Metal nanoparticles have demonstrated broad and promising biomedical applications in research laboratories, but to fulfill their potential in the clinic demands extensive effort to minimize their non‐specific accumulation in the body.
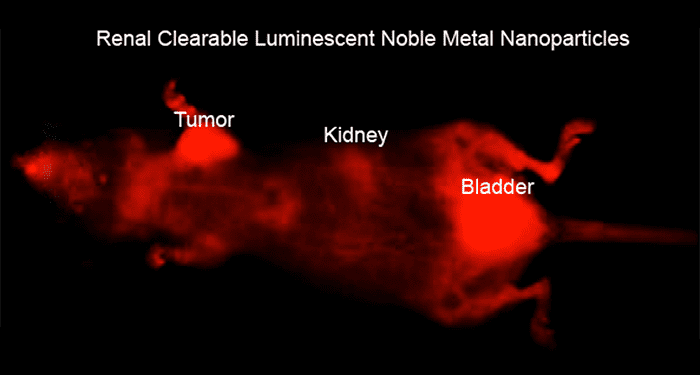

Metal nanoparticles have demonstrated broad and promising biomedical applications in research laboratories, but to fulfill their potential in the clinic demands extensive effort to minimize their non‐specific accumulation in the body.
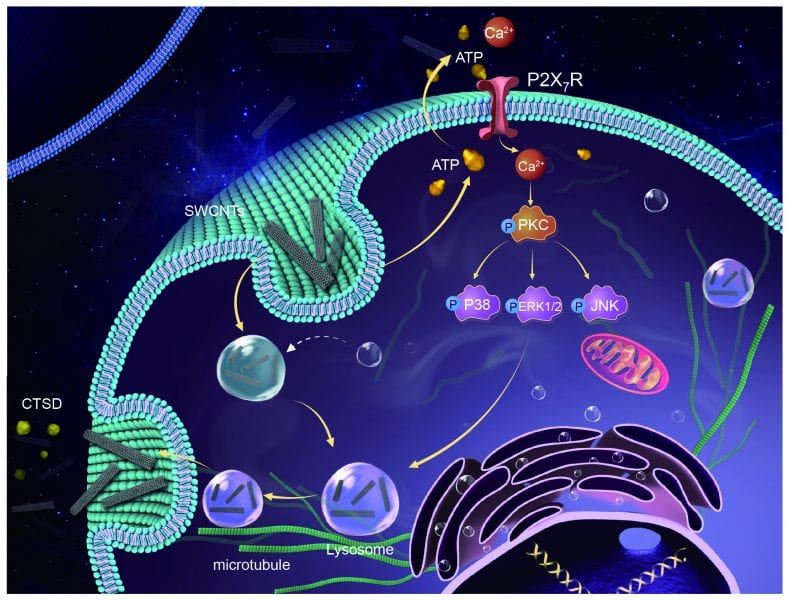
To design nanoproducts with improved therapeutic efficiency and controlled toxicity, we need to understand the mechanisms of cellular uptake and exocytosis of nanoparticles.
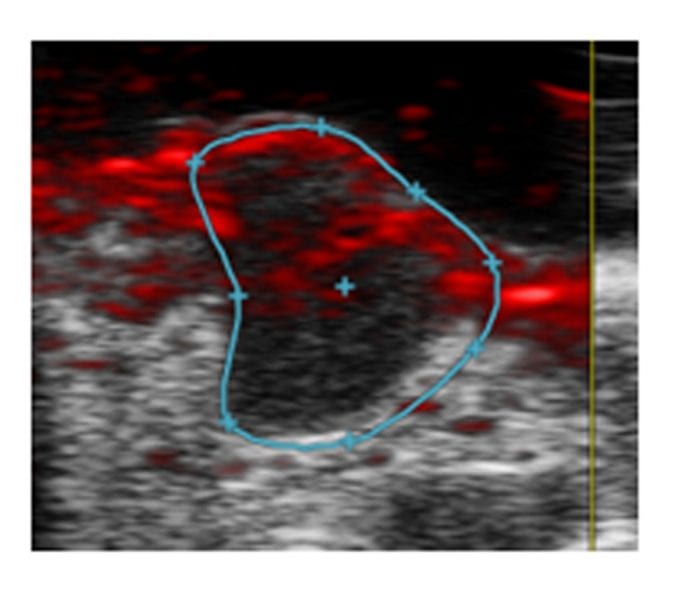
A novel melanin-based contrast agent may help assess the tumor vasculature after antiangiogenic treatment via Dynamic Contrast Enhanced Photoacoustic Imaging.
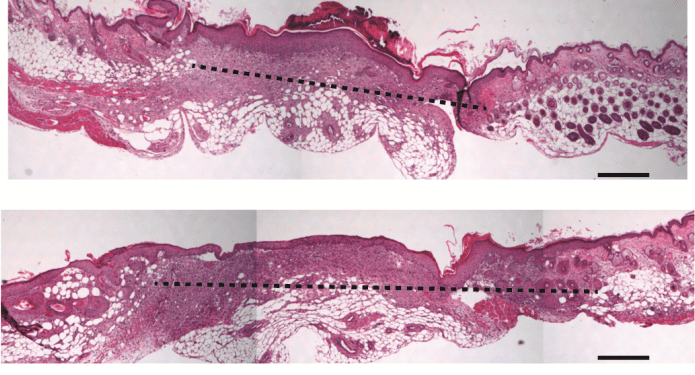
Researchers from the University of South Australia reveal how they use non-toxic porous silicon nanoparticles (pSi NPs) for the controlled release of FnAb to diabetic wounds.
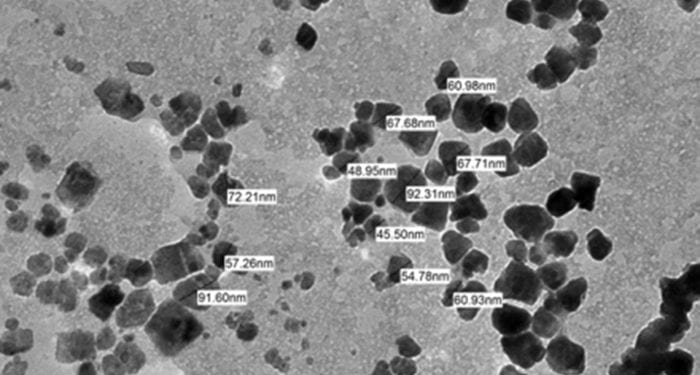
Natural polymers- based nanoparticles are widely used for biomedical purposes as they are highly biocompatible and biodegradable. Yet potential unexpected side effects have to be taken into account.
Researchers at the University of Science and Technology of China have developed mesoporous silicon nanospheres that can be used for photocatalytic hydrogen production.
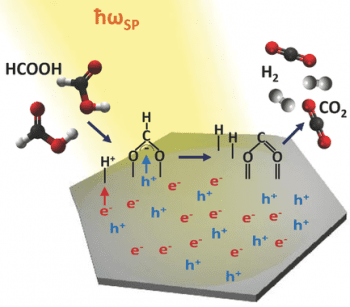
Pd nanosheets function both as broadband light absorbers and as synthetic catalysts for the dehydrogenation of formic acid to hydrogen and oxygen.
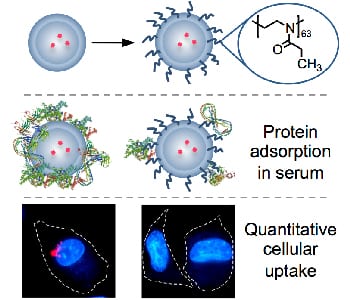
To avoid an undesired protein adsorption, nanoparticles were masked with poly(2-oxazoline)s resulting in a stealth coating comparable or superior to PEG.
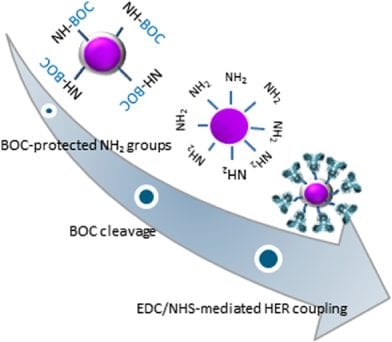
A novel method for preparing biodegradable polyurethane nanoparticles that will actively recognize cancer cells.