Technology is based on metal di-chalogenides, which are emerging as potential candidates to replace current CMOS materials.
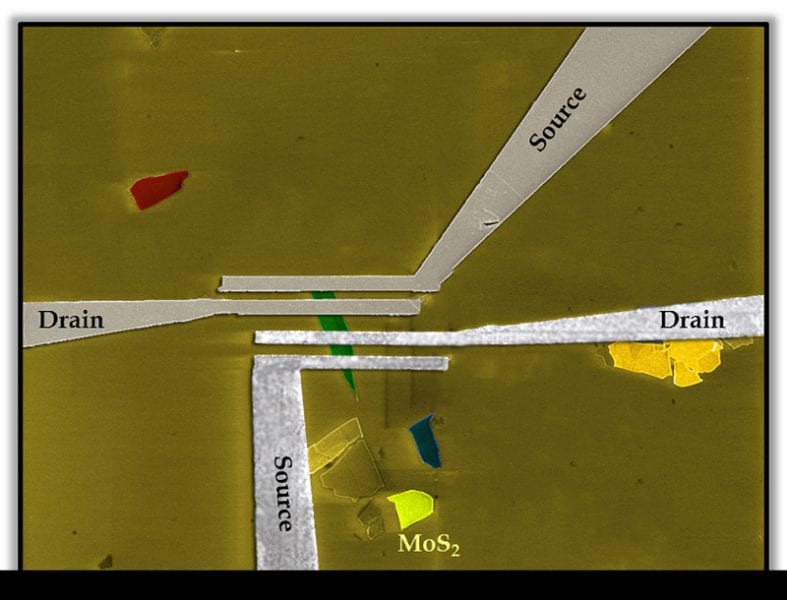

Technology is based on metal di-chalogenides, which are emerging as potential candidates to replace current CMOS materials.
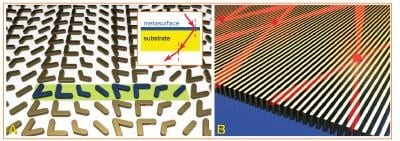
New optical technologies using “metasurfaces” capable of the ultra-efficient control of light are nearing commercialization.

Recent research offers a new spin on using nanoscale semiconductor structures to build faster computers and electronics.
Purdue and Harvard researchers create stackable indium-gallium-arsenide transistors.
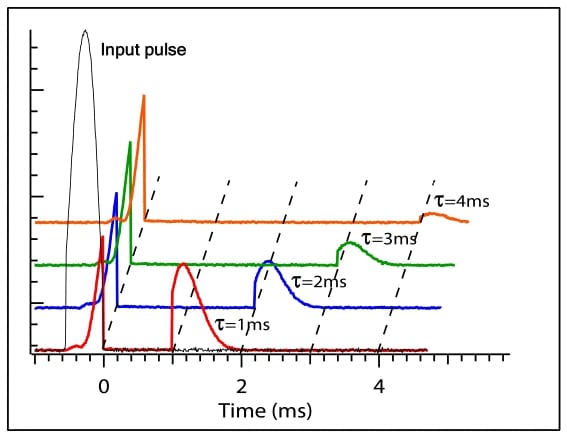
One of the exciting potential applications of electromagnetically induced transparency and slow and stored light is for practical realization of quantum memory, and, ultimately, quantum computing. Recent advances using ensembles of warm atoms in vapor cells have been made.
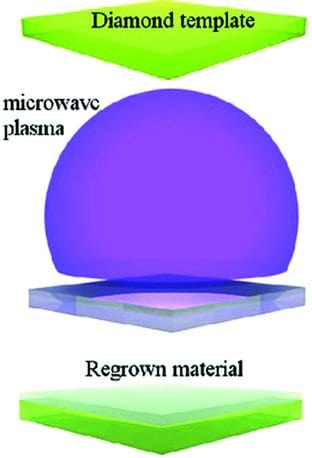
By using microwave CVD, high quality, single crystal diamond membranes have been epitaxially grown. The resulting material exhibits bright luminescence and good electron spin coherences times, suitable for application in quantum computing.
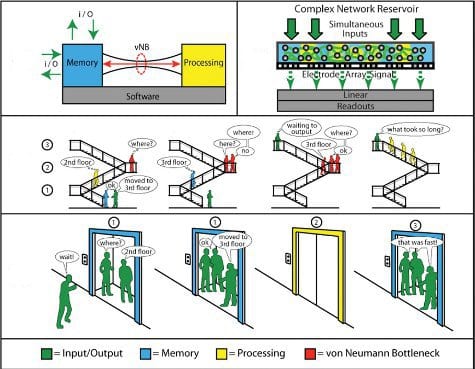
A computing network that exhibits emergent behavior similar to that in biological brains is hypothesized by Adam Z. Stieg of the California NanoSystems Institute
Low-loss router based on an interferometer preserves polarization while directing single photons and entangled pairs.
A new study targets feature selection, a key step in machine learning where the algorithm determines which parts of the input data are most relevant to making accurate predictions.

Rectangular fiber optic cables could increase data transfer rates, benefiting telecommunications and quantum computing advancements.