A recent review by Donati, Sander and Link tries to answer this question.
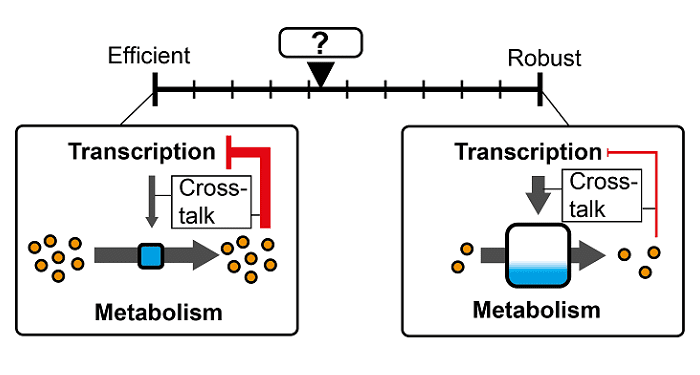

A recent review by Donati, Sander and Link tries to answer this question.

Nominate a colleague for the Biopolymers Murray Goodman Memorial Prize, awarded for accomplishments in biochemistry, biophysical chemistry, biophysics and/or chemical biology.
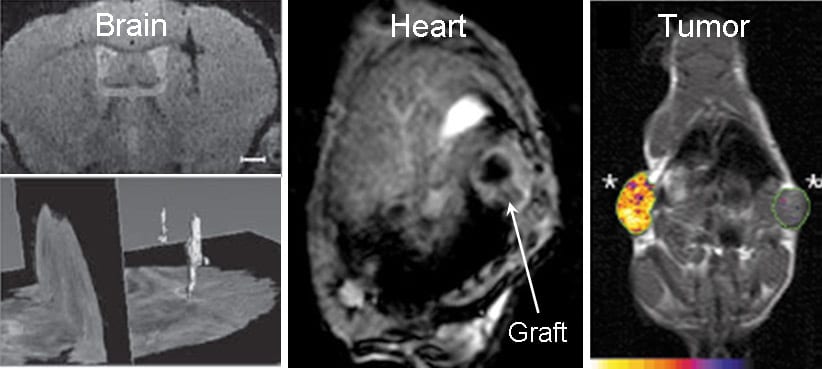
Visualization of cells contributing to disease or cell therapy is critical for the success of regenerative medicine. Genetically encoded iron-associated proteins detectable with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can be utilized for cell tracking in the brain, heart, and cancer.
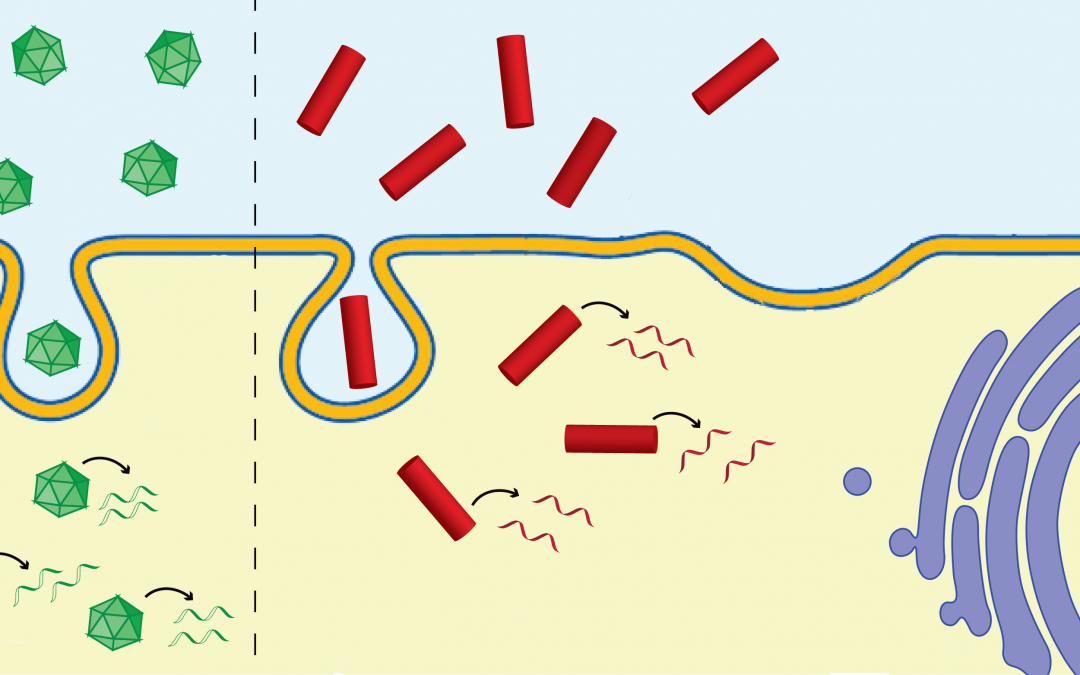
Different shaped plant viruses and bacteriophages can be used to deliver nucleic acids into the cell for disease treatment
A recent review discusses the intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms underlying intestinal cell plasticity.
Review by Kubyshkin and Budisa in Biotechnology Journal explores the why and the how.
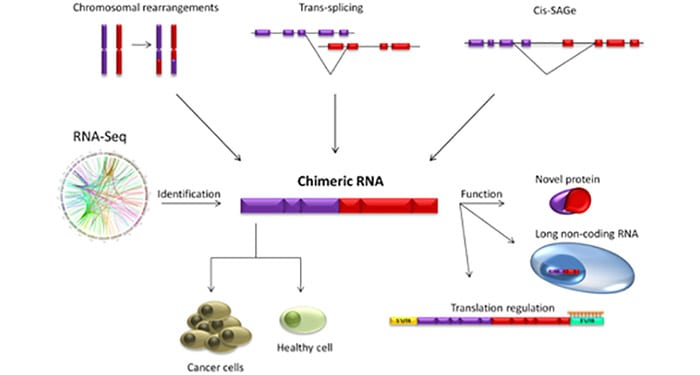
Chimeric RNAs can be generated by not only chromosomal rearrangements at the DNA level, but also intergenic splicing at the RNA level. Chimeric RNAs are demonstrated to be not the elusive features of cancer cells, but also present in normal physiology and with diverse functions.
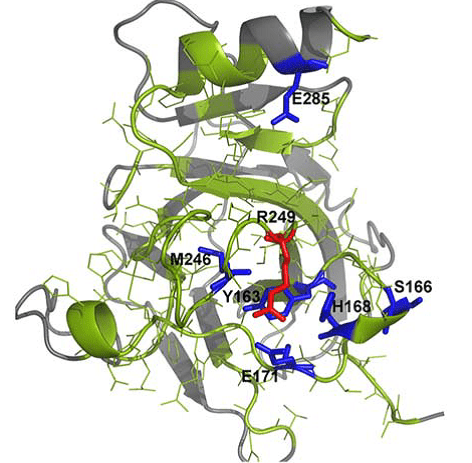
The electrostatic potential of proteins determines their ability to interact with specific biological targets. A recent article discusses the application of a novel tool (Mutantelec) in understanding mutations in the tumor suppressor protein p53 and its consequence.s
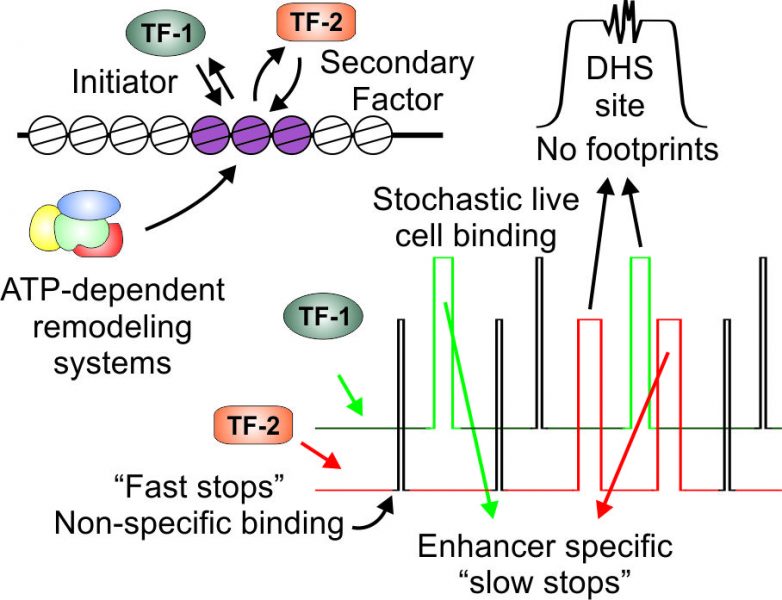
In live cells, many enhancer-binding transcription factors exchange rapidly with their binding sites and leave no footprints in chromatin. Available data suggests a highly dynamic mechanism for enhancer activation, involving numerous stochastic binding events at a target enhancer.
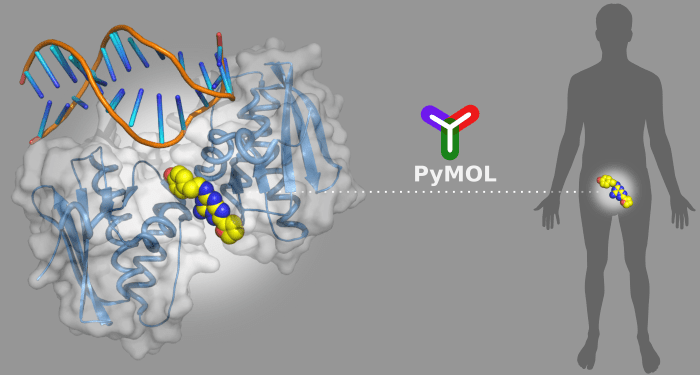
New apps and software may bring convenience to our daily lives, but their reach also extends to areas like drug discovery research.