Fluorescent carbon dots could change the way in which we visualize cells.
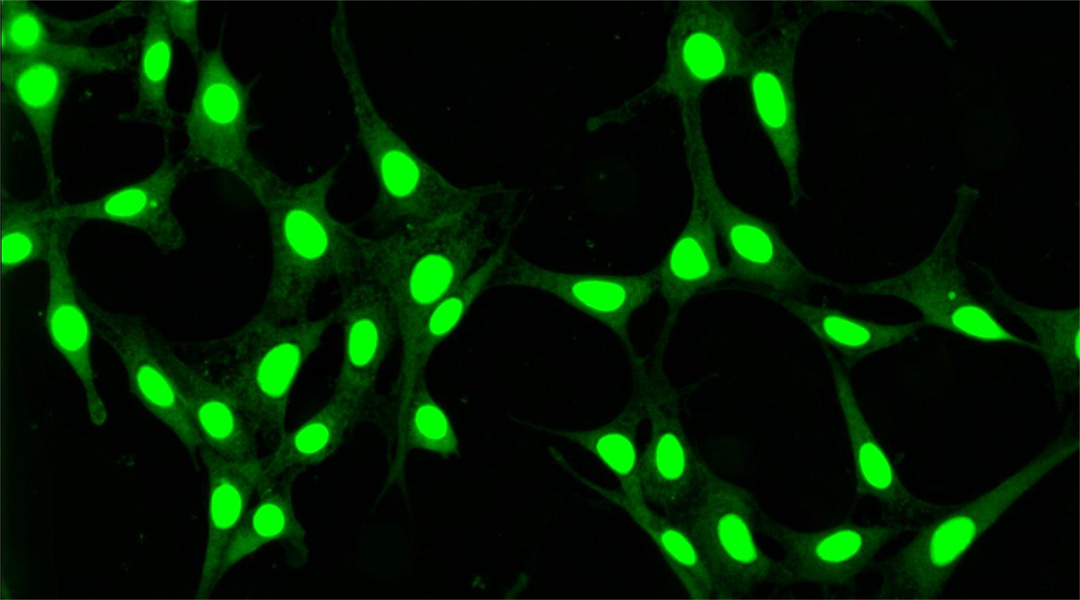

Fluorescent carbon dots could change the way in which we visualize cells.

What were the driving factors behind organelle evolution?

In this essay, scientists from Spain and Denmark delve into the spectrum of possibilities offered by wearable and implantable healthcare devices and provide new insight into the cyborganic era.
Why mitochondria produce reactive oxygen species, and how they drove eukaryotic evolution.

In today’s fast-changing scientific landscape, interdisciplinary fields are the new normal and clinical trials for new therapies are exploding. On the scientific information side, the WIREs series presents current, comprehensive reviews of the pioneering research that...
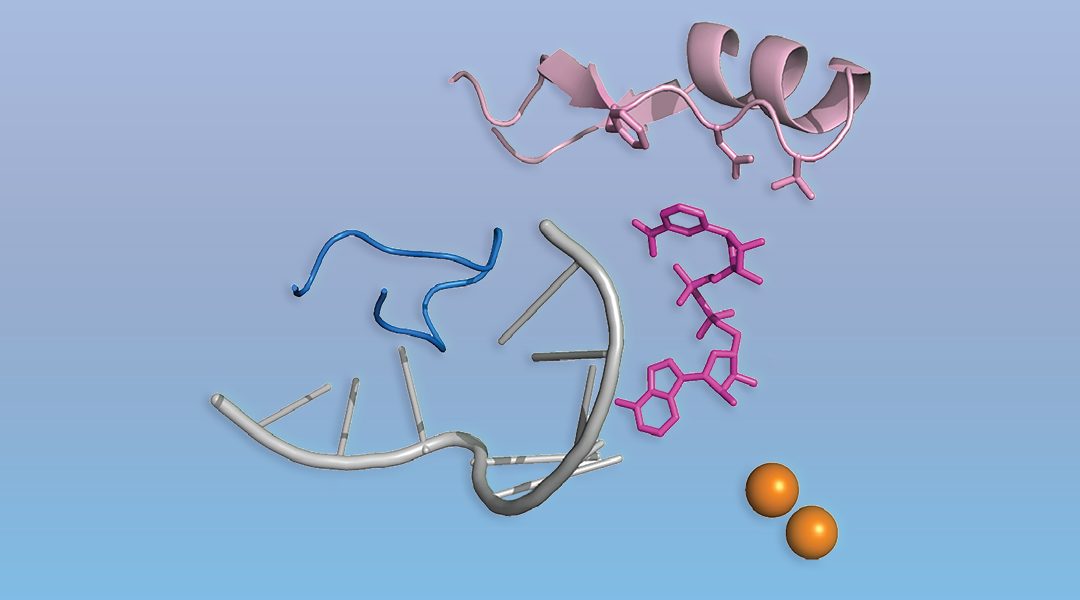
A new type of 5′‐RNA cap was discovered, and in contrast to the specialized eukaryotic m7G cap, the novel caps are abundant cellular cofactors like NAD+.

The Editors of Small Methods are pleased to publish this special biomedical virtual issue. This collection highlights outstanding research in Small Methods from the very first issue to now, in the areas of biosensing, biomedical engineering, nanomaterials,...
![Monitoring Reactive Oxygen Species in Cells and Tissue [Video]](https://www.advancedsciencenews.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/09/smll201800310_ASN_image.jpg)
Researchers report a highly sensitive detection method for monitoring the nanotoxicity associated with reactive oxygen species (ROS).

Sequencing of the human genome led to the surprising discovery that we do not have many more protein coding genes than presumably simpler organisms.
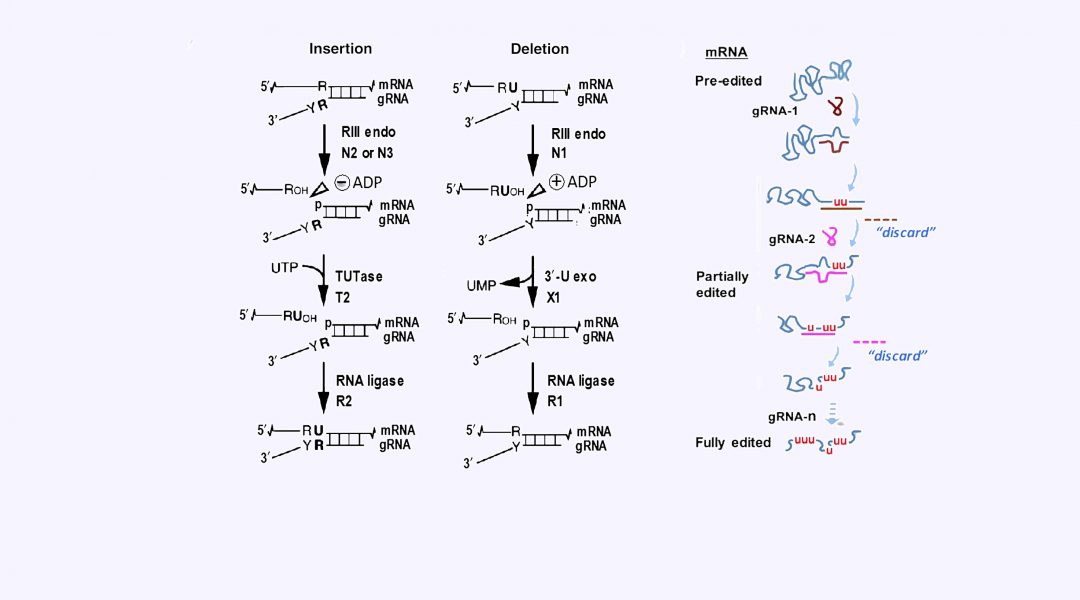
Specific examples of complex variants, differential effects of editing proteins on the mRNAs within and between T. brucei life stages, and possible control points in the holo-editosomes are examined.