From materials to processing, the Journal of Applied Polymer Science showcases select research from the Asia-Pacific region.


From materials to processing, the Journal of Applied Polymer Science showcases select research from the Asia-Pacific region.

René Janssen, Paul Blom, Jan Hummelen and collaborators top the inaugural Advanced Energy Materials Top 40.
The most downloaded papers from the physica status solidi family in June.
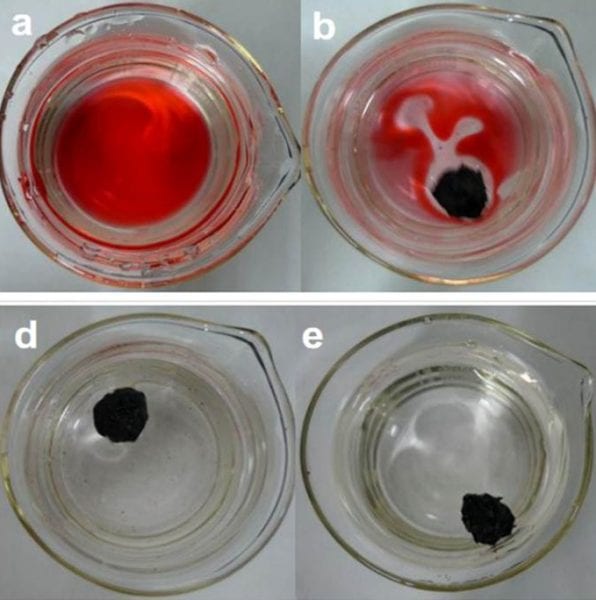
Rodney Ruoff and co-workers demonstrate the potential of graphene sponges as recyclable absorbents for cleaning up oil spills.

The University of Kiel’s aerographite maintains its grip at the top of the Advanced Materials Top 40 this week.
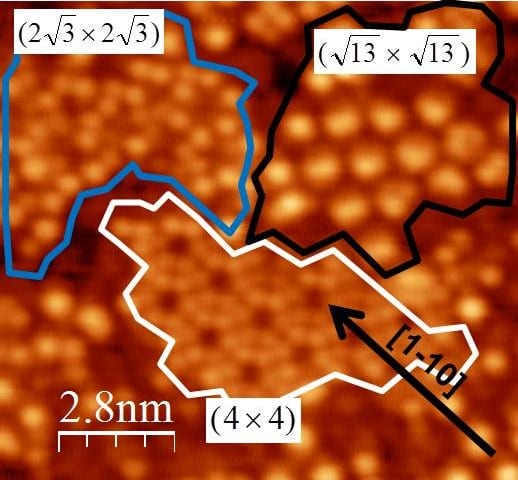
The next generation of computing could be performed with silicene, an atomically thin form of silicon which could revolutionize electronics.
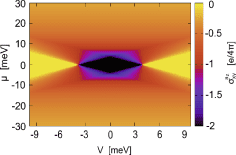
Spin Hall effects, scintillators, and nanotubes – these and more in July’s physics highlights.
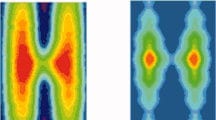
New work looks at recent progress in STM and DFT studies on the electronic structure of reduced rutile titanium dioxide.

Work on the synthesis of Aerographite, a new type of ultra-lightweight material, moves up five places to number 1 in this week’s Advanced Materials top 40.
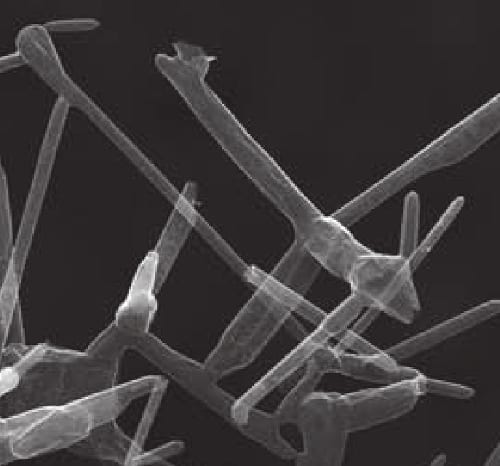
A German materials science lab have reported the fabrication of a new material that breaks the record for lightest solid.