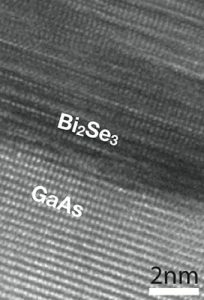
The atomic layers of the topological insulator bismuth selenide are visible in this high-resolution electron microscope image. Credit: Penn State.
The discovery of a new material combination that could lead to a more efficient approach to computer memory and logic has been published in Nature. The research, led by Penn State University and Cornell University physicists, studies “spintorque” in devices that combine a standard magnetic material with a novel material known as a topological insulator. The team’s results show that such a scheme can be 10 times more efficient for controlling magnetic memory or logic than any other combination of materials measured to date.
“This is a really exciting development for the field because it is the first promising indication that we actually may be able to build a practical technology with these topological insulator materials, which many condensed-matter physicists have been studying with spintronics applications as the motivation,” said co-principal-investigator Nitin Samarth, a professor of physics and the George A. and Margaret M. Downsbrough Department Head of Physics at Penn State. “Our experiment takes advantage of the very special surface of bismuth selenide — a material that is a topological insulator — which inherently supports the flow of electrons with an oriented spin,” he said. “Our collaborators at Cornell found that, at normal room temperatures, we can use these spin-oriented electrons to very efficiently control the direction of the magnetic polarity in the adjacent material.”
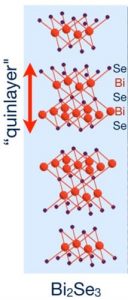
This illustration shows the crystal structure of the topological insulator bismuth selenide, Se-Bi-Se-Bi-Se, consisting of five atomic layers (“quinlayers”) of alternating selenide (Se) and bismuth (Bi). Credit: Penn State.
Professor Dan Ralph, the co-principal-investigator at Cornell University, said “Our team’s research has overcome one of the key challenges to developing a spintronics technology based on spin-orbit coupling — the efficiency with which an ordinary charge current can be converted into a spin current.” The experiment used thin-film materials that were synthesized in Samarth’s molecular-beam-epitaxy facility at Penn State by Graduate Student Joon Sue Lee and Research Associate Anthony Richardella. Graduate Student Alex Mellnik, in Ralph’s laboratory at Cornell, fashioned these thin films into devices and carried out the spin-torque measurements. Professor Eun-ah Kim and her group at Cornell developed the theoretical interpretation of the experiments.
Earlier this year, Samarth’s group also co-authored a manuscript in Nature Communications with Professor Zahid Hasan’s group at Princeton University. In that experiment, a systematic series of ultrathin bismuth selenide films synthesized at Penn State were used by Research Associate Madhab Neupane and Graduate Student Su-yang Xu of his lab to demonstrate how the spin orientation of surface electrons in a topological insulator could be manipulated at room temperature using quantum tunneling.
“The rapid progress shown in this field at Penn State and at laboratories around the world indicates that ‘topological spintronics’ shows great promise of becoming an attractive offshoot of more traditional approaches to spintronics technology,” Samarth said.
Source: Penn State (thumbnail image credit: Fredric Weber, Penn State University)

















