A rare group of patients have been found to maintain a very low viral load and a functional immune system after stopping antiviral treatment.


A rare group of patients have been found to maintain a very low viral load and a functional immune system after stopping antiviral treatment.
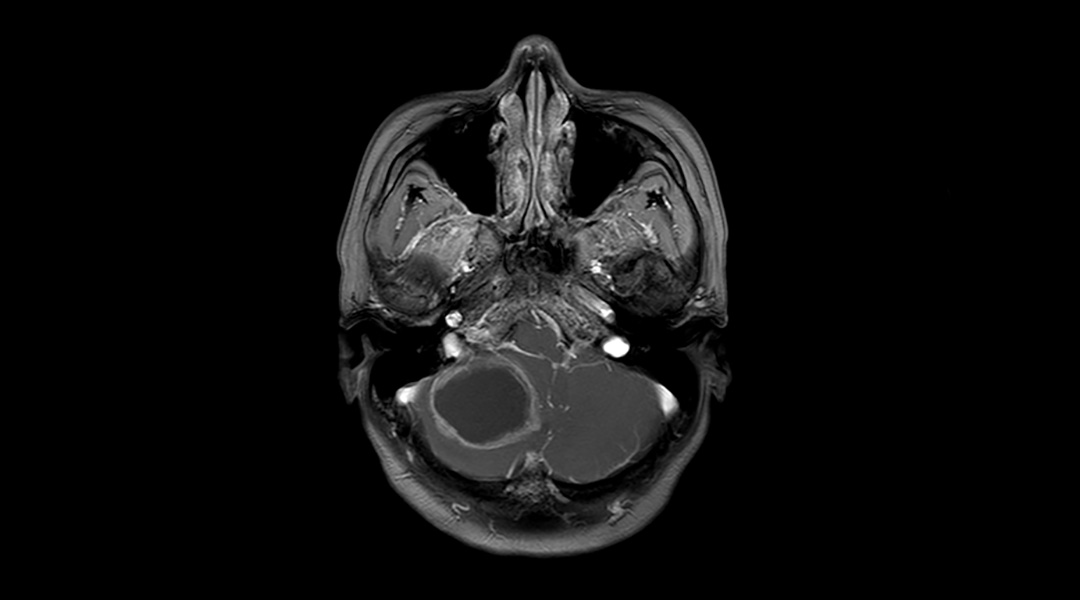
Inspired by brain-invading bacteria, researchers have created nanocapsules that covertly shuttle drugs across the blood–brain barrier.
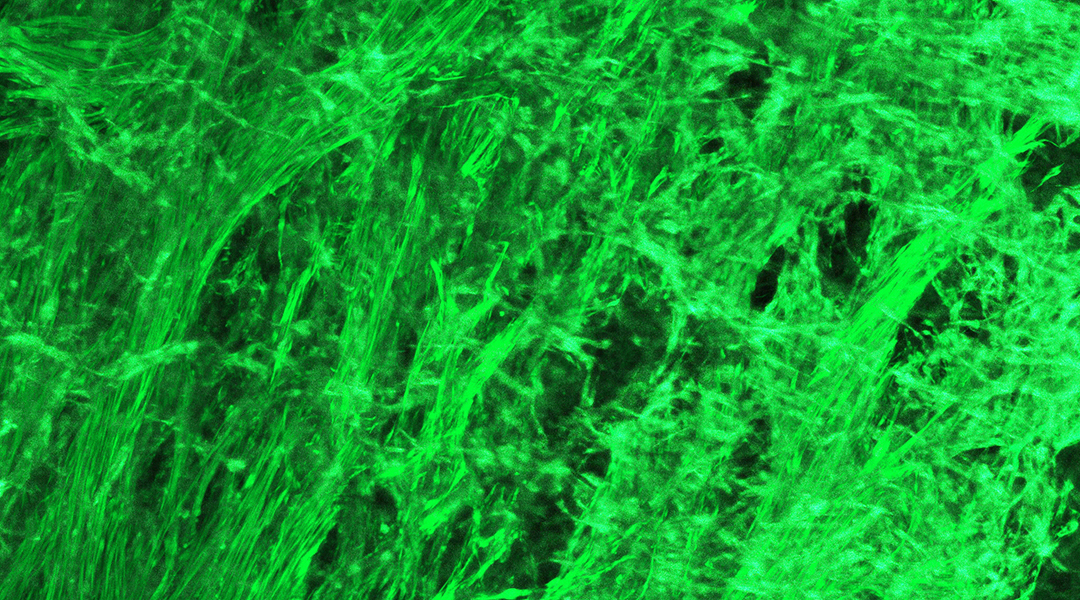
Engineered tissue mimics the contractions of the small intestine to break down artificial materials simulating partially digested food.
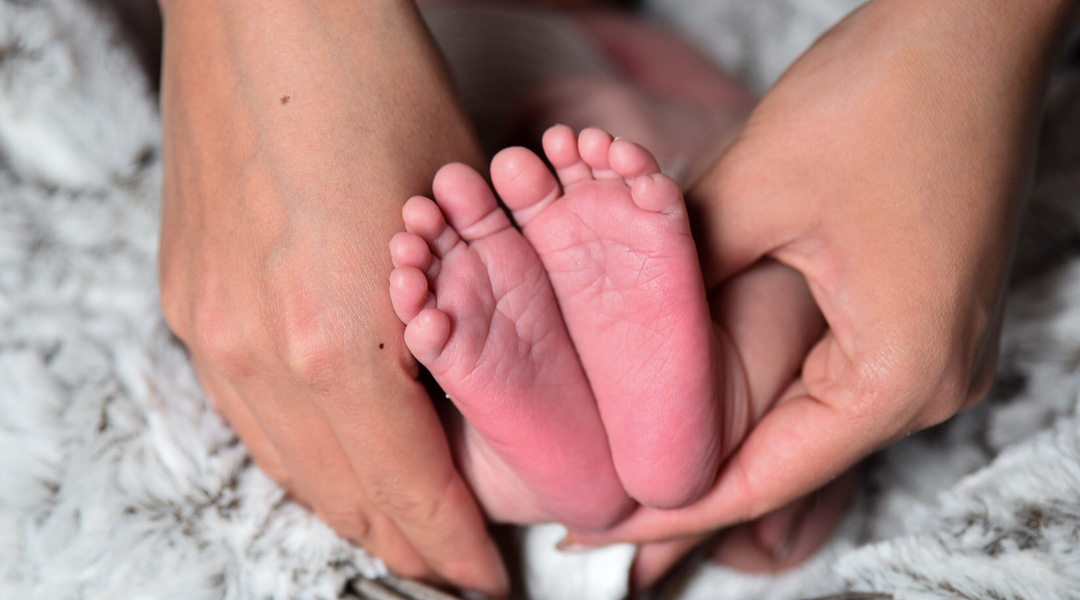

The infant microbiome can be built from a dizzying array of different sources.
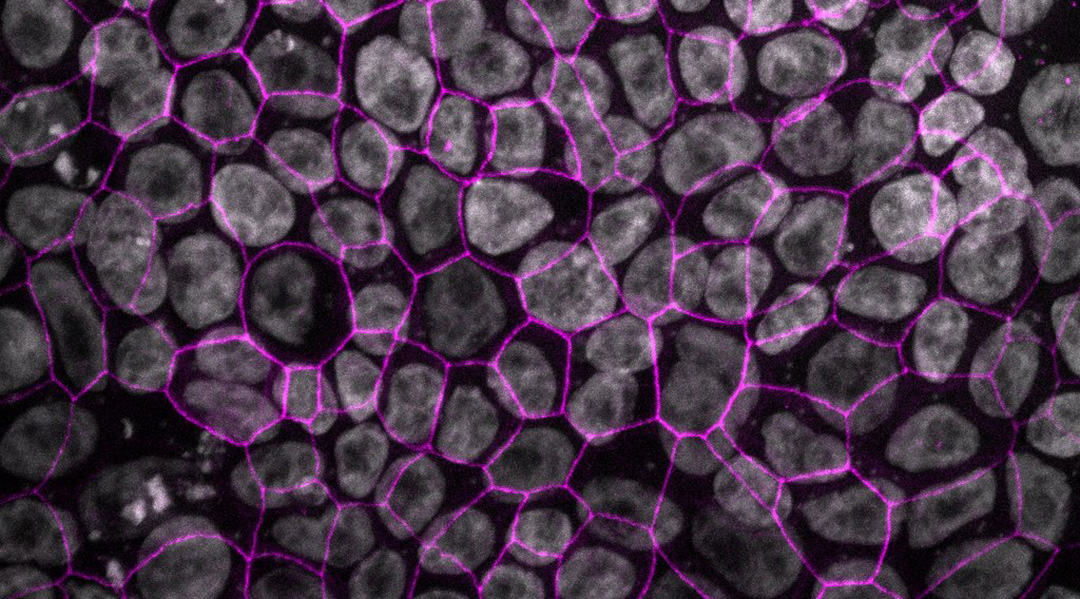
New lung model raises hopes for more realistic modeling of new drugs and therapies.
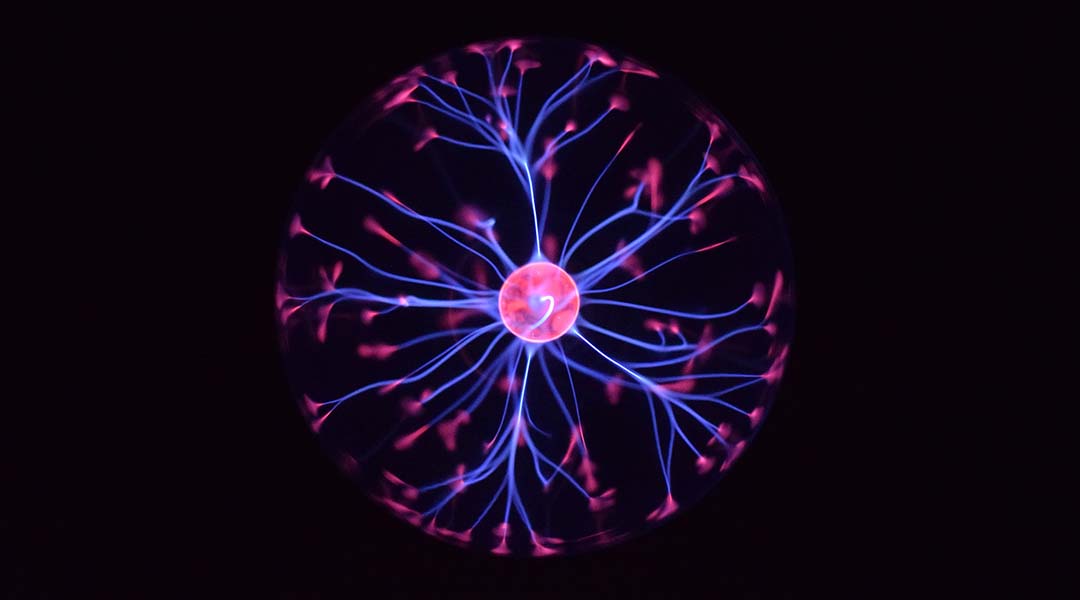
To make computers faster and more efficient, scientists are using the brain as a model in this blossoming area of computer science.
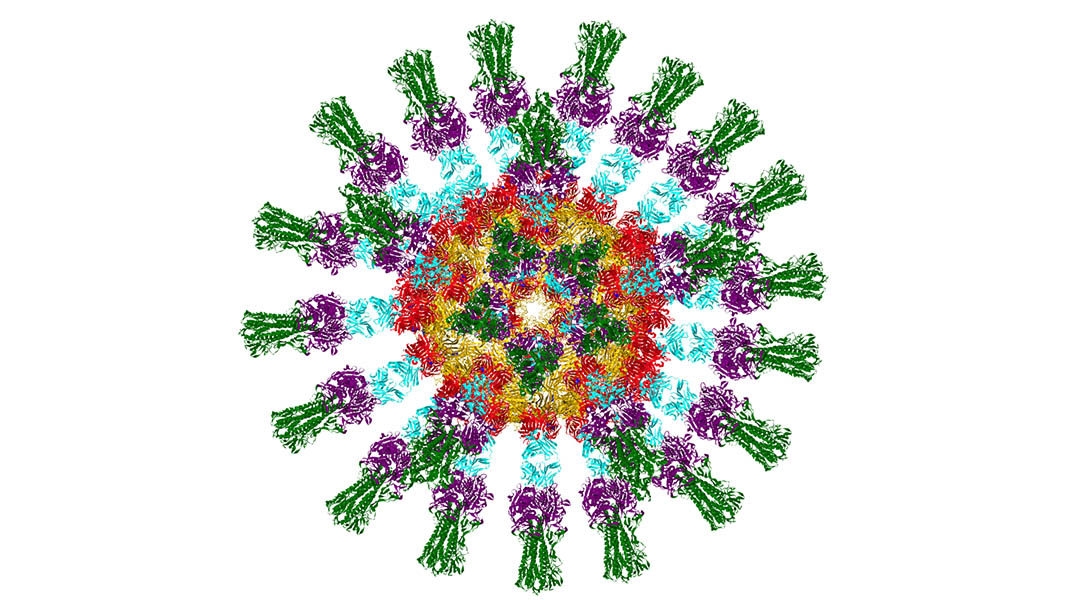
To create a flu vaccine that doesn’t require annual tweaking, researchers develop a nanovaccine that uses an inverted hemagglutinin protein.
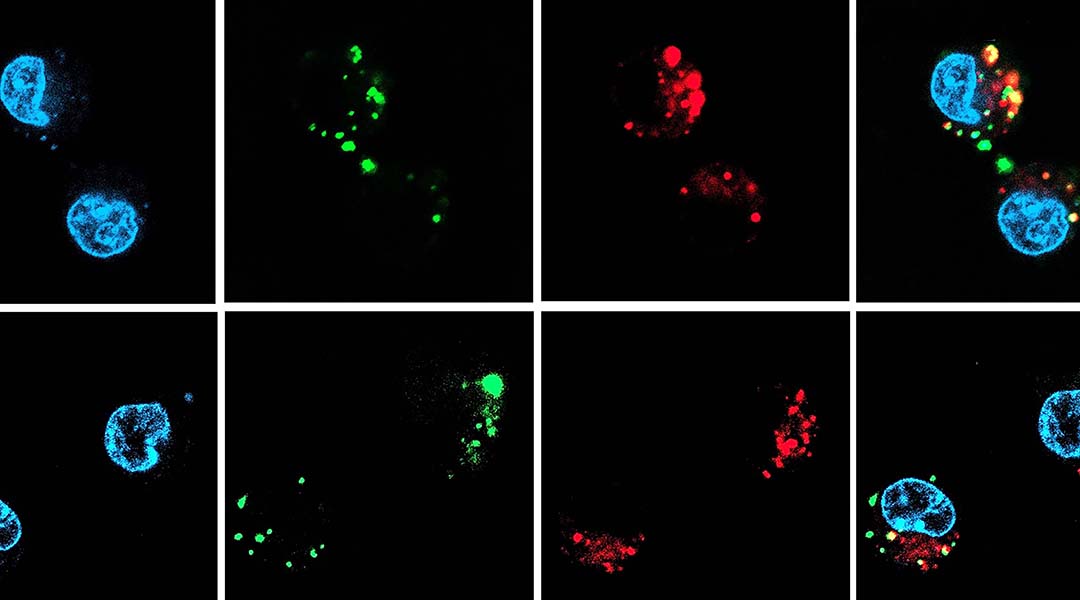
Drugs based on nucleic acids are easily degradable and tough to deliver, but a way around this is to coat them in protective carrier.
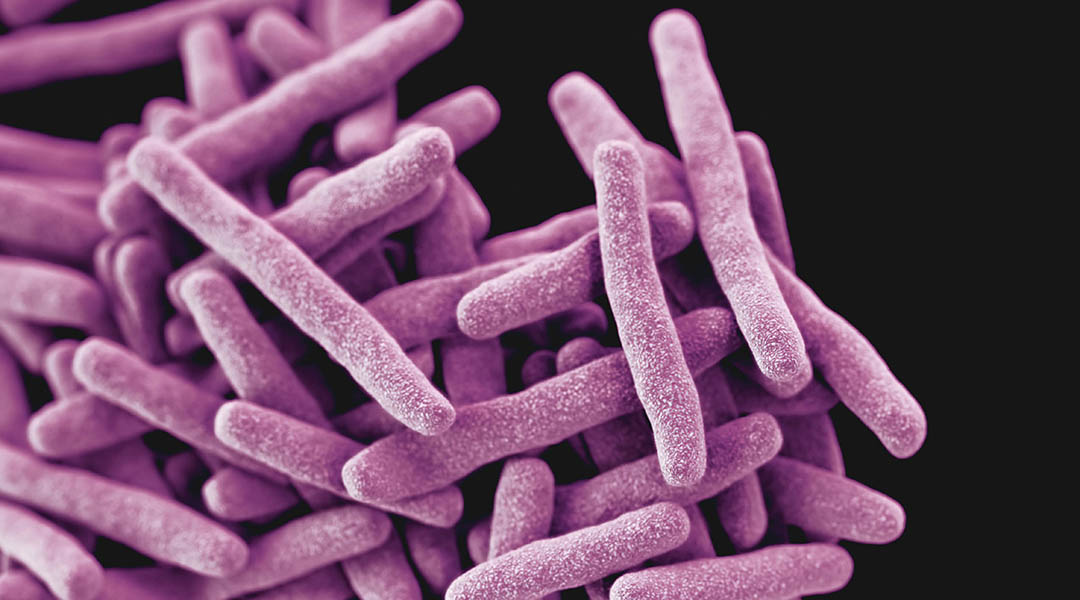
The genetic variant that causes Gaucher disease may have helped breakdown tuberculosis-causing bacteria in cells through lipid buildup.
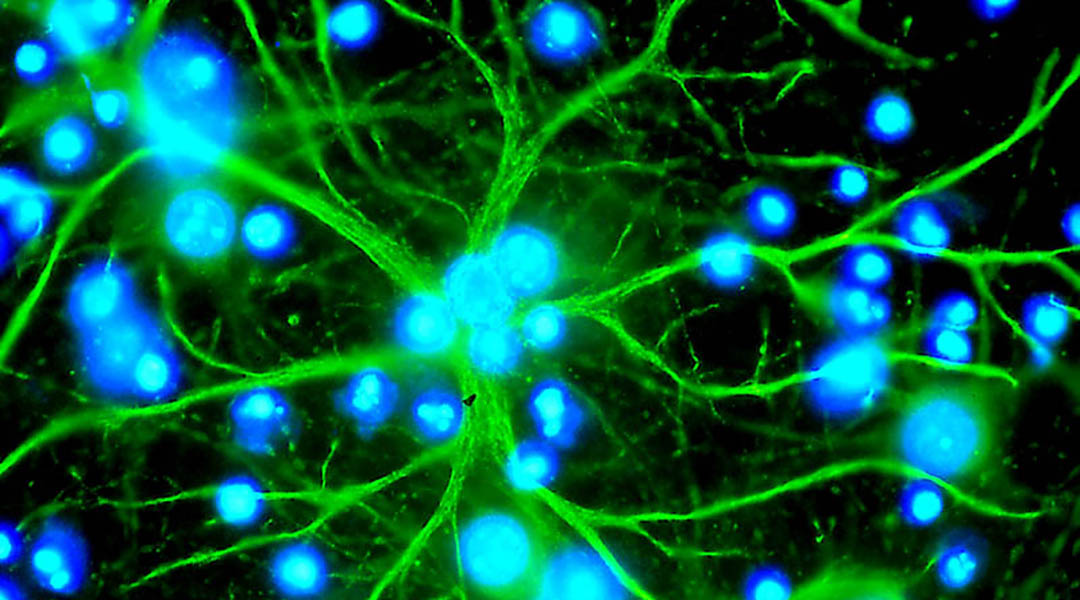
A group of brain cells called astrocytes might be involved in how information is conveyed within the brain’s neural networks.