Researchers at the State University of New York-Binghamton have constructed a stackable, 3D-foldable bacteria-powered battery within a single sheet of paper for on-chip, disposable paper-based electronics.


Researchers at the State University of New York-Binghamton have constructed a stackable, 3D-foldable bacteria-powered battery within a single sheet of paper for on-chip, disposable paper-based electronics.
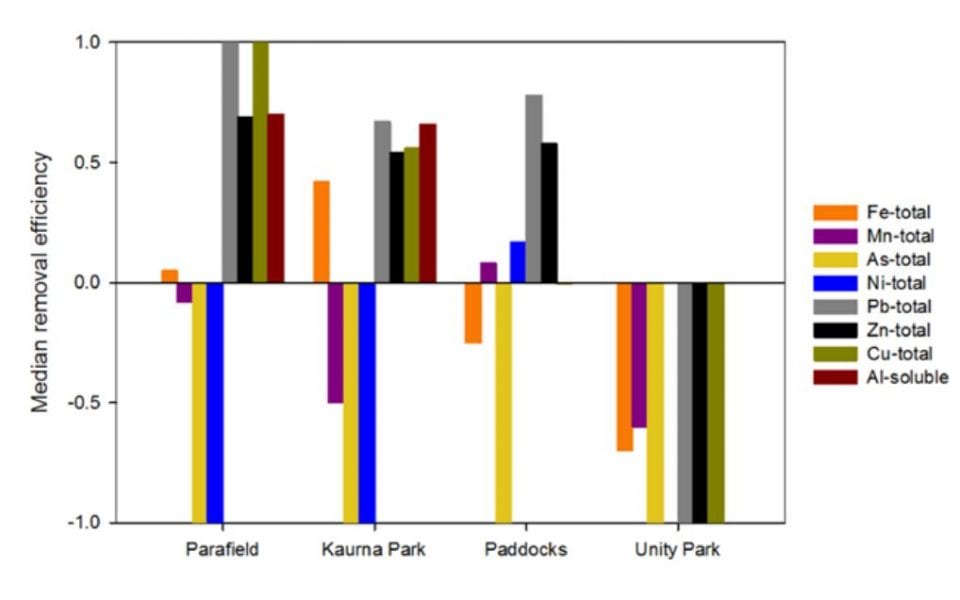
A probabilistic approach is applied to quantify metal(loid) fate in urban stormwater recycling via the aquifer.

A recent report explores the pro- or anti-inflammatory effects of caffeine to gain a better understanding of the potential effects of coffee consumption on inflammation.
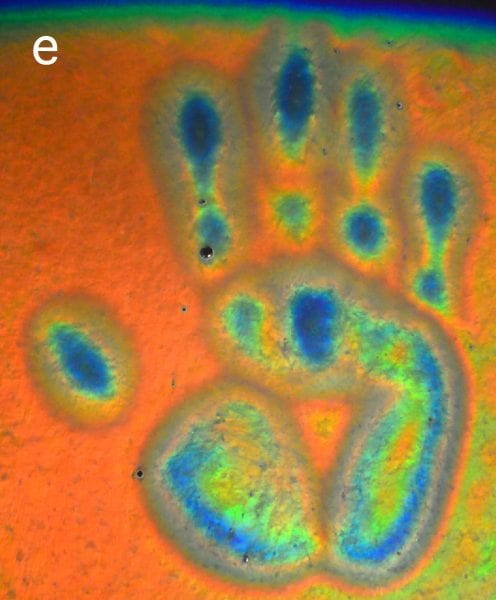
In a recent study published in Advanced Optical Materials, researchers make use of hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC) to develop optical strain sensors.
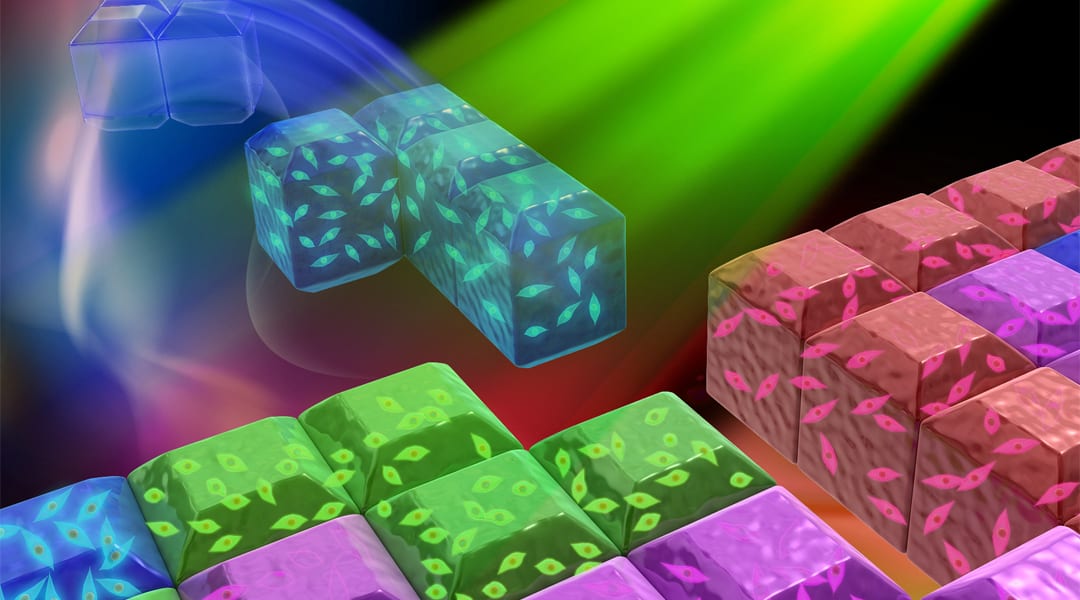
A Tetris-inspired approach to fabricate microscale tissue from hydrogel building blocks affords a non-contact assembly method to build complex and reconfigurable 3D architectures.
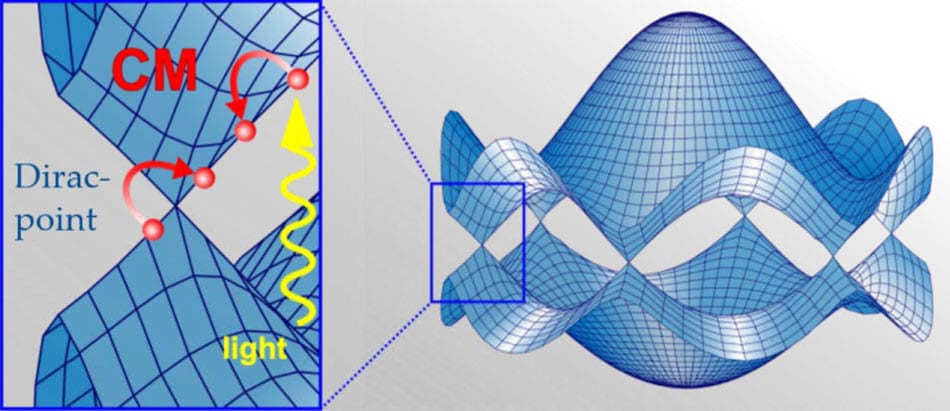
The remarkable electronic properties of graphene open up new carrier relaxation channels that can result in a significant multiplication of optically excited carriers.
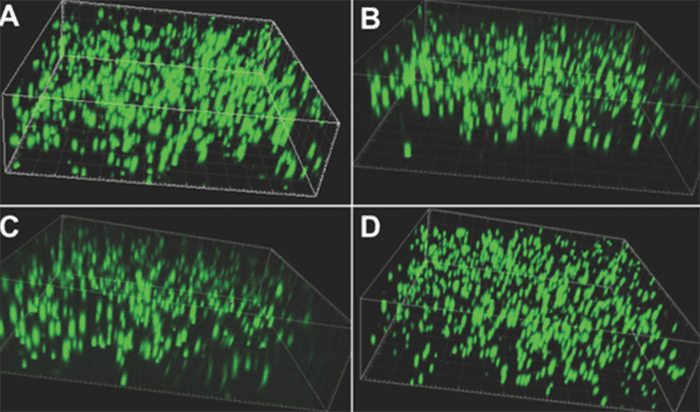
Researchers report the first example of a hydrogel for wound healing with both rapid self-healing ability and high mechanical strength.
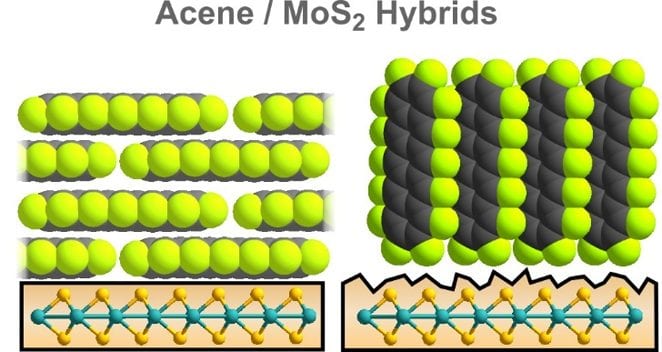
A group of scientists from Philipps-Universität Marburg have performed a careful and systematic study of organic film formation on molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) crystals.
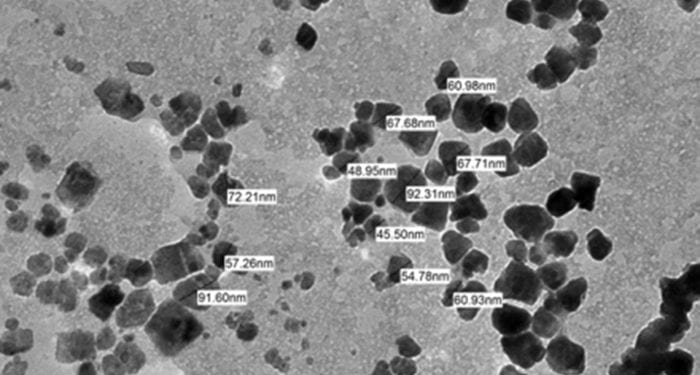
Natural polymers- based nanoparticles are widely used for biomedical purposes as they are highly biocompatible and biodegradable. Yet potential unexpected side effects have to be taken into account.
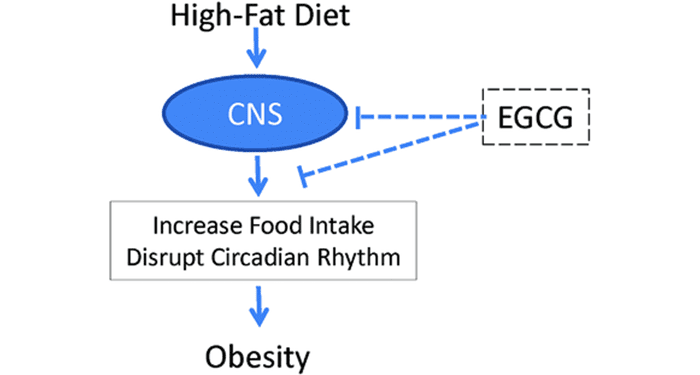
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), the active compound in green tea, counteracts overeating brought about by consumption of excessive amounts of high-fat foods.