New research on dwarf galaxies challenges the idea that dark matter is collisionless, suggesting it may interact in unexpected ways


New research on dwarf galaxies challenges the idea that dark matter is collisionless, suggesting it may interact in unexpected ways

Is it time to start looking for alternatives to WIMPs?

Subtle inflaton interactions may reshape our understanding of cosmic inflation, altering predictions about dark matter, black holes, and gravitational waves.

Dark matter could be composed of much lighter particles, with masses roughly ten times smaller than that of a proton.

Researchers at CERN’s Large Hadron Collider explore subtle energy signals to search for new physics beyond the Standard Model.

Dark matter may be gathering in dense clouds around neutron stars, potentially making it easier to observe it from Earth.

Could neutron stars hold the key to observing dark matter? Researchers believe studying them might one day reveal this elusive substance.
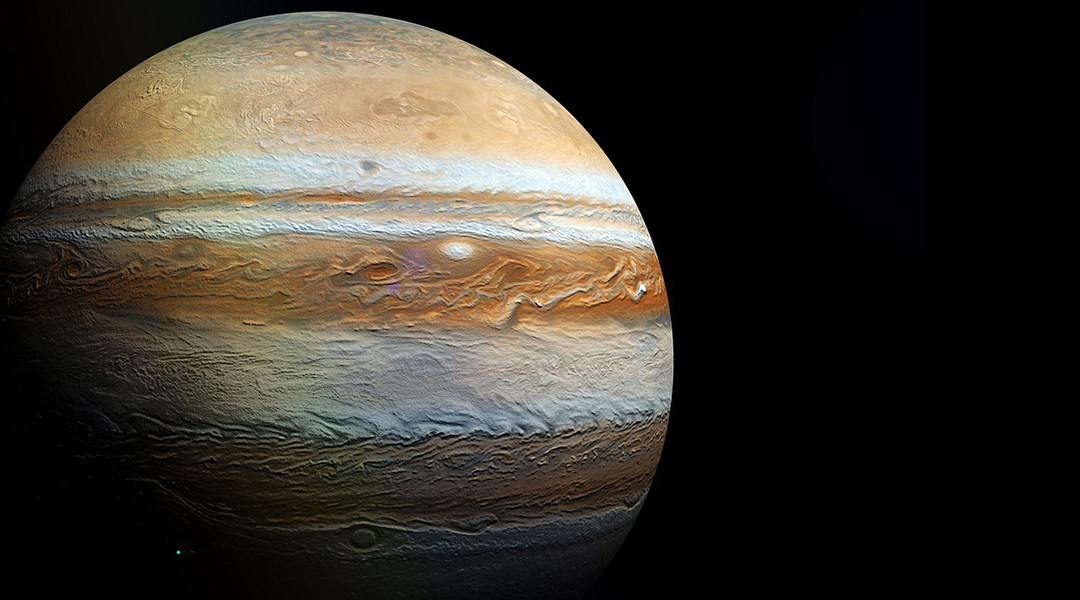
Astronomers propose that an infrared glow observed in Jupiter’s atmosphere may be dark matter particles colliding.

In this third and final article in a series on philosophy and science, we look at how modern science shows the validity of dialectical processes and how this can help guide science.

Tiny interactions between dark matter particles may resolve discrepancies between theory and astronomical observations caused by quantum tunneling.