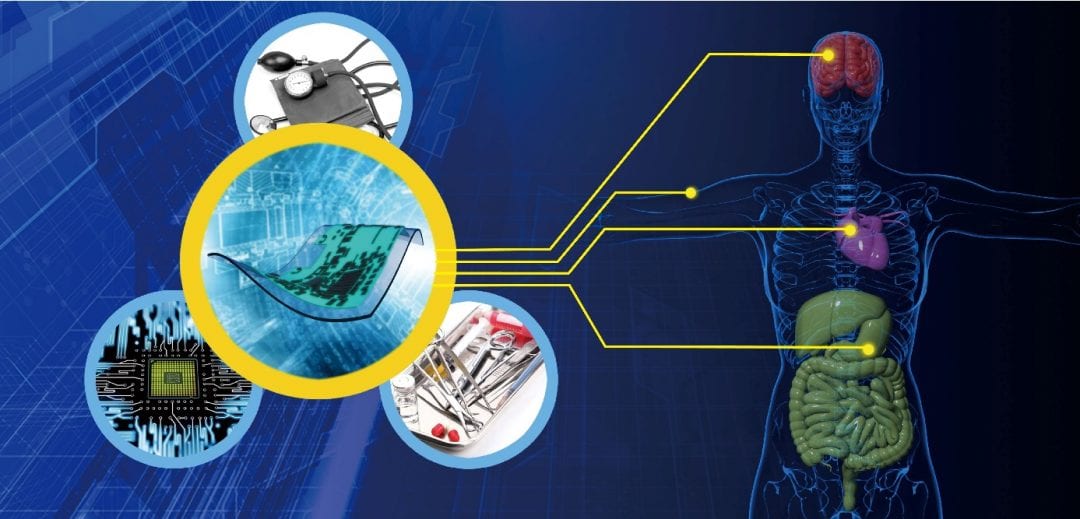
Healthcare has been a key challenge for our society. Due to limited resources of in situ clinical health care systems, medical devices or systems which enable patients to monitor and manage their own health conditions are highly desirable. The recently developed soft bioelectronic systems have provided tremendous opportunities in personalized and self-administered healthcare. Unlike conventional rigid electronics, soft bioelectronics enable conformal and compliant integration onto the soft, curvilinear and dynamic human skin, or internal organs, for not only personal health monitoring, but also self-controlled precision therapy, such as medical surgery and drug delivery.
There has been significant amount of work in the fabrication and characterization of soft and stretchable sensors for monitoring of physical conditions and vital signs of the human body over the past decade; the development of soft bioelectronics based medical treatment and intervention systems has just begun. In addition to health monitoring, active treatments are essential for disease control in the healthcare domain, and medical therapy and surgery realized by sophisticated soft bioelectronic systems demonstrate significant utility in healthcare. In their recent article published in Advanced Healthcare Materials, Prof. Hao Wu and Prof. Zhouping Yin from Huazhong Univeristy of Science and Technology and Dr. Wei Gao of University of California, Berkeley, summarize recent key research achievements in soft bioelectronics enabled precision therapy, with emphasis on drug delivery, therapeutic and surgical mechanisms and tools enabled by integrated systems.
The latest progress of advanced materials, fabrication procedures, structural design and integration schemes in soft bioelectronics for skin-mounted devices, implantable systems and surgical tools are analyzed, highlighting the exciting prospects of this new therapeutic modality, alongside conventional medicines and vaccines developed through chemistry and biology. Recent progress, opportunities and challenges in commercialization are also discussed.