Researchers at North Carolina State University develop nanostructures that suppress the “thin-film interference” phenomenon commonly observed in nature.
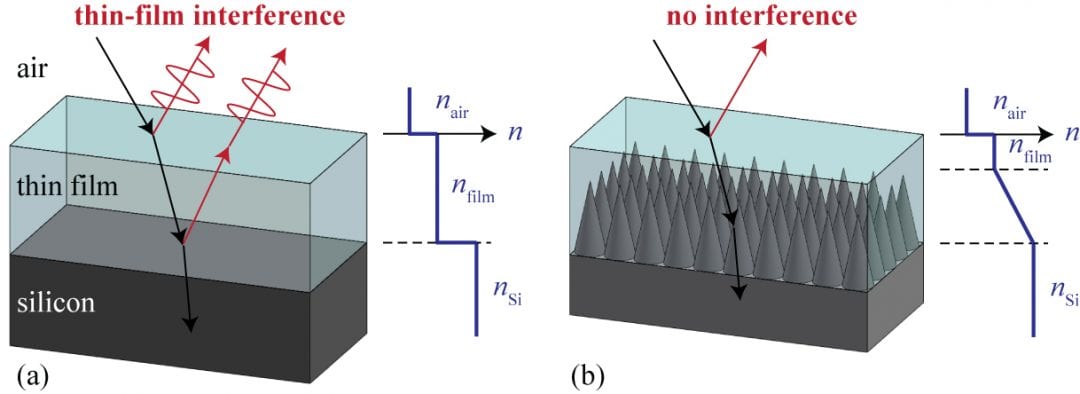

Researchers at North Carolina State University develop nanostructures that suppress the “thin-film interference” phenomenon commonly observed in nature.
Ferroelectricity, Photoconductivity, and auxetic foams – these and more in May’s physics highlights.

This special issue on low-dimensional carbon materials for Small is dedicated to the 20th anniversary of the Center for Nanochemistry at Peking University.
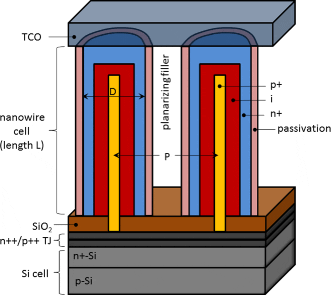
Review paper analyzes opportunities and obstacles for III-V nanowires in solar energy harvesting.

The Journal of Polymer Science Part A: Polymer Chemistry highlights some important research in the latest issue.

Martin Green from UNSW, a pioneer in solar photovoltaic science and engineering, has been elected into the prestigious Fellowship of the Royal Society.
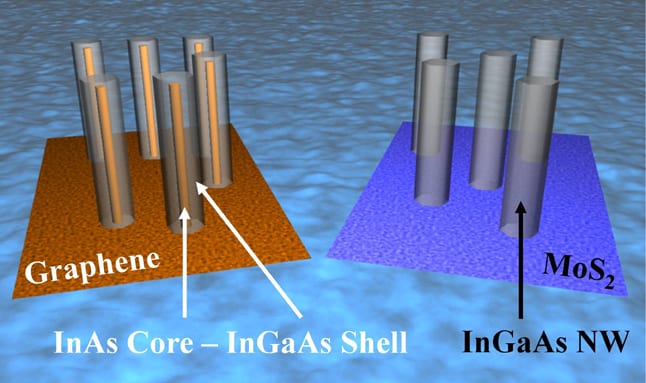
Discovery comes as researchers set out to grow nanowires of a compound semiconductor on top of a sheet of graphene.

Fabricated nanorods are not only straight and tall (at least by nano-standards), but also have an optimal crystal structure.

Thin germanium films, with properties similar to graphene, could lead to lighter, faster electronics.
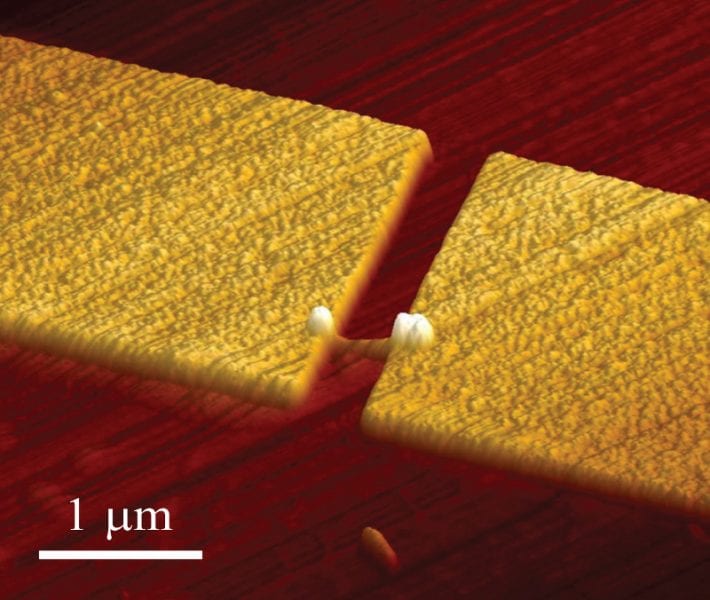
Researchers have demonstrated a simpler, more efficient single-photon emitter that can be made using traditional semiconductor processing techniques.