of an experimental cancer treatment works.
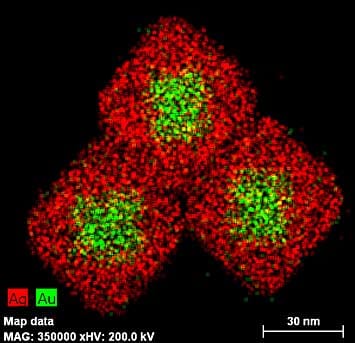
A team of scientists has developed a new, simpler way to discern molecular handedness, known as chirality, using gold-and-silver cubic nanoparticles.
Scientists from Aalto University, Finland, have succeeded in organising virus particles, protein cages and nanoparticles into crystalline materials.

A group from FZ Juelich have investigated methods for controlling magnetic particle clouds on microwire crossbar chips.
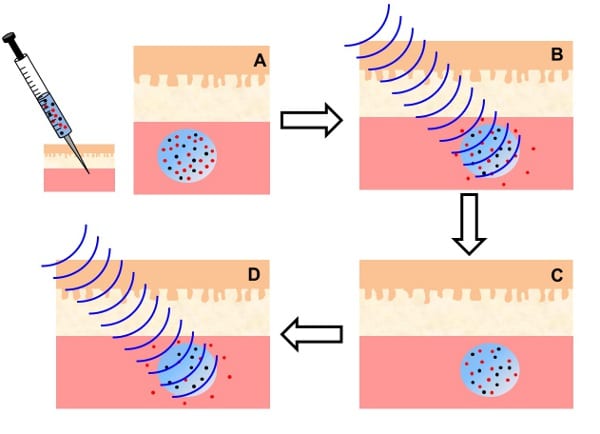
Iron oxide nanoparticles can be used to provide a local source of heating in a thermoresponsive sol–gel copolymer solution.
Chinese researchers have used lasers to made tiny springs and turbines out of a polymerized ferrofluid, which could be used in micro- or nanomachines.
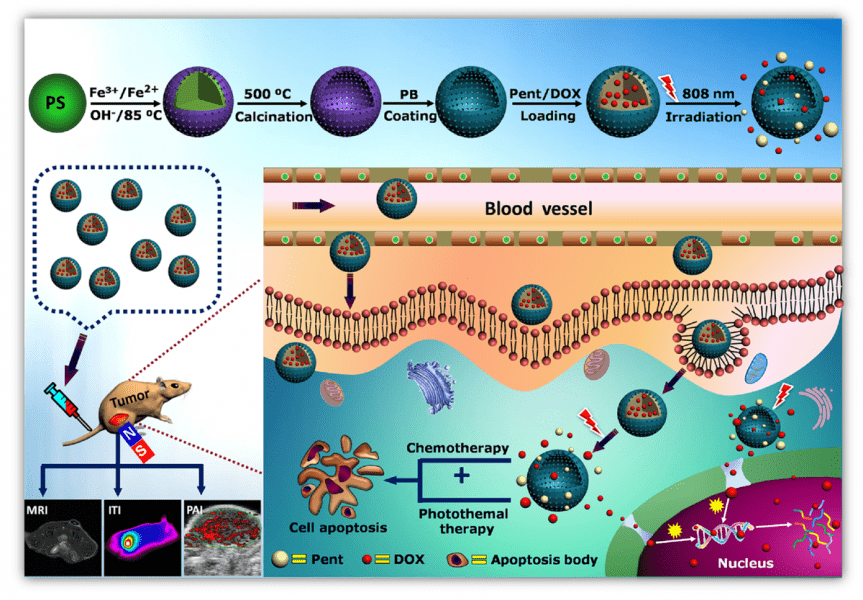
Controlled delivery of anti-tumor drug with a new design incorporating a phase-change material in magnetic nanoparticles allowing chemo-photothermal combined tumor therapy with multimodal tumor imaging.
Gossuin, Sandre, et al. describe the design of magnetic nanoparticles with optimised relaxivity for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).