Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a minimally invasive treatment method of tumors. It is based on the systemic or local administration of a photosensitizer and its subsequent activation by appropriate wavelength of light. In the presence of oxygen, the activated photosensitizer can generate various reactive oxygen species (ROS) to kill tumor cells. Compared with other conventional cancer treatments such as chemotherapy and radiotherapy, PDT shows minimal side effects, high selectivity and relatively low cost.
However, it is usually not efficient in long-lasting tumor control. At least to some extent, this is due to the intelligence of cancer cells. They can develop some protective mechanisms that help them to cope with the attack by ROS in an environment that otherwise might kill them.
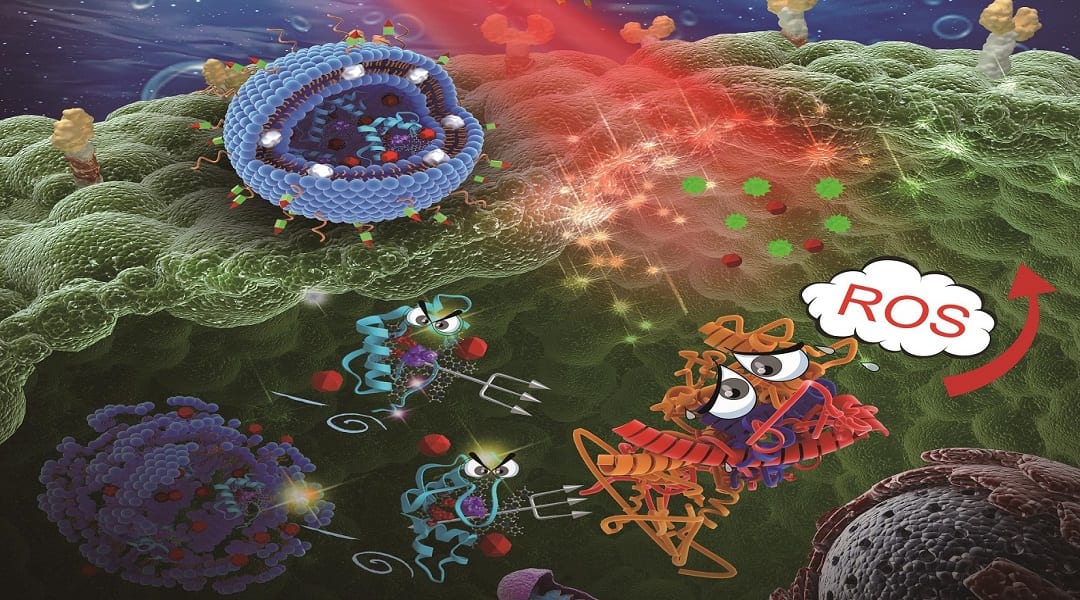
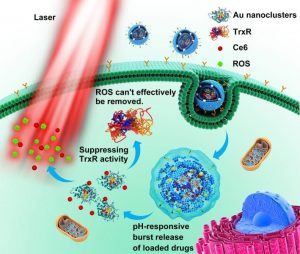
The thioredoxin system in tumor is an important antioxidant defense system. In PDT-treated cells, tumor cells overexpress thioredoxin reductase (TrxR) or improve its enzymatic activity in response to increased intracellular ROS levels. The study by Dr. Fuping Gao, Prof. Xueyun Gao and their co-workers, published recently in Advanced Helthcare Materials, reports on gold nanoclusters that efficiently suppress the activity of TrxR. They simultaneously loaded gold nanoclusters and the photosensitizer chlorin e6 (Ce6) into pH sensitive liposomes.
With this system, gold nanoclusters and Ce6 were quickly released into the cytoplasm under the acidic environment of lysosomes. Gold nanoclusters could effectively inhibit TrxR in the cytoplasm and improve the levels of intracellular ROS, ultimately enhancing the effect of PDT. When the liposomes were administered intravenously to tumor-bearing mice, tumors in mice treated with PDT alone started to regrow on day 16 after commencement of the treatment, while combinatorial PDT using liposomes loaded with gold nanoclusters and Ce6 showed no evidence of cancer recurrence in the 35 day follow-up period with a substantial tumor inhibition ratio. This study demonstrates a new application of gold nanoclusters and offers a simple yet effective treatment option for cancer patients.