Modeling involuntary aspects of human behavior, such as blinking or even jet lag, might help build trust in robot-human interactions.
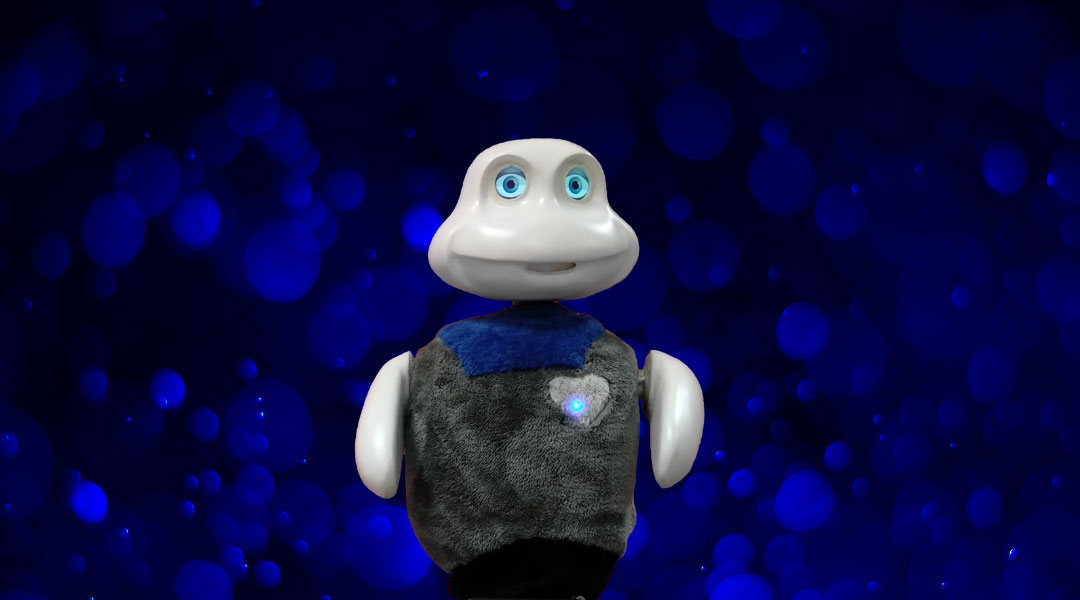


Modeling involuntary aspects of human behavior, such as blinking or even jet lag, might help build trust in robot-human interactions.
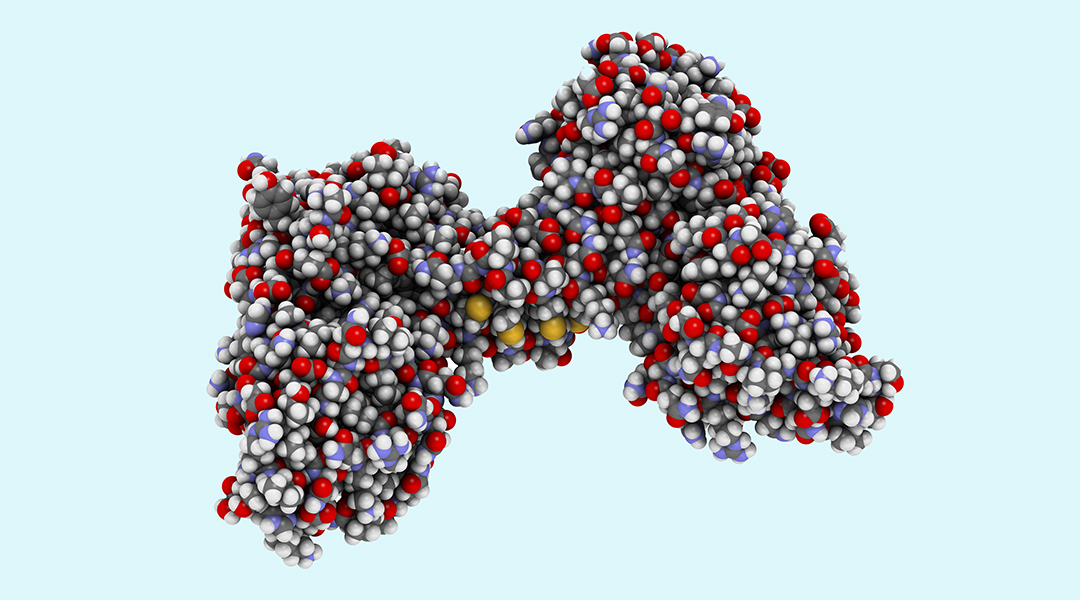
Important findings from an animal study have prompted the exploration of a gene therapy for Duchenne muscular dystrophy in an ongoing human trial.
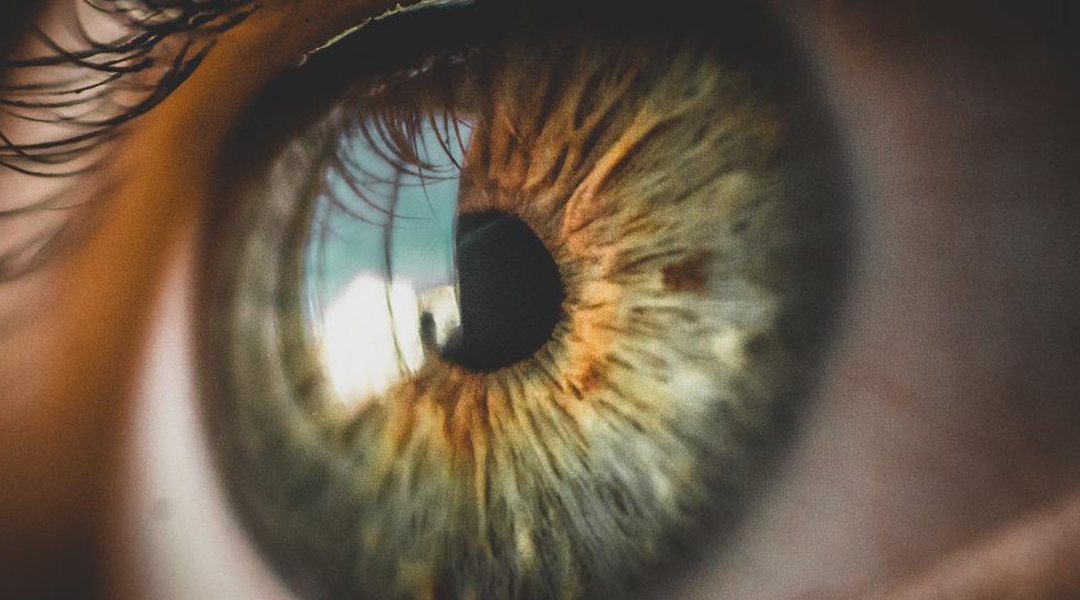
Forcing robots to see through a human’s eyes is limiting. Smart robotic eyes that can think for themselves could be the answer.

Researchers calculate the automation risk of almost 1000 existing occupations and provide alternatives based on skill set.
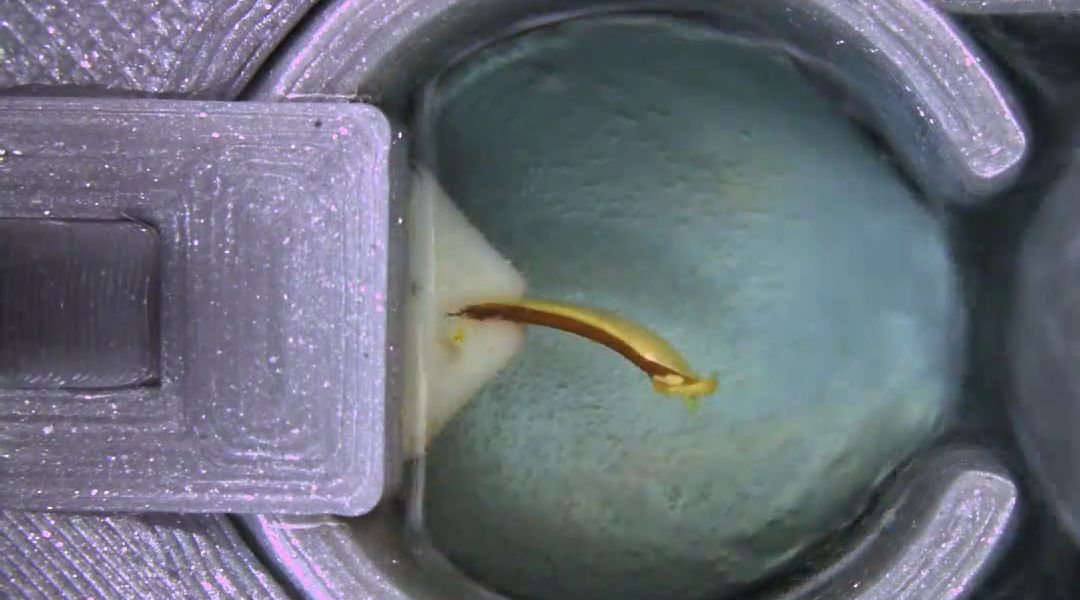

Scientists have developed the first artificial muscles made from natural proteins that contract autonomously and consume chemical fuel.
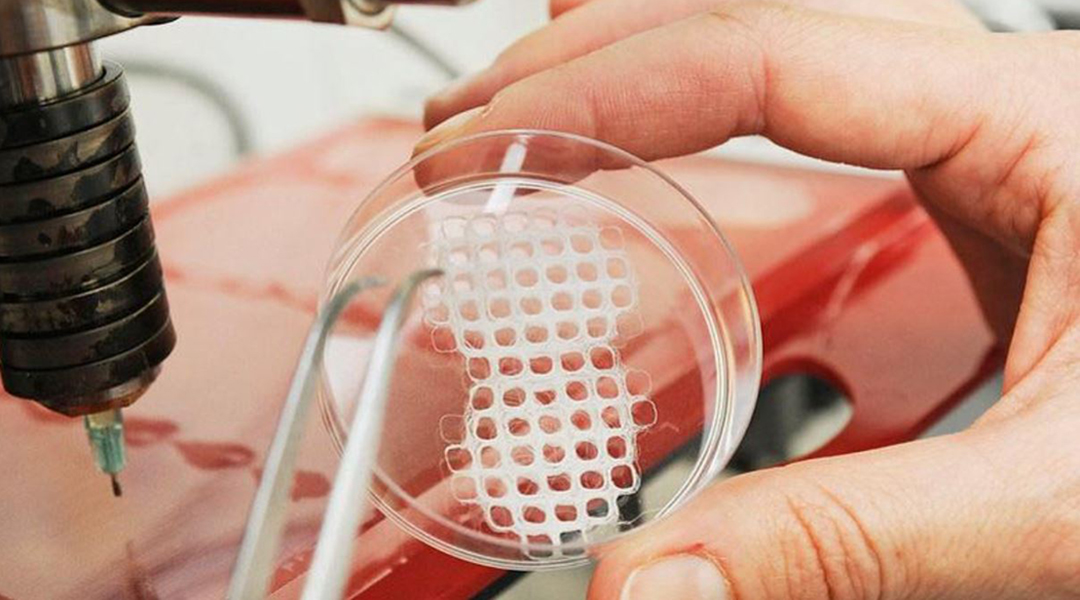
Machine vision and artificial intelligence can fine tune medical 3D printers to enable custom made tissue implants to suit the individual patient.
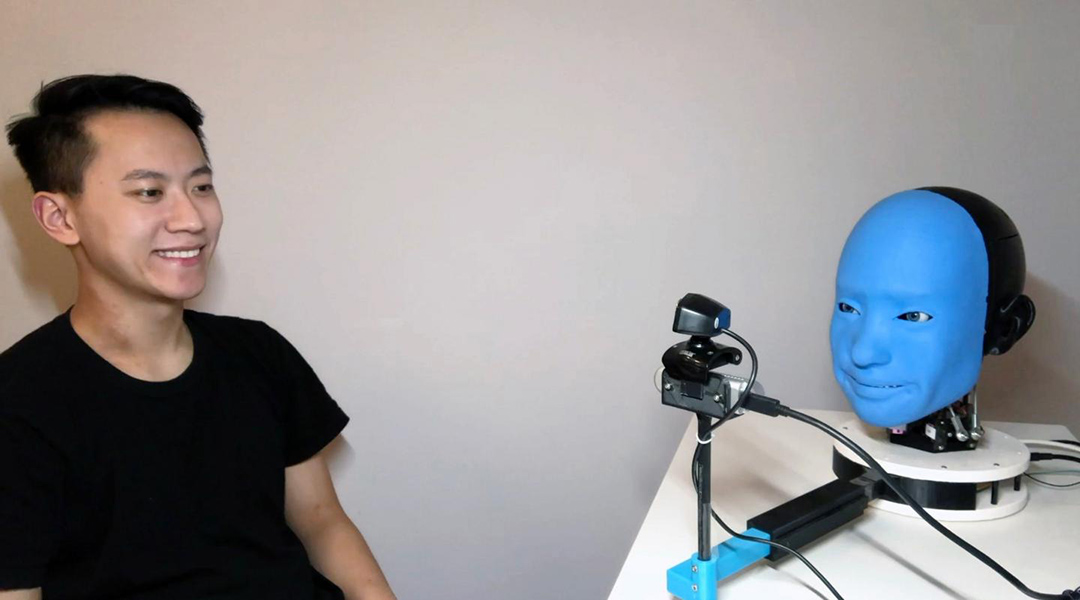

Researchers teach robots to make appropriate reactive human facial expressions, an ability that could build trust between humans and their robotic co-workers and care-givers.

The Singapore-based materials scientist on her love for science, promoting gender equality in STEM, and how innovations in materials can propel advances in healthcare.
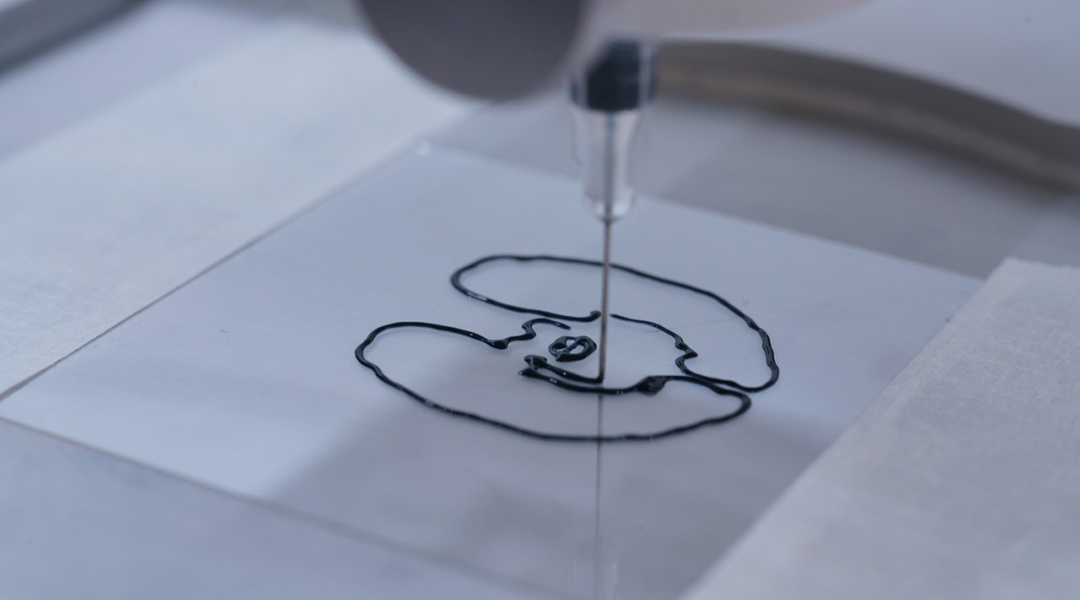

Researchers demonstrate the controlled growth of artificial synapses, paving the way for computers that can grow, evolve, and adapt like the human brain.
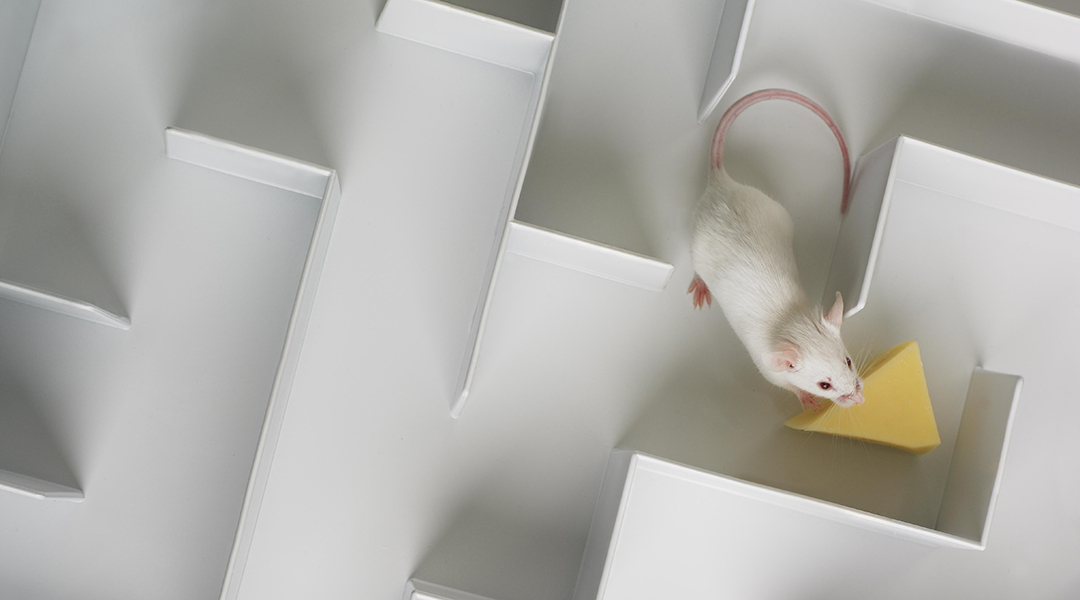

Replacing animal testing with the ever-growing capabilities of AI and deep learning could help minimize the need for animals in scientific discovery.