Advanced Optical Materials Issue 3 is now live, with thirteen contributions from a range of leading research groups and covering the whole spectrum of light–matter interactions.
All articles are free to access.
To contribute a paper to the next issue of Advanced Optical Materials, visit http://www.advopticalmat.de/call-for-papers/ .
Table of Contents: Advanced Optical Materials, Issue 3
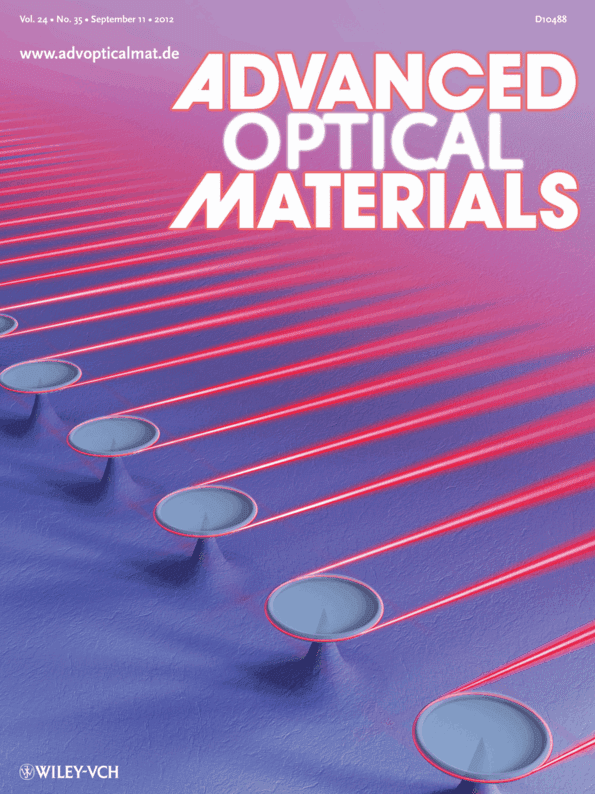
Microcavities: Highly Unidirectional Emission and Ultralow-Threshold Lasing from On-Chip Ultrahigh-Q Microcavities (Adv. Mater. 35/2012) (page OP185)
Xue-Feng Jiang, Yun-Feng Xiao, Chang-Ling Zou, Lina He, Chun-Hua Dong, Bei-Bei Li, Yan Li, Fang-Wen Sun, Lan Yang and Qihuang Gong
Article first published online: 4 SEP 2012 | DOI: 10.1002/adma.201290211

Ultra-high-Q optical whispering gallery microcavities are promising platforms for fundamental studies and applied photonics. A new type of on-chip microcavity is experimentally realized, which features both highly unidirectional emission and ultra-high-Q factors exceeding 100 million in near infrared. By doping erbium into the microcavity, lasing emission in 1550 nm band is observed under a convenient freespace optical pumping, with the threshold as low as 2 μW. More details can be found in the article by Q. Gong, Y.-F. Xiao, and co-workers on page OP260.
Inside Front Cover: Advanced Optical Materials
Jian Yao Zheng, Yongli Yan, Xiaopeng Wang, Wen Shi, Huimin Ma, Yong Sheng Zhao and Jiannian Yao
Article first published online: 4 SEP 2012 | DOI: 10.1002/adma.201290212

A core/sheath structure is fabricated by decorating single-crystal organic nanowires with H2O2-reactive peroxalate ester, as reported by J. Yao, Y. S. Zhao, and co-workers on page OP194. The shell of the nanocable is highly sensitive and selective to the H2O2 molecules, demonstrated by the generation of chemiluminescence on exposure to H2O2vapors. The cable-like optical waveguide sensing platform can rapidly and selectively monitor H2O2 vapors through the amplified optical variation across the wire waveguiding, showing that a single nanocable is very promising for developing optical probes to detect individual responses on-chip.
Back Cover: Advanced Optical Materials
Nanostructures: Distributing the Optical Near-Field for Efficient Field-Enhancements in Nanostructures (Adv. Mater. 35/2012) (page OP272)
V. K. Valev, B. De Clercq, C. G. Biris, X. Zheng, S. Vandendriessche, M. Hojeij, D. Denkova, Y. Jeyaram, N. C. Panoiu, Y. Ekinci, A. V. Silhanek, V. Volskiy, G. A. E. Vandenbosch, M. Ameloot, V. V. Moshchalkov and T. Verbiest
Article first published online: 4 SEP 2012 | DOI: 10.1002/adma.201290213

Circularly polarized light can impart a sense of rotation on the electron density in ring-shaped gold nanostructures. V. K. Valev and co-workers show on p. OP208that the near-field enhancement becomes more homogeneous on the surface of the nanostructures, thereby increasing the opportunity for interaction with molecules. This type of nanostructured samples can find applications in chemical processes where the interaction between molecules and local field enhancements is important.
Editorial: Advanced Optical Materials
Bringing a Diverse Field into Focus (page OP193)
Article first published online: 4 SEP 2012 | DOI: 10.1002/adma.201290216
Communications: Advanced Optical Materials
Hydrogen Peroxide Vapor Sensing with Organic Core/Sheath Nanowire Optical Waveguides (pages OP194–OP199)
Jian Yao Zheng, Yongli Yan, Xiaopeng Wang, Wen Shi, Huimin Ma, Yong Sheng Zhao and Jiannian Yao
Article first published online: 3 JUL 2012 | DOI: 10.1002/adma.201200867

By decorating single crystal organic nanowires with H2O2-reactive peroxalate ester, a core/sheath structure for the rapid and selective detection of H2O2 vapors is demonstrated via the optical waveguide of a single wire. Such a compact sensing configuration may act as the “nano-alarm-lamp” for the H2O2 vapors and be attractive for on-chip optical detection in complex chemical or biological environments.
Ruibin Jiang, Huanjun Chen, Lei Shao, Qian Li and Jianfang Wang
Article first published online: 20 JUN 2012 | DOI: 10.1002/adma.201201896

Evolution of the sizes and plasmonic properties of (Au core)−(Ag shell) nanorods is studied. Four plasmon bands are observed on the core−shell nanorods and their properties are investigated. The lowest-energy one belongs to the longitudinal dipolar plasmon mode, the second-lowest-energy one belongs to the transverse dipolar plasmon mode, and the two highest-energy ones are ascribed to octupolar plasmon modes.
V. K. Valev, B. De Clercq, C. G. Biris, X. Zheng, S. Vandendriessche, M. Hojeij, D. Denkova, Y. Jeyaram, N. C. Panoiu, Y. Ekinci, A. V. Silhanek, V. Volskiy, G. A. E. Vandenbosch, M. Ameloot, V. V. Moshchalkov and T. Verbiest
Article first published online: 3 JUL 2012 | DOI: 10.1002/adma.201201151

Circularly polarized light imparts a sense of rotation on the electron density in ring-shaped gold nanostructures. As a consequence, the near-field enhancement becomes homogeneous on the surface of the nanostructures, thereby increasing the opportunity for interaction with molecules. This type of nanostructured samples can find a broad range of applications in chemical processes where the interaction between molecules and local field enhancements play an important role.
Zhenzhen Xu, Qing Liao, Qiang Shi, Haoli Zhang, Jiannian Yao and Hongbing Fu
Article first published online: 16 JUL 2012 | DOI: 10.1002/adma.201201579

Low-threshold nanolasers based on slab nanocrystals (SNCs) of highly emissive H-aggregated organic semiconductors are reported. A lasing threshold as low as 100 nJ cm−2 is achieved in a high-quality (cavity quality factor ≈ 1000) Fabry–Pérot cavity constituted by the two lateral-faces of SNCs at the wavelength scale. Moreover, the laser light generated in the ultrasmall radial cavity of SNCs can propagate along its length up to hundreds of micrometers, making them attractive building blocks for miniaturized photonic circuits.
Andrea Camposeo, Pompilio Del Carro, Luana Persano and Dario Pisignano
Article first published online: 18 JUL 2012 | DOI: 10.1002/adma.201201453

The emission of polymer distributed feedback lasers is tuned by integrating nonlinear optical organics. The nonlinearity allows reversible tuning of the amplified spontaneous emission of a conjugated polymer by 30 nm, and the lasing wavelength by 17 nm, with a lasing tunability coefficient of 0.17 nm/V.
Broadband Terahertz Plasmonic Response of Touching InSb Disks (pages OP226–OP230)
S. M. Hanham, A. I. Fernández-Domínguez, J. H. Teng, S. S. Ang, K. P. Lim, S. F. Yoon, C. Y. Ngo, N. Klein, J. B. Pendry and S. A. Maier
Article first published online: 16 JUL 2012 | DOI: 10.1002/adma.201202003

The plasmonic behavior of dimers of touching semiconductor disks is studied experimentally in the difficult-to-realize regime where the disks are only marginally overlapping. Previous theoretical studies have shown that this geometry exhibits a highly efficient broadband response that may be very promising for light harvesting and sensing applications. By taking advantage of the plasmonic character of InSb in the terahertz regime, we experimentally confirm this broadband response and describe the associated strong field enhancement and sub-micrometer field confinement between the disks.
Iwan Moreels, Gabriele Rainò, Raquel Gomes, Zeger Hens, Thilo Stöferle and Rainer F. Mahrt
Article first published online: 16 JUL 2012 | DOI: 10.1002/adma.201202067

By careful engineering of the core and shell dimensions in CdSe/CdS colloidal hetero-nanocrystals, amplified spontaneous emission can be triggered from either the core, shell, or both states simultaneously. The ASE threshold is almost constant over a temperature interval of 5–325 K. This feature is unique to quantum dots and highlights their potential as a gain material, suitable for lasing at elevated temperatures.
Weihua Zhang, Fei Ding and Stephen Y. Chou
Article first published online: 3 JUL 2012 | DOI: 10.1002/adma.201200220

Plasmon-enhanced upconversion luminescence of NaYF4: Yb3+/Er3+ co-doped nanocrystals is investigated using a 3D plasmonic antenna architecture: a disk-coupled dots-on-pillar antenna array (D2PA). By tuning and optimizing the resonance frequency of the D2PA structure for upconversion luminescence, a 310-fold luminescence enhancement and an 8-fold reduction of the luminescence decay time are observed.
John T. Bahns, Subramanian K. R. S. Sankaranarayanan, Noel C. Giebink, Hui Xiong and Stephen K. Gray
Article first published online: 20 JUN 2012 | DOI: 10.1002/adma.201104749

Directed colloidal synthesis of conductive organic–inorganic hybrid mesoscale structures is reported. The technique is simple but allows hierarchical assembly and 2D patterning of materials. A focused laser spot is used to direct the colloidal assembly of nanoparticles into electrically conductive organic–inorganic hybrid mesoscale filaments with arbitrary permanent patterns on a glass surface.
Jun Zhao, Chunjie Zhang, Paul V. Braun and Harald Giessen
Article first published online: 16 JUL 2012 | DOI: 10.1002/adma.201202109

Large-area low-cost plasmonic nanostructures with high-quality Fano resonances have been fabricated for the first time. Hole-mask colloidal nanolithography is utilized and the degree of asymmetry of double split-ring resonators is varied to optimize the modulation depth of the Fano resonances for refractive index sensing. In situ optical spectroscopy during thermal annealing monitors the spectral change to control improvement of sample quality. Liquids with different refractive indices yield experimental sensitivities of up to 520 nm/RIU and figures of merit of 2.9.
Kuang-Li Lee, Min-Jian Chih, Xu Shi, Kosei Ueno, Hiroaki Misawa and Pei-Kuen Wei
Article first published online: 16 JUL 2012 | DOI: 10.1002/adma.201202194

A multi-polarization spectral integration method to increase the refractive index detection limit of gold nanostructures is presented. For a dual-period nanogrid structure, the proposed method increased signal-to-noise ratio and refractive index detection limit about 8 times larger than the simple intensity method. The nanogrid achieves a detection limit of 1.92 × 10−6refractive index unit when the intensity stability is 0.2%.
Xue-Feng Jiang, Yun-Feng Xiao, Chang-Ling Zou, Lina He, Chun-Hua Dong, Bei-Bei Li, Yan Li, Fang-Wen Sun, Lan Yang and Qihuang Gong
Article first published online: 13 AUG 2012 | DOI: 10.1002/adma.201201229

Ultrahigh-Q optical whispering gallery microcavities are promising platforms for fundamental studies and applied photonics. A new type of on-chip microcavity is experimentally realized, which supports both highly unidirectional emission and ultra-high-Q factors exceeding 100 million in near infrared. By doping erbium, the unidirectional-emission lasing is observed in 1550 nm band with the threshold as low as 2 μW.
Electrochromic Bragg Mirror: ECBM (pages OP265–OP269)
Engelbert Redel, Jacek Mlynarski, Jonathon Moir, Abdinoor Jelle, Chen Huai, Srebri Petrov, Michael G. Helander, Frank C. Peiris, Georg von Freymann and Geoffrey A. Ozin
Article first published online: 13 AUG 2012 | DOI: 10.1002/adma.201202484

The colloidal assembly of a nanoporous electrochromic 1D Bragg mirror comprising NiO and WO3 nanoparticle multilayers enables the convolution of electrically tunable electronic crystals and photonic crystals into a single device, providing thereby a distinctive means of creating and manipulating color.