Latest

Scientists discover a new class of antibiotics
A bacterium found in a backyard could offer new hope in the fight against antibiotic resistance.

New material emitting spinning light could revolutionize optics and computing
“We’ve essentially reworked the standard recipe for making organic light emitting diodes, like those found in smartphones.”
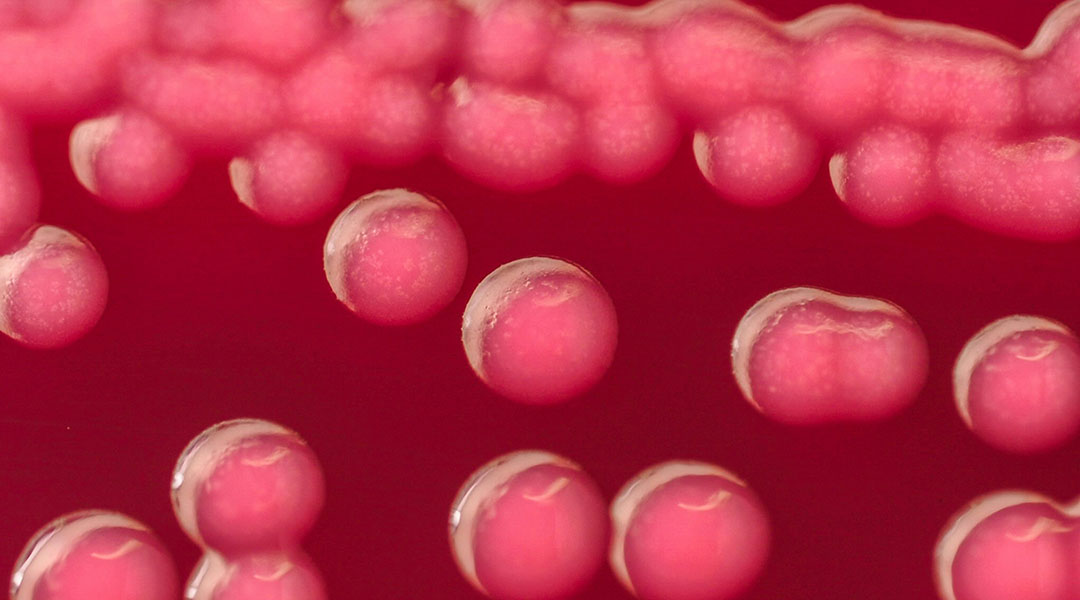
Common bacteria could be used to produce biodegradable bioplastics
Engineered Escherichia coli bacteria could be used to make sustainable biobased plastics.
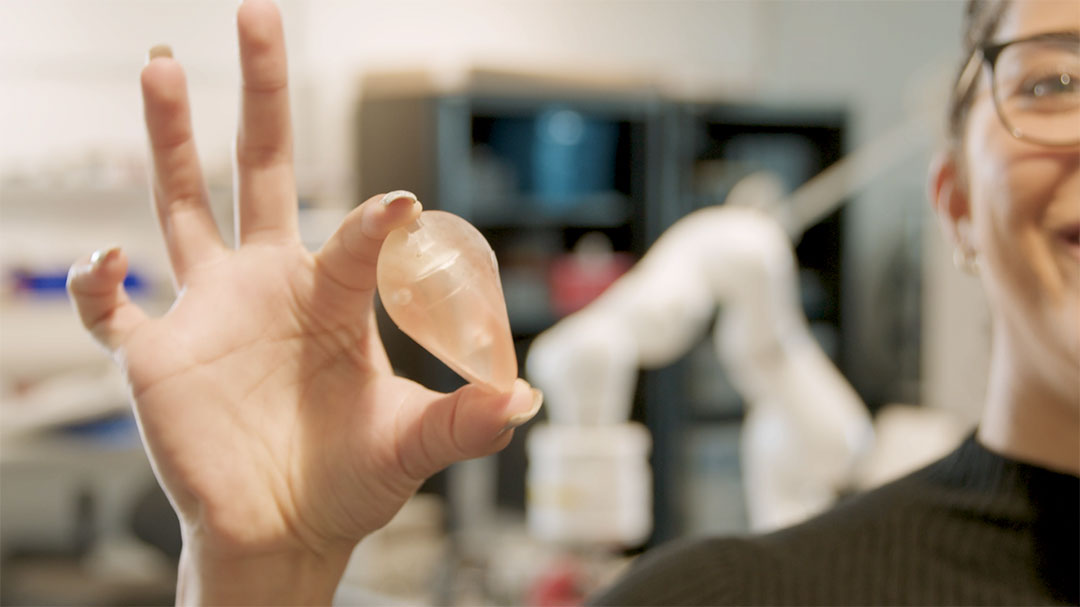
Tiny robots take 3D scans from inside the gut to diagnose cancer
A robot with a unique shape could make it possible to perform ultrasound scans deep within the gut, helping doctors diagnose colorectal cancer.
Ultra-sensitive CRISPR test detects pathogens in minutes—No lab needed
Scientists have developed a CRISPR-based diagnostic that detects pathogens in blood with million-fold greater sensitivity—without the need for DNA amplification.
Light-activated therapy and antibiotics join forces to improve in situ cancer vaccines
Scientists integrate light therapy and antibiotics into a single platform to help the body create its own tumor vaccine.
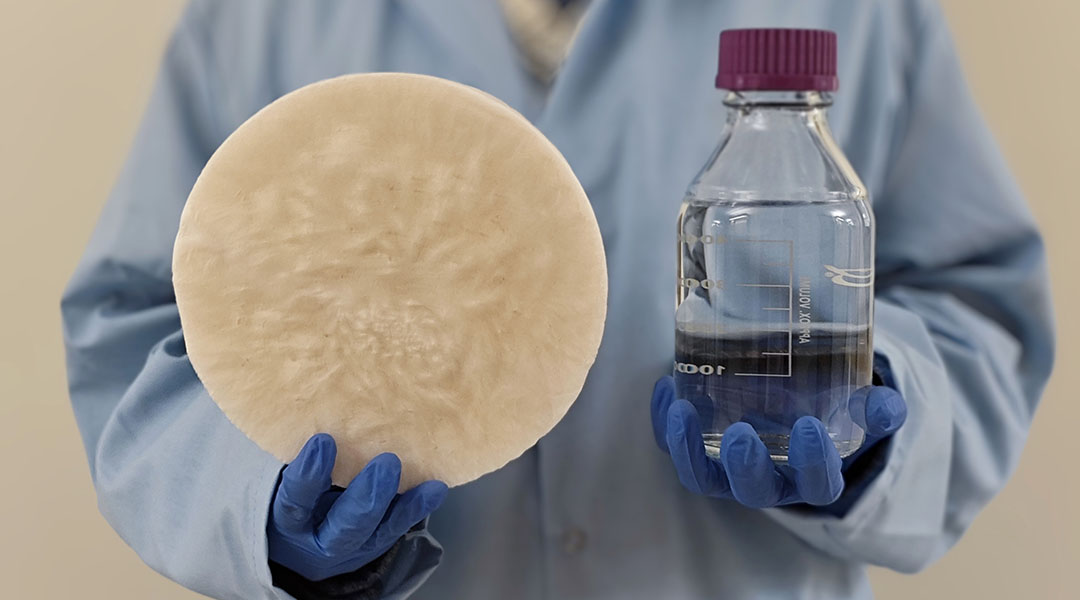

Plant-based hydrogel harvests water from air, addressing global water scarcity
A new hydrogel extracts water from the air, offering a sustainable alternative to bottled water and addressing global water shortages.
ASN Weekly
Sign up for our weekly newsletter and receive the latest science news directly to your inbox.
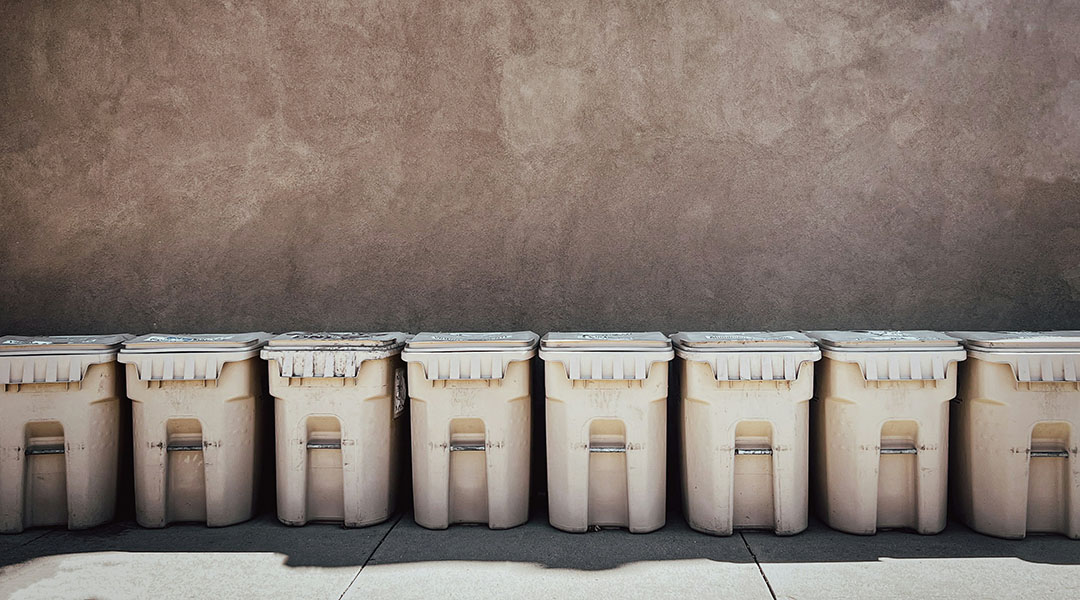

Scientists report airborne bacteria found in garbage may age our blood vessels
Pathogenic bioaerosols detected at household garbage collection sites may contribute to vascular aging with high chronic exposure.
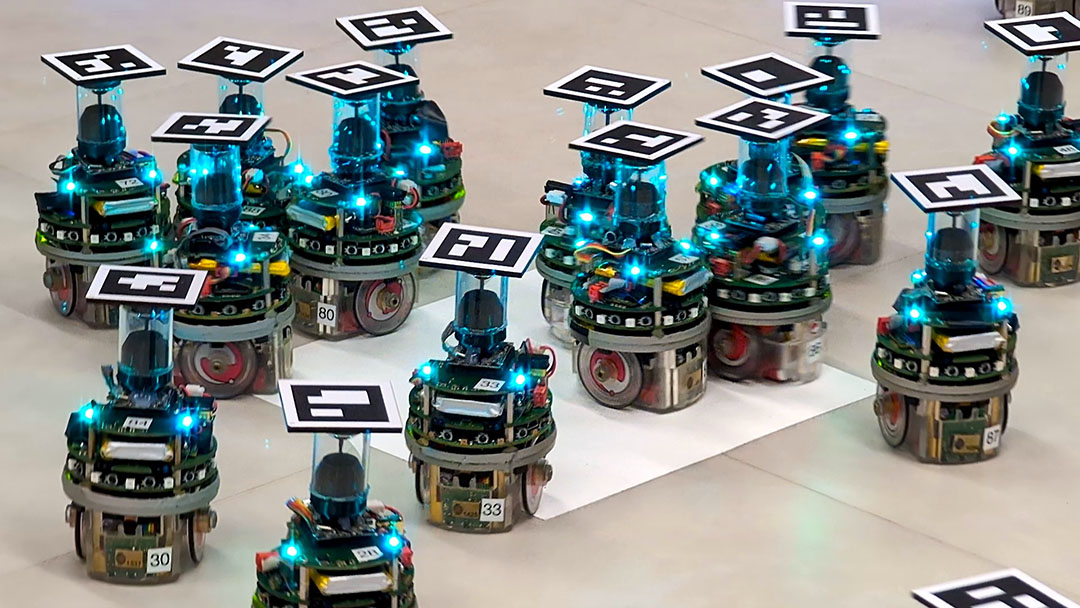

Autonomous robot swarms come together to perform a variety of missions
Researchers have developed an optimization program to design the behavior of small e-puck robots to allow them to work in unison.
Samples recovered from Ryugu asteroid reveal how our solar system formed
An ancient magnetic field drew matter inward and helped form our solar system’s planets, moons, and asteroids.

Liver protein linked to weight loss during intermittent fasting
The protein helps convert white fat tissue into calorie-burning beige fat, providing a potential target for weight loss and obesity treatments.

Fast radio bursts lead scientists to the origins of magnetars
Links to observational data may have revealed the nature of magnetars and the origins of their extreme magnetic fields.
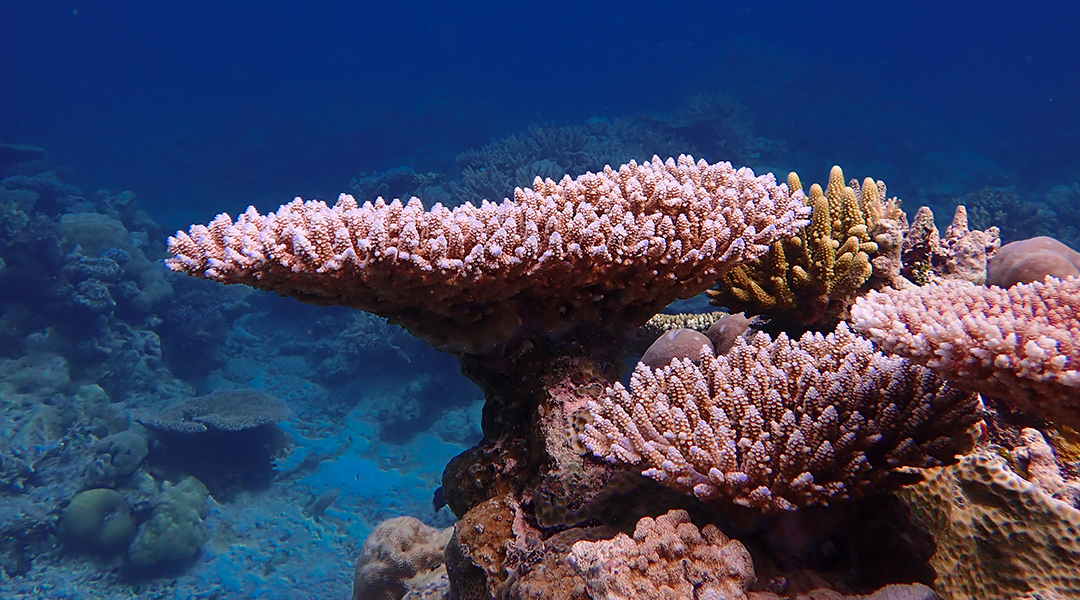

Can coral evolution keep pace with climate change?
Scientists explore how corals could adapt to climate change to survive, but stress that cutting emissions is crucial for their future.

Women with a genetic risk of depression are more likely to suffer from heart disease
Data from over 300,000 participants has revealed a potential genetic link between depression and cardiovascular disease in women.
New antenna design promises major advances in quantum sensing
An antenna designed to create an optimized magnetic field puts electrons into the required quantum states for quantum sensing devices.

Solar concentrators are turning glass into clean energy generators
Transparent solar concentrators capture the Sun’s energy, making windows and building facades more energy-efficient and sustainable.
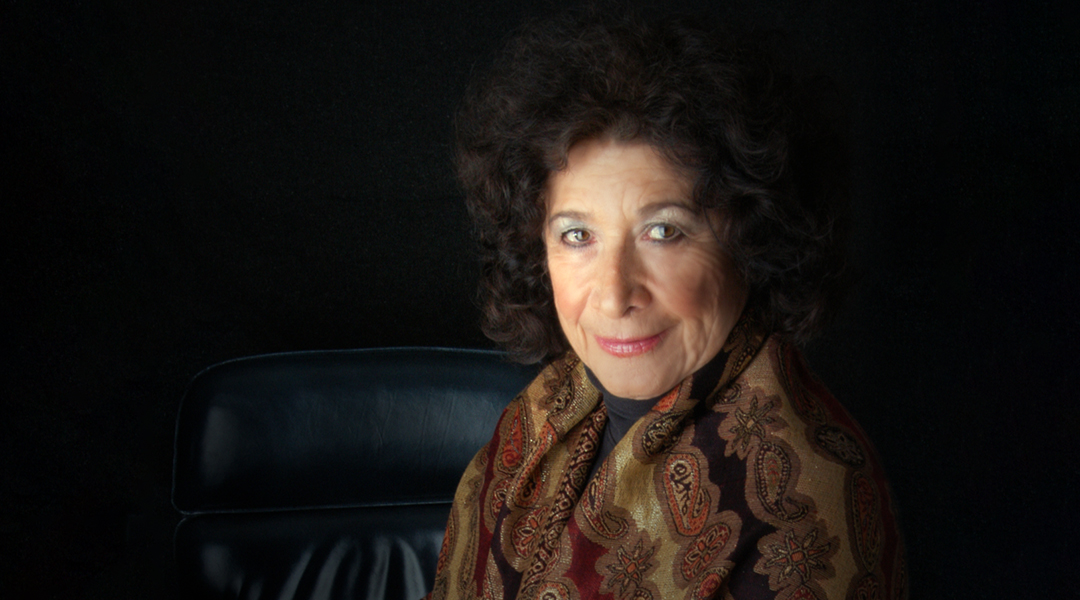

Zafra Lerman: Scientific exchange can promote peace
Chemist, teacher, humanitarian, and peace activist, Zafra Lerman uses science to break down barriers and foster peace.

Oded Rechavi: “Do anything in your own style, the way you want to do it”
Neurobiologist Oded Rechavi investigates epigenetics, a curative use for brain parasites, and helped piece together the Dead Sea Scrolls using DNA.

César Rodriguez-Emmenegger: “Be passionate, creative, and bold”
Through innovative, interdisciplinary work, chemist César Rodriguez-Emmenegger is seeking a way to communicate with biological systems.
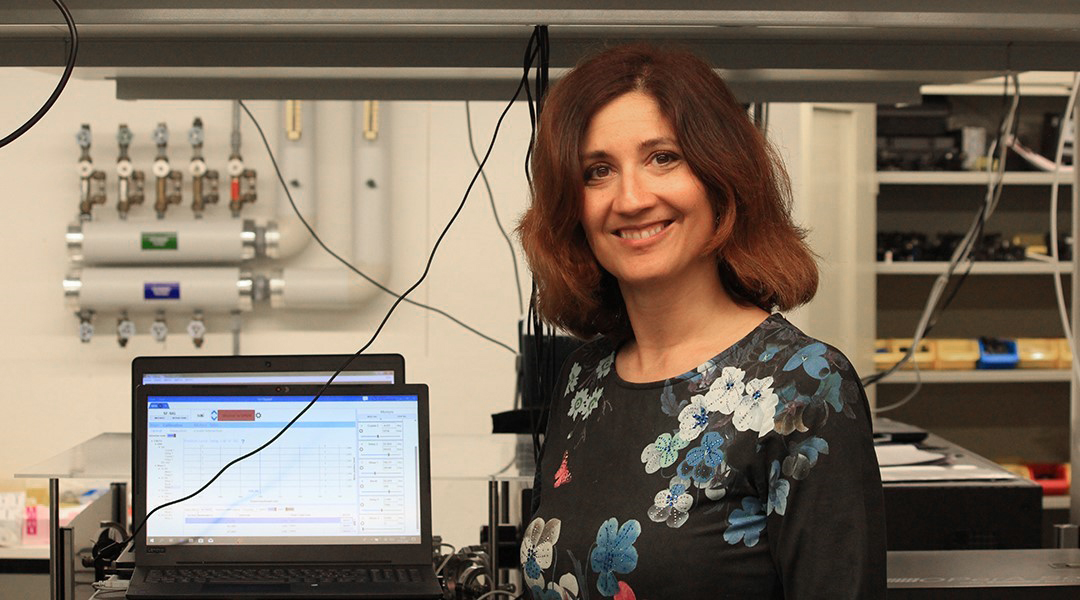

Natalie Banerji: “You do not go very far by yourself”
At the interface of light and matter, Natalie Banerji is using spectroscopy to advance technologies such as solar cells and bioelectronics.
No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
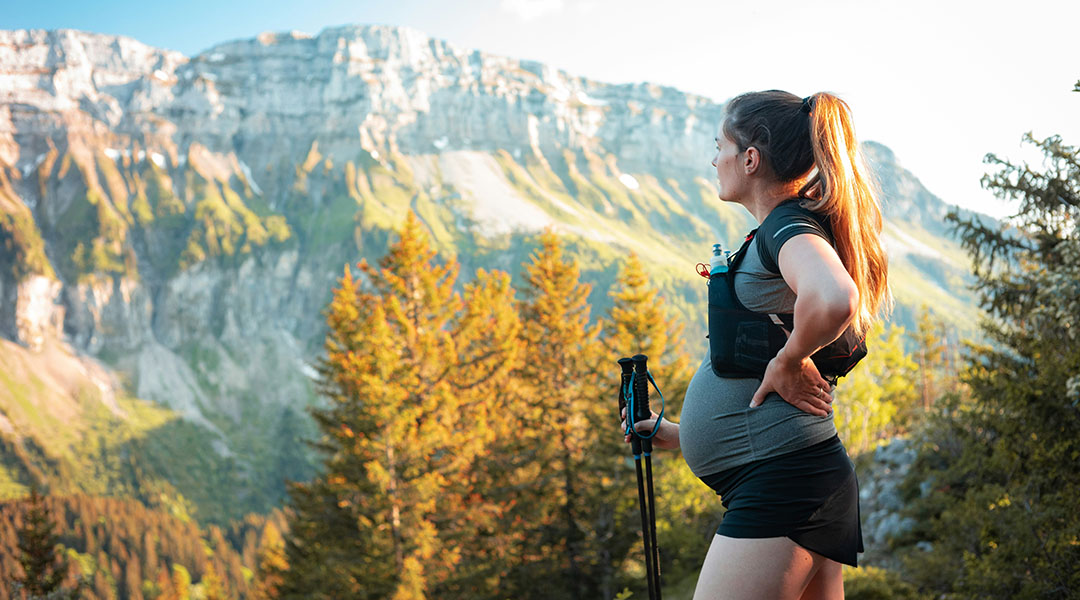

Mouse study reveals multi-generational benefits of exercising during pregnancy
Maternal exercise during pregnancy enables multiple generations of mice to inherit enhanced fitness, with vitamin C playing a key role.
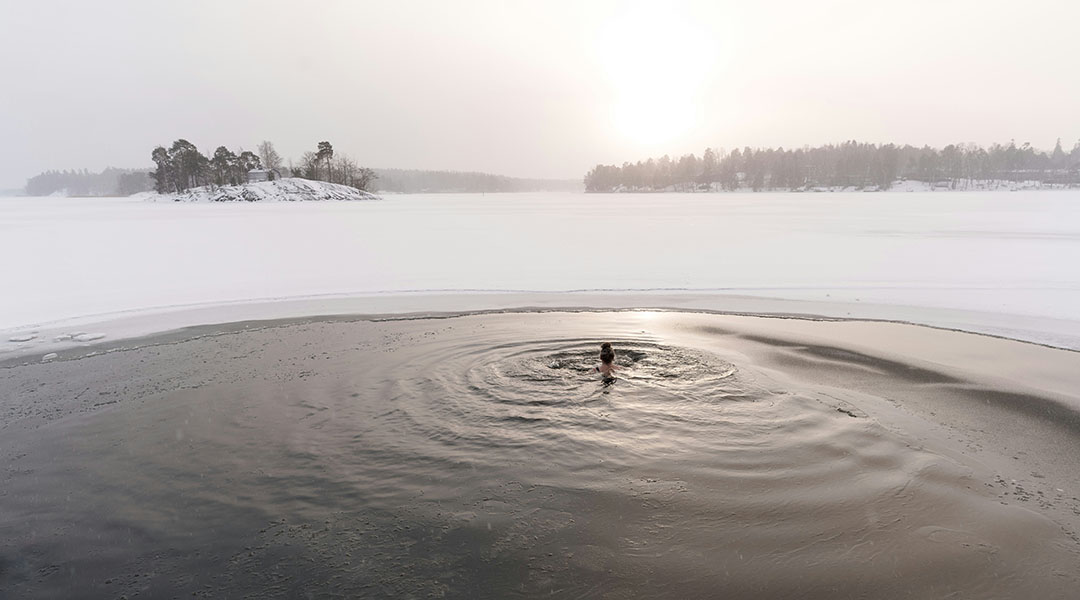

Cold shock from ice baths leads to stronger cells
New study reveals how repeated cold-water exposure enhances the cellular defenses, promoting adaptation to extreme temperatures.
3D microgel device puts stem cells under pressure
A new 3D cell culture allows researchers to study how mechanical pressure influences stem cells for regenerative medicine and cell therapy.
Xenon gas protects brain cells against Alzheimer’s disease, clinical trial underway
Inhaled xenon gas reduced neuroinflammation, brain atrophy, and boosted protective neurons in mouse models of Alzheimer’s.
Securing data with bright entangled photons
Secure data sharing methods using quantum key distribution via satellites promise advancements in long-distance quantum communication.

Quantum communication could be integrated into existing fiber optic networks, new study shows
Quantum communication doesn’t necessarily need to be delayed; it might be possible to integrate it into existing fiber optic networks.

Calculating the true environmental costs of AI
The rapid growth of AI brings hope of unprecedented advancements in many sectors but what is its real carbon footprint?
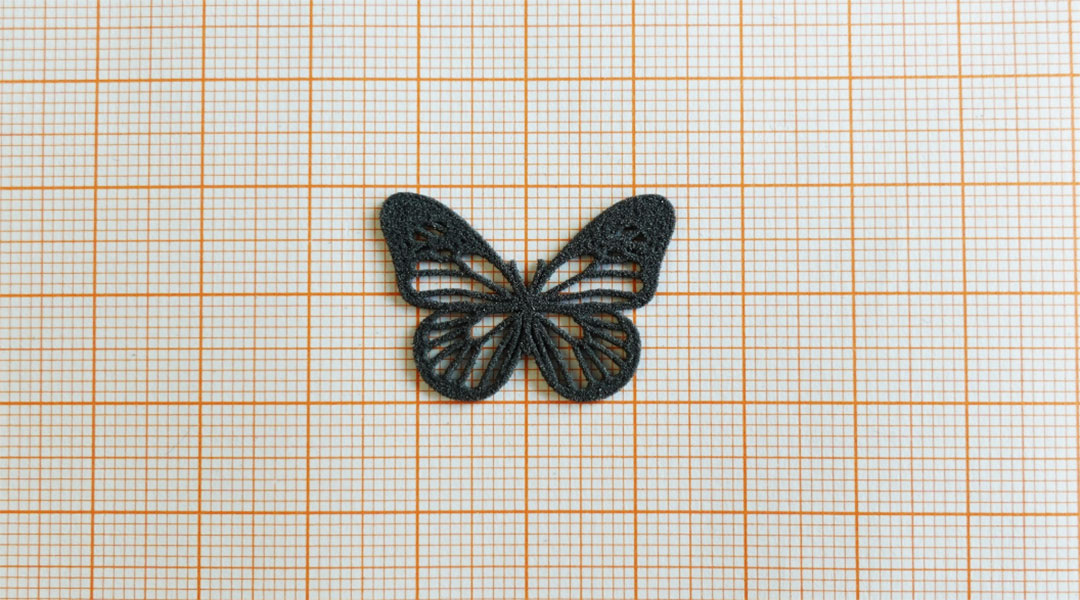

Butterflies inspire magnetic robots that fly more efficiently
Monarch butterflies have inspired the design of 3D-printed robotic wings that rely on magnetic fields to generate their delicate movements.
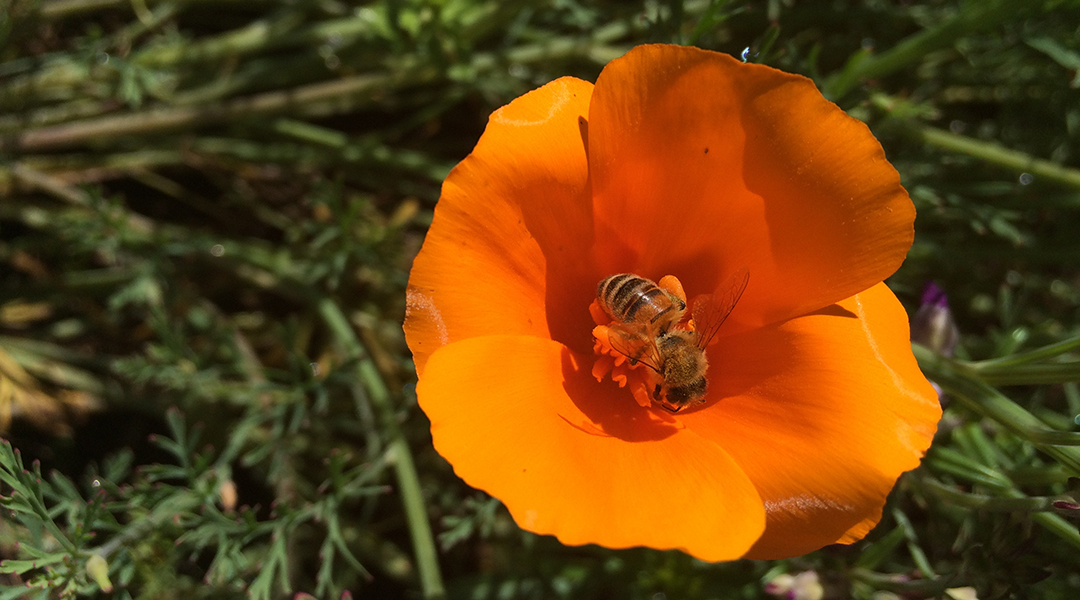

Honey bees boost crop pollination, but at a cost to wild bees
Honey bees compete with wild bees for resources in croplands, but nutritious wildflower plantings can mitigate these effects.

Turning banana peels and coconuts into clean energy
Researchers develop a device that generates clean energy from food waste, using banana peels and coconuts to power communities sustainably.

Scientists report airborne bacteria found in garbage may age our blood vessels
Pathogenic bioaerosols detected at household garbage collection sites may contribute to vascular aging with high chronic exposure.

Biowaste finds new life in energy-harvesting devices
In the future, small electronics could be powered by fallen leaves, shed fur, and other waste materials found in nature.

How gamma rays developed the chemical complexity of the cosmos
Researchers have built a better picture of how complex molecules developed in the early Universe before becoming essential for life.

Researchers take a glimpse at the structure of rare tetraquarks
A new study explores tetraquarks, predicts new exotic particles, and offers deeper insights into their complex structure and behavior.

CERN scientists search for new physics in unusual energy patterns linked to hidden particles
Researchers at CERN’s Large Hadron Collider explore subtle energy signals to search for new physics beyond the Standard Model.
Scientists take a closer look at rare particles called hypernuclei
Scientists use cutting-edge techniques to study rare atomic systems called hypernuclei shedding light on subatomic forces and neutron stars.