Natural polymers- based nanoparticles are widely used for biomedical purposes as they are highly biocompatible and biodegradable. Yet potential unexpected side effects have to be taken into account.
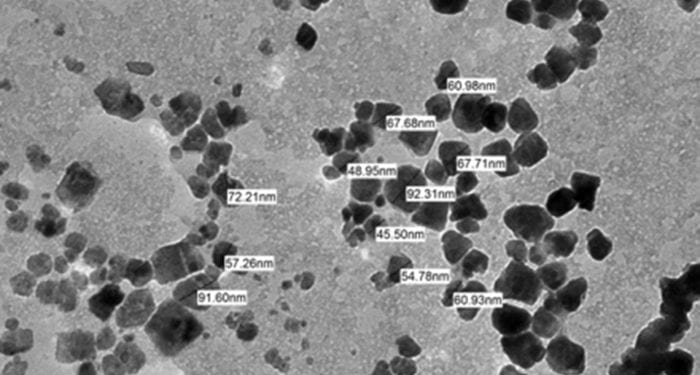

Natural polymers- based nanoparticles are widely used for biomedical purposes as they are highly biocompatible and biodegradable. Yet potential unexpected side effects have to be taken into account.
Researchers at the University of Science and Technology of China have developed mesoporous silicon nanospheres that can be used for photocatalytic hydrogen production.
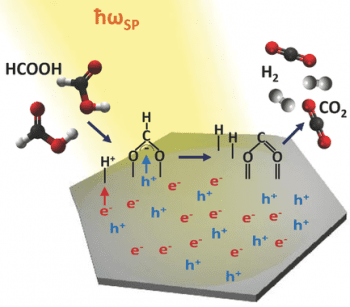
Pd nanosheets function both as broadband light absorbers and as synthetic catalysts for the dehydrogenation of formic acid to hydrogen and oxygen.
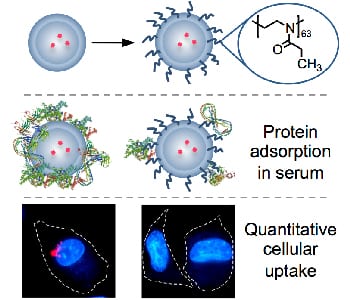
To avoid an undesired protein adsorption, nanoparticles were masked with poly(2-oxazoline)s resulting in a stealth coating comparable or superior to PEG.
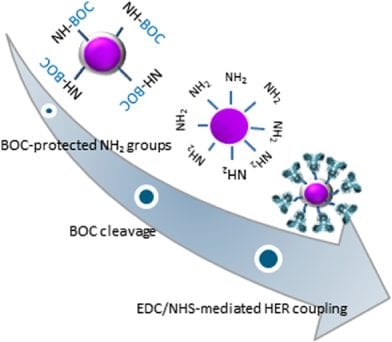
A novel method for preparing biodegradable polyurethane nanoparticles that will actively recognize cancer cells.
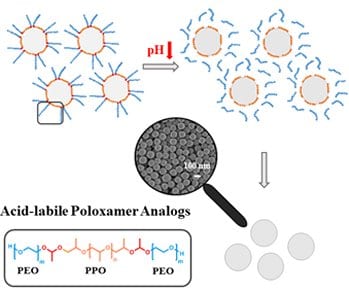
Researchers from Germany introduce acid-triggered precipitation which facilitates the removal of surfactant fragments from nanoparticles simplifying the purification and enabling nanoparticle precipitation “on demand.”
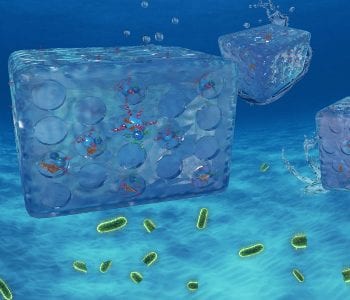
Using a variety of techniques to develop hybrid scavenger nanoparticles, researchers in China have created an efficient and reusable water filter to effectively clean polluted water up to safe drinking standards.
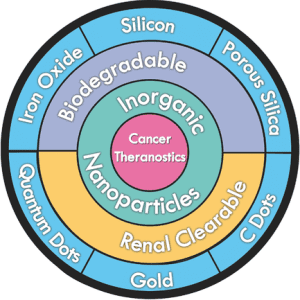
Nanoparticles have proven to be a powerful tool in fighting cancer through the development of personalized therapy options.
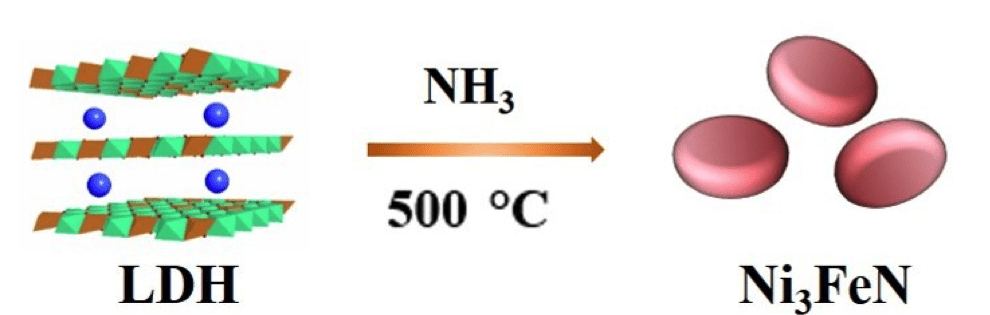
Chinese researchers have reported Ni3FeN nanoparticlessynthesized by thermal ammonolysis of ultrathin NiFe- layered double hydroxide (LDH) nanosheets.

Researchers from Texas, USA, and Spain, used the technique multiphoton plasmonic lithography (MPPL) to achieve immobilization of bovine serum albumin hydrogels on a single gold nanotriangle (AuNT).