Scientists theorize that cosmic strings interacting with dense matter in the early universe provided the seeds for galaxies and black holes.



Scientists theorize that cosmic strings interacting with dense matter in the early universe provided the seeds for galaxies and black holes.
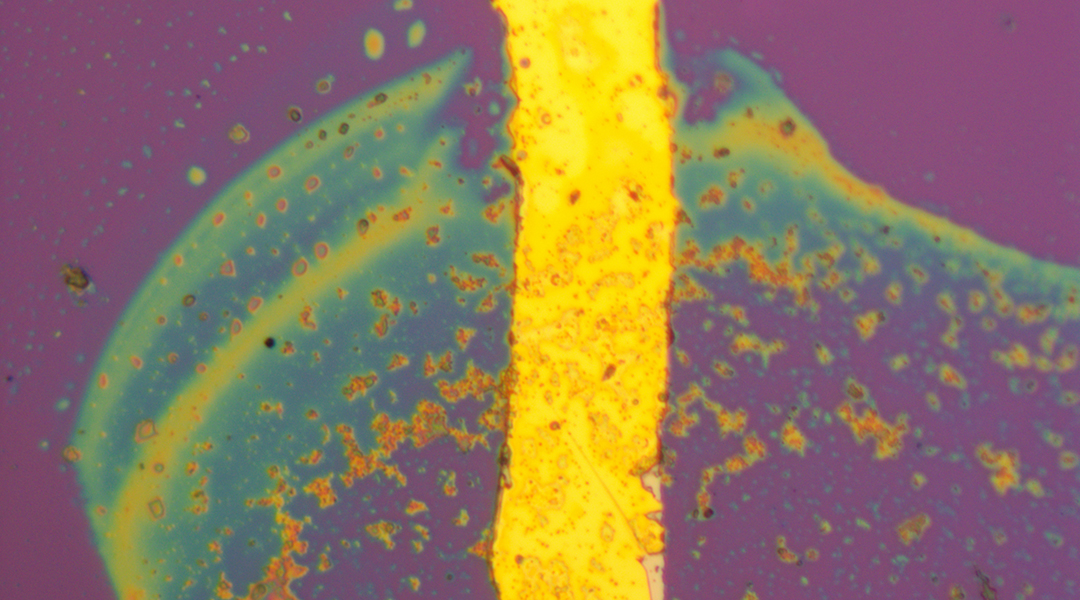
Scientists have optimized nanodiamond sensors, with potential breakthroughs in electronics, medicine, and quantum tech.

The discovery of colossal structures like the Big Ring is reshaping established theories about the physics of the Universe.

Scientists have uncovered the cause of rapid degradation in powerful gallium nitride lasers and develop a solution to extend their lifespan.

Scientists create designs for quantum batteries, which harness the potential of quantum mechanics to enhance energy storage.

Adding extra dimensions to a theory known as “fuzzy gravity” may help bridge the gap between quantum mechanics and relativity.

A state-of-the-art printer with nanometer-scale precision enables the production of quantum emitters, advancing secure quantum communication.
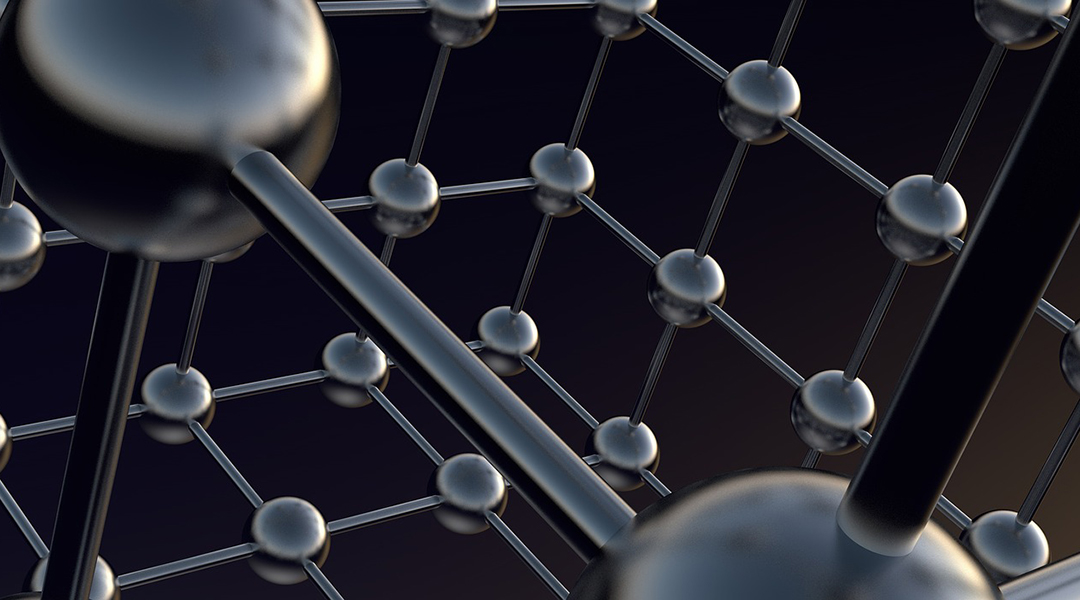
Understanding this unique form of superconductivity is crucial and could lead to exciting applications, like functional quantum computers.

Data gathered about the M-class asteroid challenges earlier assumptions that it is unaltered planetary core.

Could neutron stars hold the key to observing dark matter? Researchers believe studying them might one day reveal this elusive substance.