Latest
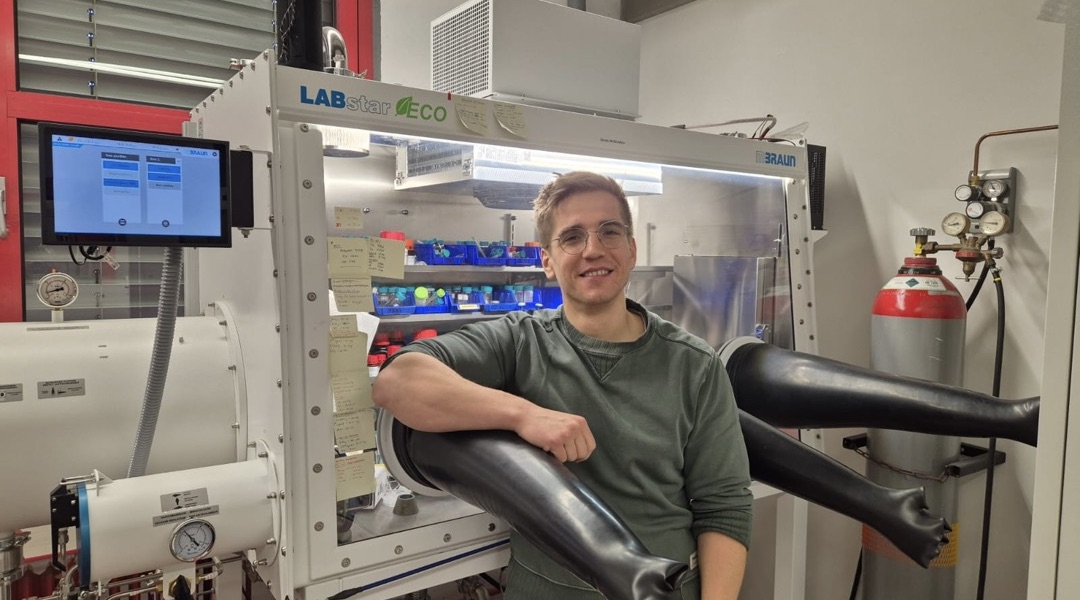

Alex Plajer – From Postdoc to PI: Combining Unusual Monomers Into Functional Polymers
Polymer chemist Alex Plajer talks about his research journey, transitioning into a group-leader role, and his vision for the field.

Microplastics in gastric tissue: A newly discovered risk factor for cancer development?
For the first time, scientists have detected microplastics in cancerous gastric tissue.
A single blood test could spot multiple cancers early, saving lives
Yearly screening with multi-cancer blood tests could nearly halve late-stage diagnoses.

Pesticide-free, climate-smart agriculture with “SafeWax”
Borrowing from biology, new wax coating ‘SafeWax’ defends crops from disease and climate stress.

Teaching machines to quiet the noise in quantum computers
Machine learning quickly and precisely diagnoses sources of noise in quantum computers.
Quantum router preserving delicate photon states may advance quantum technologies
Low-loss router based on an interferometer preserves polarization while directing single photons and entangled pairs.
Edible electronics realize safe, complex monitoring devices
Edible electronics from non-toxic materials enable complex ingestible devices for healthcare and food monitoring.

Metabolic–Epigenetic Link Between Sleep Deprivation and Immune Dysregulation
Sleep deprivation alters immune cell metabolism, causing changes to epigenetics through lactylation, triggering immune dysregulation.

Micron-sized hidden dimensions could solve two of physics’ deepest puzzles
Extra dimensions at the microscale could be tested experimentally within 3-5 years.
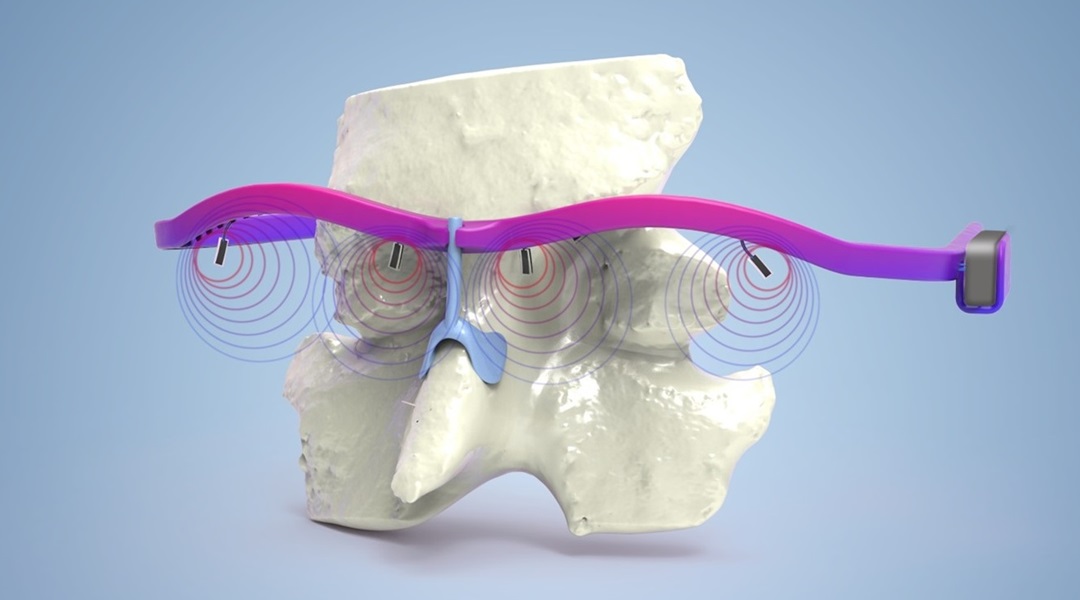

Smart Eye Sensor Warns of Dangerous Fatigue
Compact sensors enable integration of fatigue feedback into daily decision-making.
ASN Newsletter
Sign up for our newsletter and receive the latest science news directly to your inbox.
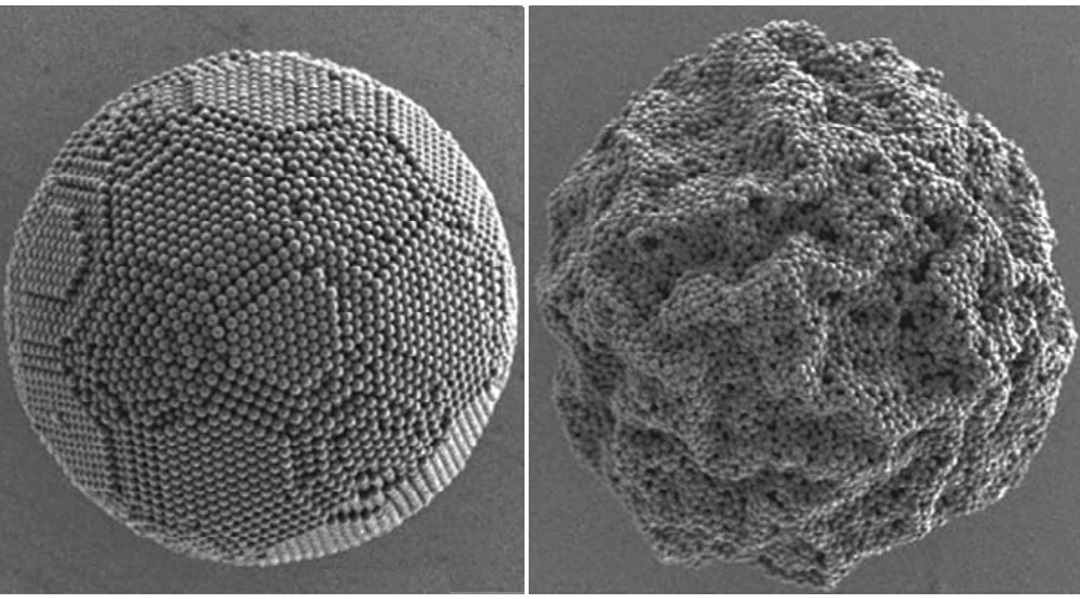
Surfactants Steer Supraparticle Structure
pH-responsive surfactants enable control over buckled supraparticle formation in emulsion-based systems.
Bone loss in obesity traced to gut microbiota
Obesity changes gut microbiota, causing immune cells to age prematurely and secrete a protein which weakens bones
Turning Periods into Power: Menstrual Blood a Valuable Resource for Medical Diagnostics
Wearable sensors help women analyse menstrual blood for affordable, non-invasive health monitoring.
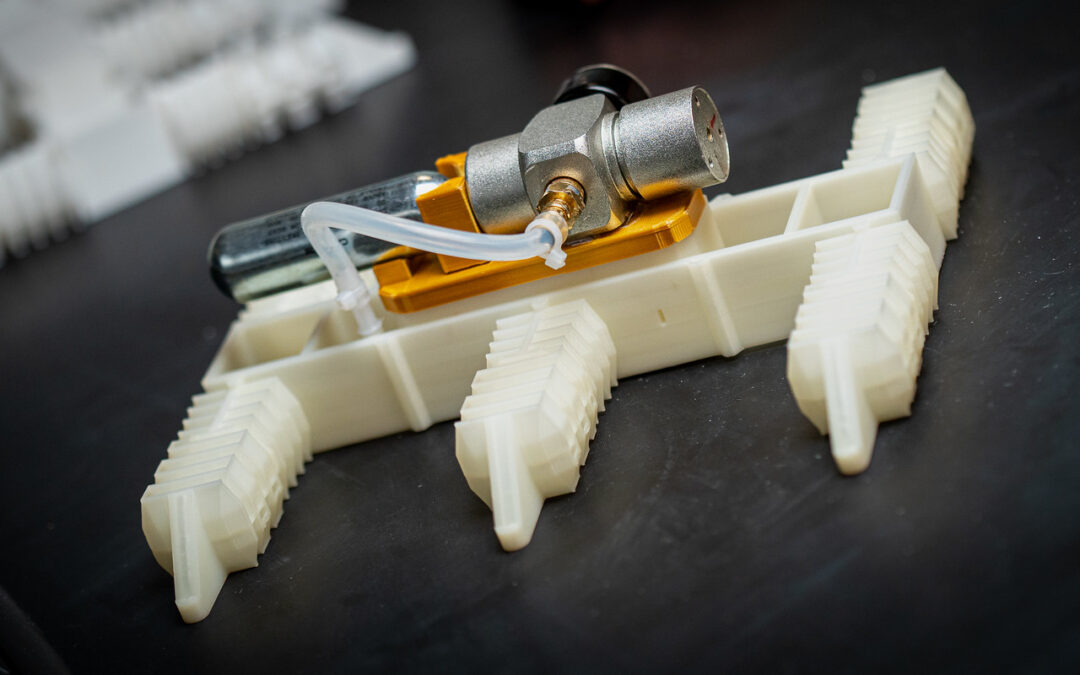
Walking on Air: Pneumatic System Enables Autonomous Motion in Soft Robots
Robot fabrication in a single step with a desktop 3D printer and pressurised gas.
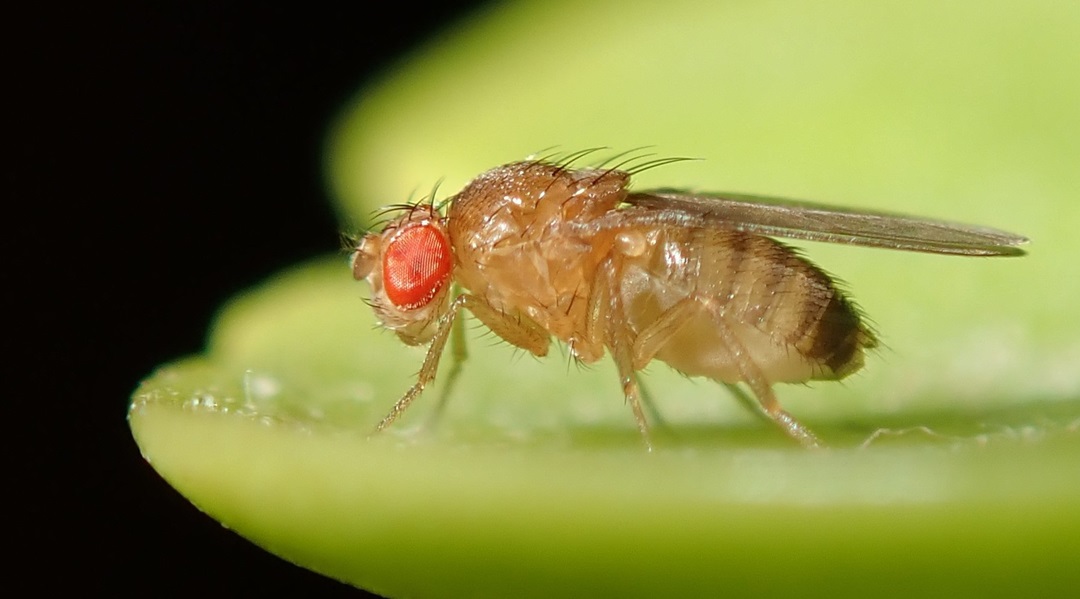

Behavioral Fever Helps Fight Parasitic Infections
Infected fruit flies use behavioral fever against deadly parasitoid wasps.

Non-canonical splicing: decrypting the hidden genetic architecture of male infertility
Previously overlooked non-canonical splicing variants are shown to lead to aberrant mRNA splicing in male infertility cases.
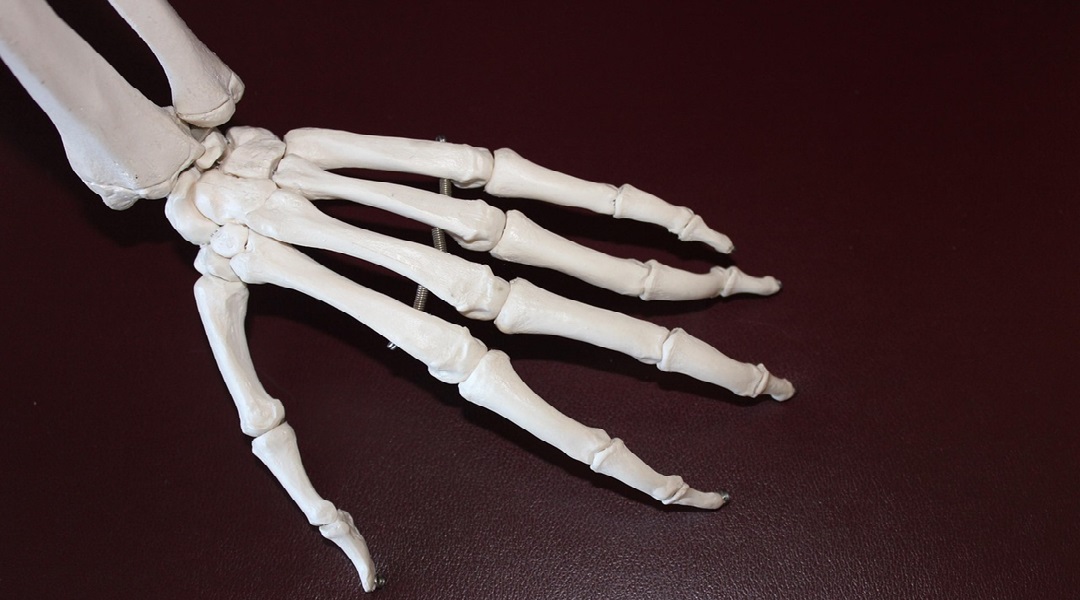
3D printed scaffolds bring artificial bone closer to reality
New 3D printed scaffolds more accurately mimic the structure and behaviour of natural bone.

Alexis Komor, Expanding the Gene Editing Toolbox
Young Innovator Awardee for 2025, Komor leads a group at UCSD developing precision genome editing methods using chemical biology.

Machine learning identifies anti-aging neuroprotective treatments
The effects of aging on the human brain could be slowed down with the help of artificial intelligence.
Non-canonical splicing: decrypting the hidden genetic architecture of male infertility
Previously overlooked non-canonical splicing variants are shown to lead to aberrant mRNA splicing in male infertility cases.
3D printed scaffolds bring artificial bone closer to reality
New 3D printed scaffolds more accurately mimic the structure and behaviour of natural bone.
Alexis Komor, Expanding the Gene Editing Toolbox
Young Innovator Awardee for 2025, Komor leads a group at UCSD developing precision genome editing methods using chemical biology.
Machine learning identifies anti-aging neuroprotective treatments
The effects of aging on the human brain could be slowed down with the help of artificial intelligence.
Organic materials bring probabilistic computing closer to reality
Scientists created flexible probabilistic bits from custom polymers, offering a new, energy-efficient path for AI and machine learning using classical physics.

Self-interacting inflaton particles may reshape our picture of the early universe
Subtle inflaton interactions may reshape our understanding of cosmic inflation, altering predictions about dark matter, black holes, and gravitational waves.
Ultra-dense electron beams set the stage for breakthroughs in physics and technology
SLAC scientists created ultra-dense electron beams with five times the peak current, using infrared lasers to unlock new frontiers in physics and materials research.

Solar panels made of lunar dust could power a future Moon base
Making solar panels on the Moon could be the solution to reliably providing energy to lunar settlements.
Organic materials bring probabilistic computing closer to reality
Scientists created flexible probabilistic bits from custom polymers, offering a new, energy-efficient path for AI and machine learning using classical physics.
Self-interacting inflaton particles may reshape our picture of the early universe
Subtle inflaton interactions may reshape our understanding of cosmic inflation, altering predictions about dark matter, black holes, and gravitational waves.
Ultra-dense electron beams set the stage for breakthroughs in physics and technology
SLAC scientists created ultra-dense electron beams with five times the peak current, using infrared lasers to unlock new frontiers in physics and materials research.
Solar panels made of lunar dust could power a future Moon base
Making solar panels on the Moon could be the solution to reliably providing energy to lunar settlements.
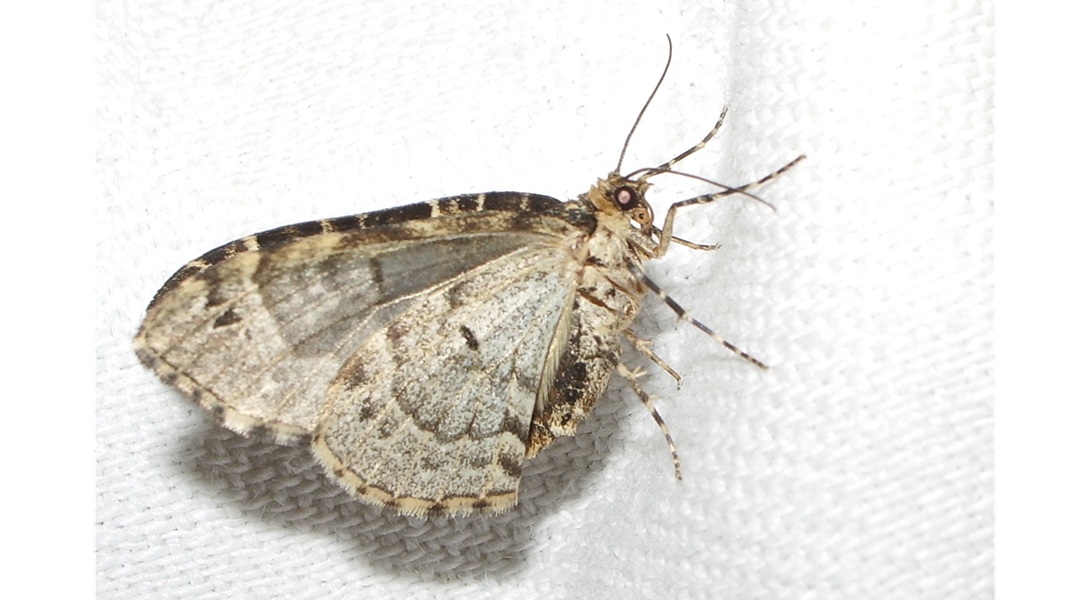

Moth eyes inspire flexible X-ray shields and sensors
Drawing from nature, scientists are creating next-generation X-ray protective clothing and equipment.

Moth eyes inspire flexible X-ray shields and sensors
Drawing from nature, scientists are creating next-generation X-ray protective clothing and equipment.

Machine learning identifies anti-aging neuroprotective treatments
The effects of aging on the human brain could be slowed down with the help of artificial intelligence.

Turning Food into Lasers: A New Era in Information Encoding and Sensing
Fabrication of microlasers using all edible components.
Moth eyes inspire flexible X-ray shields and sensors
Drawing from nature, scientists are creating next-generation X-ray protective clothing and equipment.
Moth eyes inspire flexible X-ray shields and sensors
Drawing from nature, scientists are creating next-generation X-ray protective clothing and equipment.
Machine learning identifies anti-aging neuroprotective treatments
The effects of aging on the human brain could be slowed down with the help of artificial intelligence.
Turning Food into Lasers: A New Era in Information Encoding and Sensing
Fabrication of microlasers using all edible components.
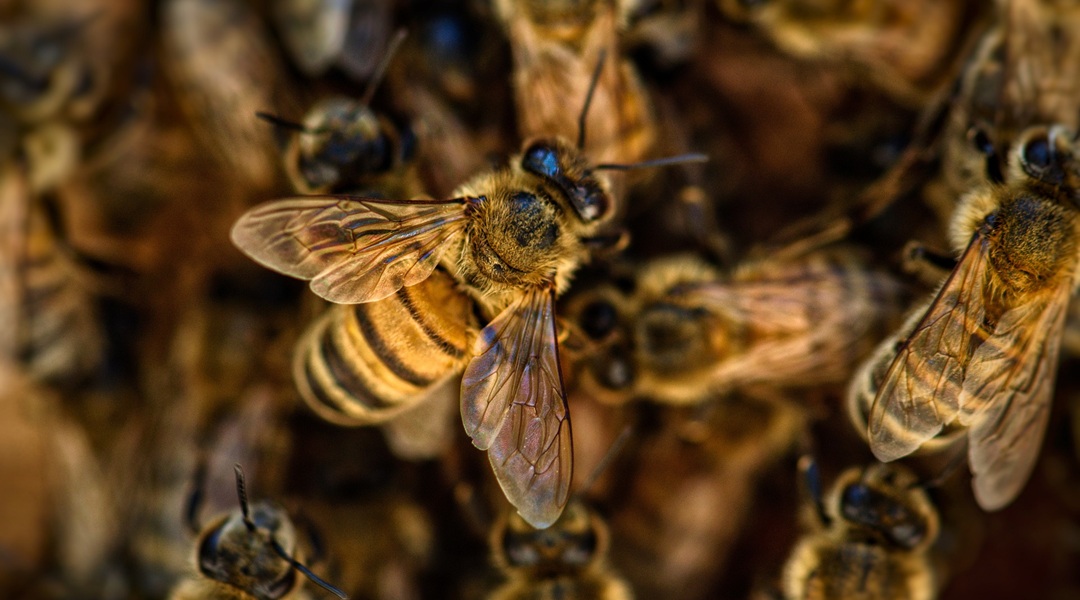

More vulnerable honey bees buffer the hive against heat stress
Honey bees more susceptible to heat are the first to initiate fanning behaviours that help the hive cool down.

Soy protein fuels the future of eco-friendly solid-state batteries
The world’s most grown legume could be used to make the batteries of the future.

Water-powered gadgets may be on the horizon thanks to new evaporation-based energy device
Scientists created an “evapolectrics” generator that draws power directly from water evaporation, offering a sustainable, battery-free energy source from humidity.

Climate pledges could shrink global cropland
The tradeoff raises concerns about food security, particularly for the Global South.
More vulnerable honey bees buffer the hive against heat stress
Honey bees more susceptible to heat are the first to initiate fanning behaviours that help the hive cool down.
Soy protein fuels the future of eco-friendly solid-state batteries
The world’s most grown legume could be used to make the batteries of the future.
Water-powered gadgets may be on the horizon thanks to new evaporation-based energy device
Scientists created an “evapolectrics” generator that draws power directly from water evaporation, offering a sustainable, battery-free energy source from humidity.
Climate pledges could shrink global cropland
The tradeoff raises concerns about food security, particularly for the Global South.

Riccardo Bassoli: How quantum computing will redefine wireless communication
Future 6G wireless networks will rely on quantum computers, but developing the technology and making it sustainable is complex.

Rose Marks, a botanist studying resurrection plants
Rose Marks uses her climbing skills in remote regions of South Africa to study how water-deprived plants might help develop drought-tolerant crops.

Shira Joudan, tackling PFAS and environmental contaminants with chemistry
Chemist Shira Joudan discusses environmental contaminants, setting up at a new university, and building a supportive community.
How a gut-on-a-chip is getting to the bottom of our gut’s microbiome
This artificial gut will allow scientists to gain deeper insights into the biome that exists there and how dysregulation can lead to disease.

Riccardo Bassoli: How quantum computing will redefine wireless communication
Future 6G wireless networks will rely on quantum computers, but developing the technology and making it sustainable is complex.

Rose Marks, a botanist studying resurrection plants
Rose Marks uses her climbing skills in remote regions of South Africa to study how water-deprived plants might help develop drought-tolerant crops.

Shira Joudan, tackling PFAS and environmental contaminants with chemistry
Chemist Shira Joudan discusses environmental contaminants, setting up at a new university, and building a supportive community.

How a gut-on-a-chip is getting to the bottom of our gut’s microbiome
This artificial gut will allow scientists to gain deeper insights into the biome that exists there and how dysregulation can lead to disease.